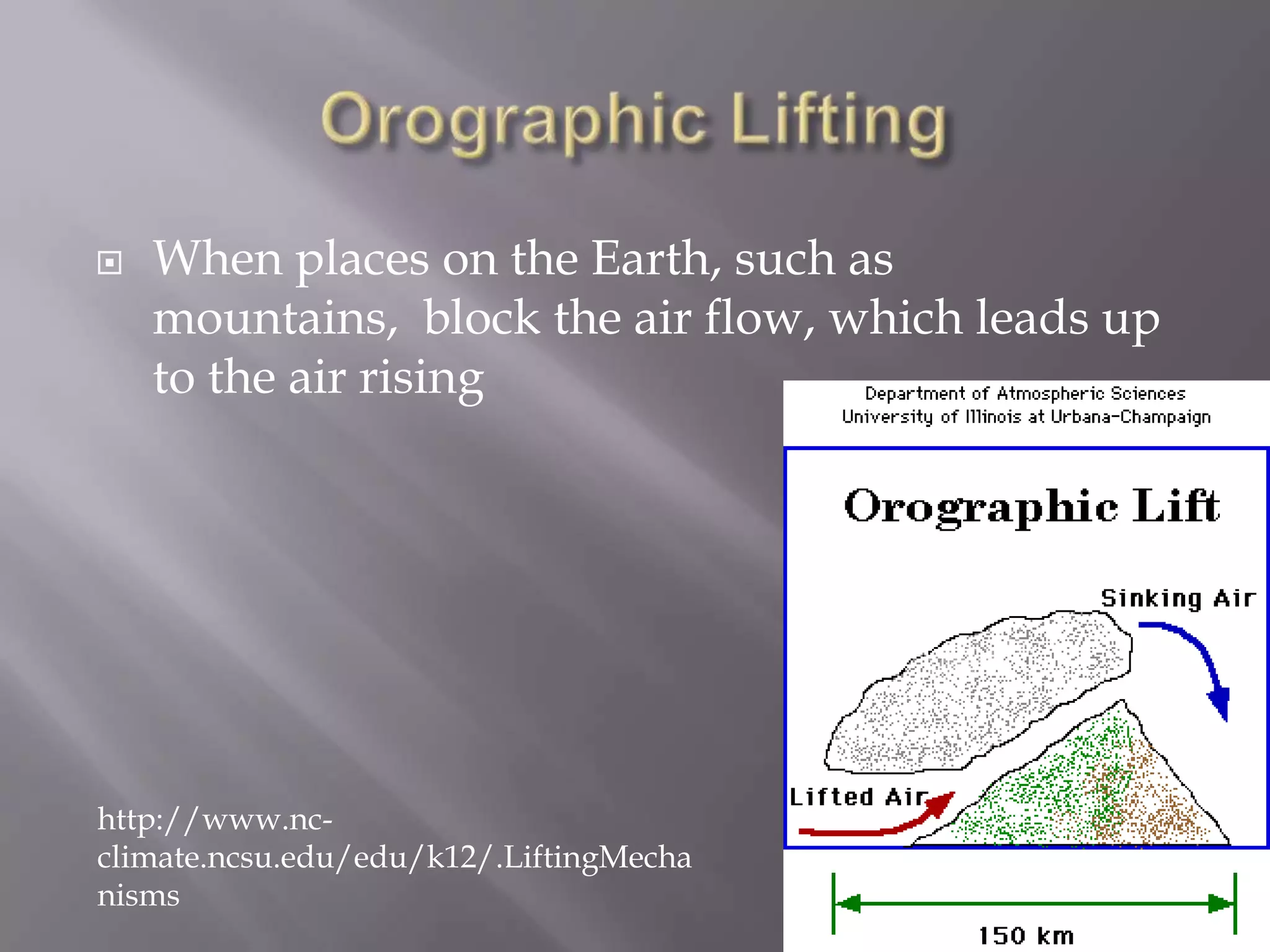
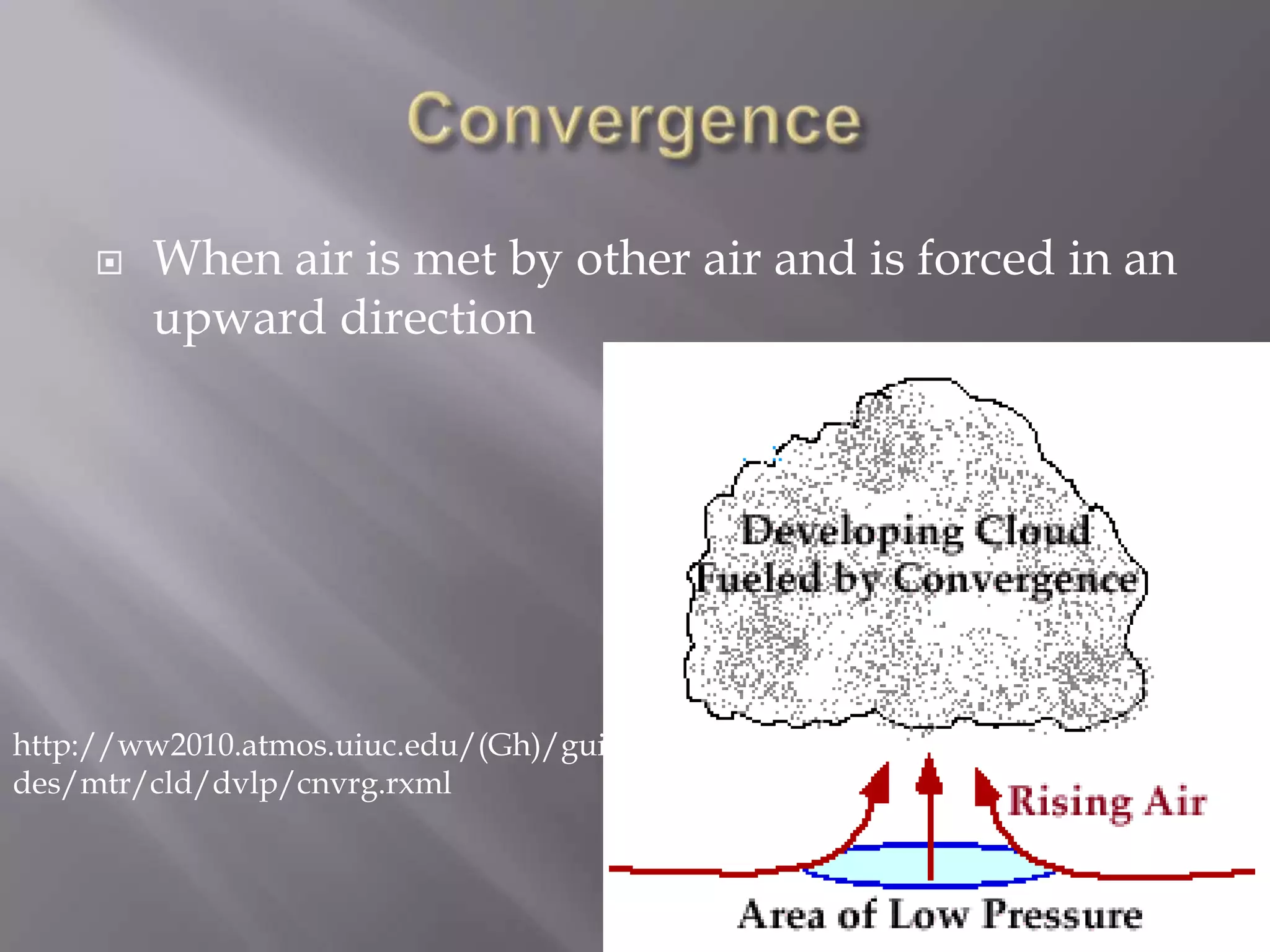
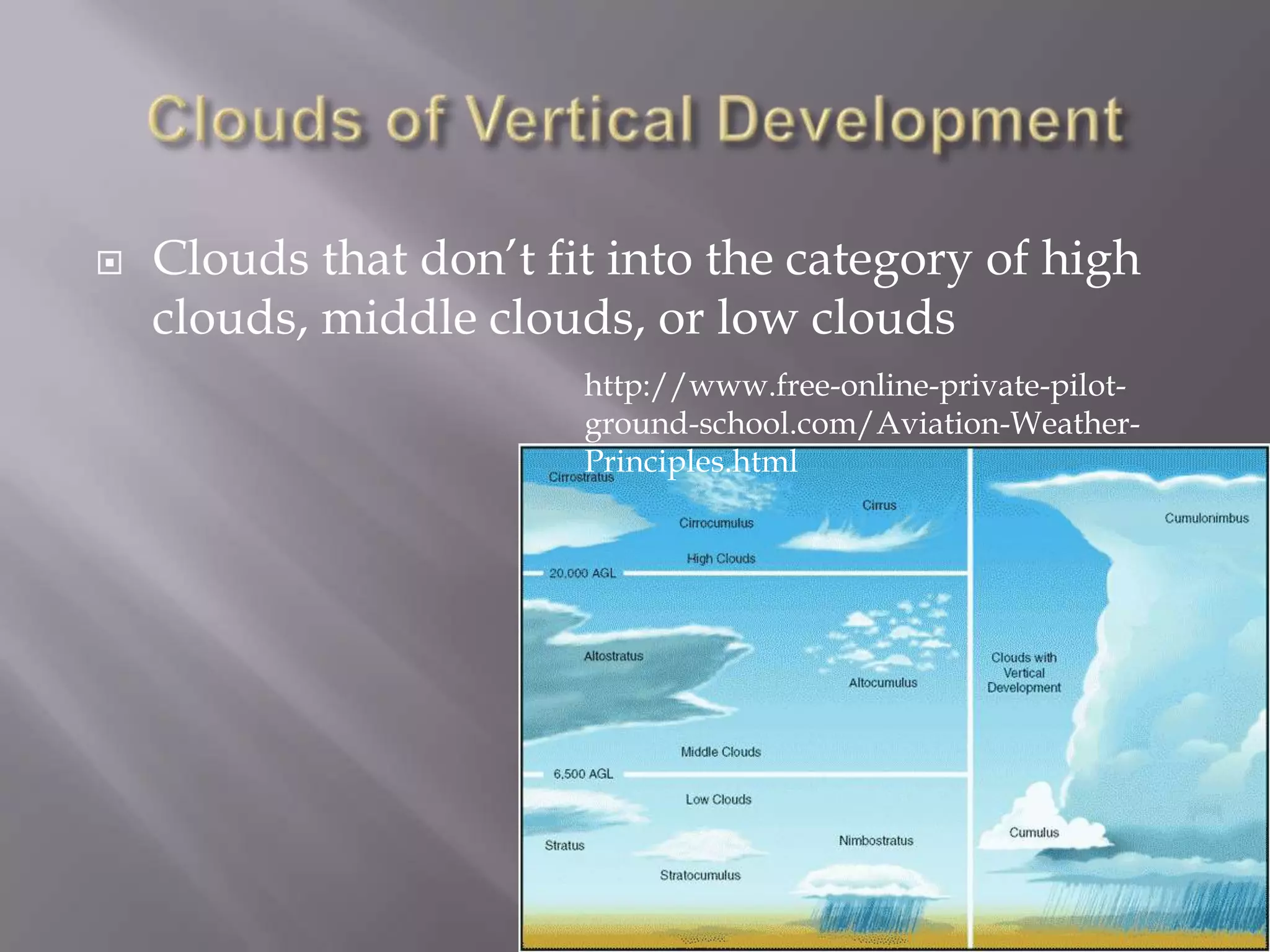
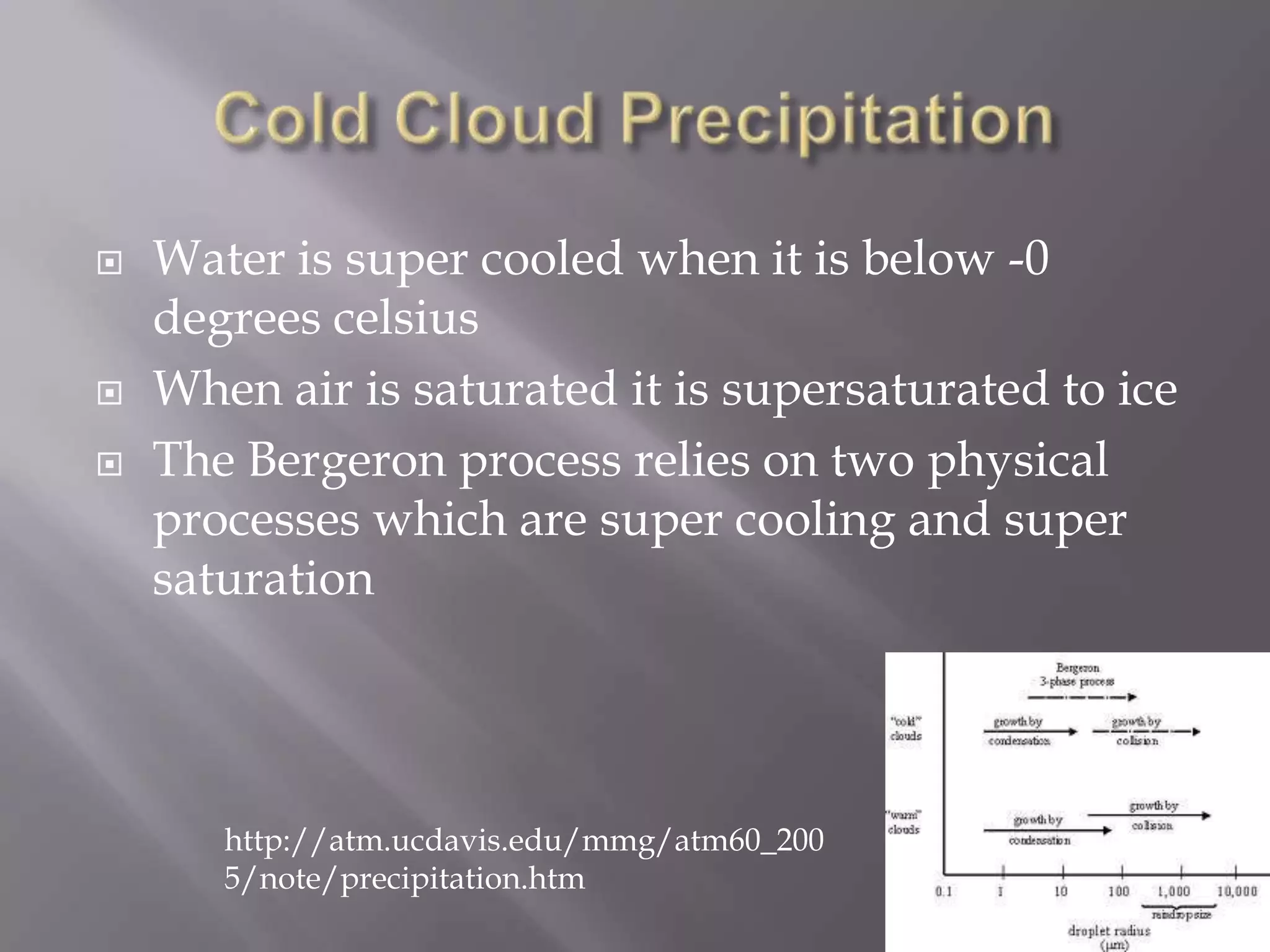
Unequal heating of the Earth's surface causes air temperatures to change without a change in energy. This leads some parts of the Earth to be warmer or cooler than others. When warm air rises and is blocked or forced upward by cooler air, various cloud types can form through condensation. Precipitation occurs through processes like collision-coalescence in warm clouds or Bergeron process in mixed-phase clouds, forming rain, snow, sleet, hail, or freezing rain depending on temperature.