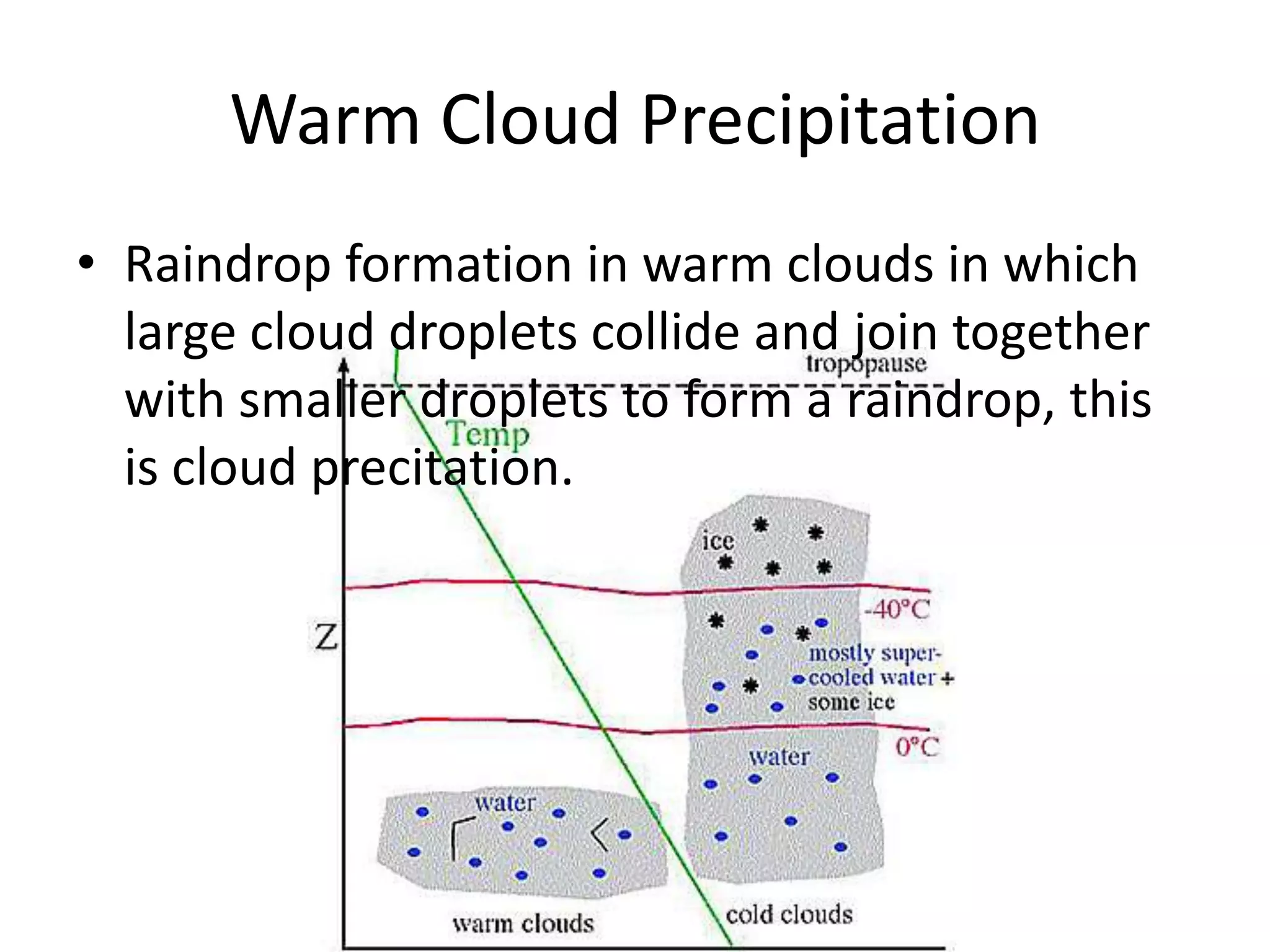
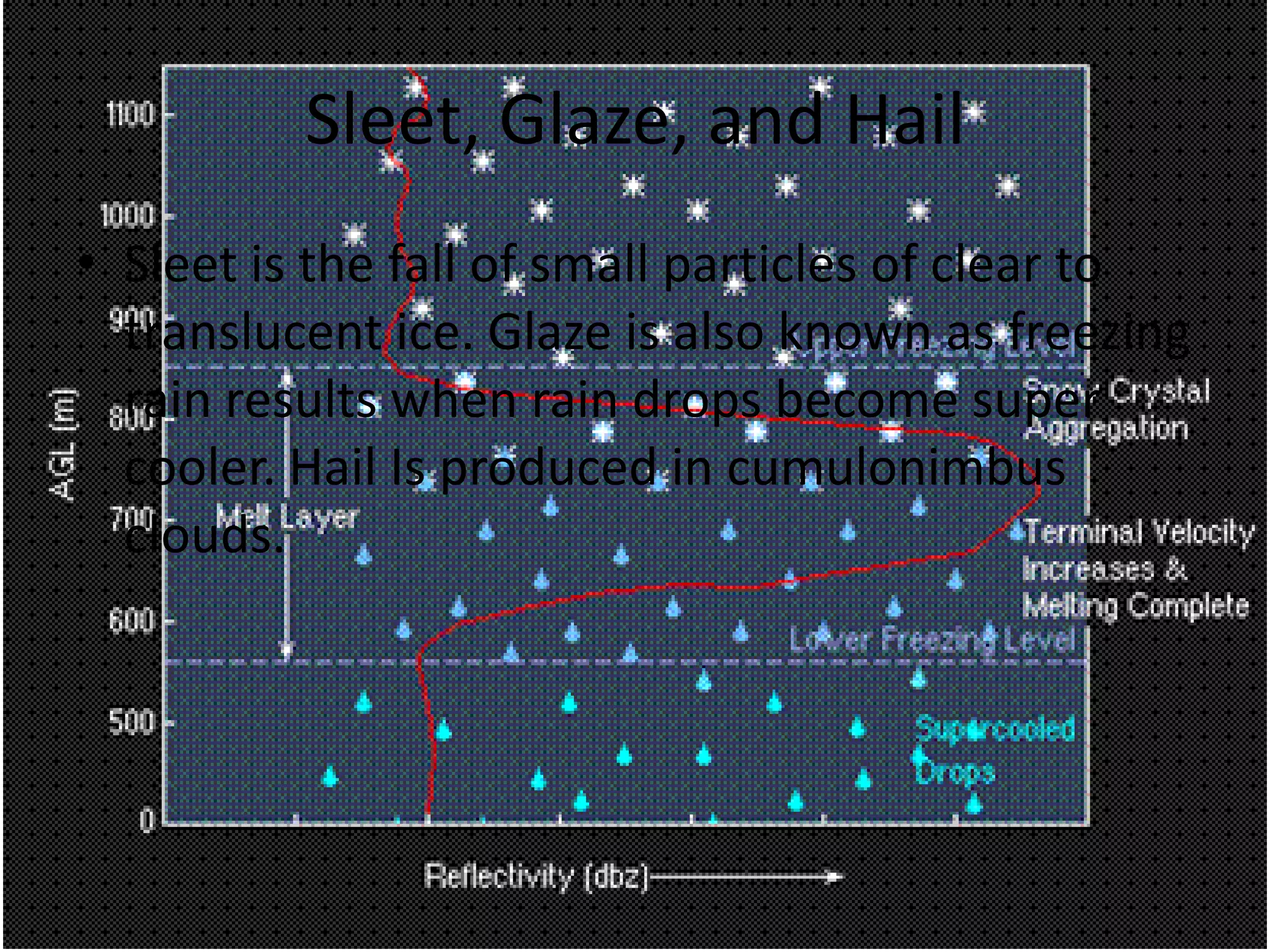
This document discusses various cloud formation processes and types of precipitation. It explains that temperature changes during cloud formation can be adiabatic. Orographic lifting and frontal wedging are processes where air is forced to rise over geographic features or air masses. Convergence and localized convergence involve the coming together of air masses. Condensation allows water vapor to change to liquid water droplets. The main cloud types are categorized by height as high, middle, and low clouds. Fog forms through similar cooling processes as clouds near the surface. Cold cloud precipitation involves freezing nuclei while warm cloud precipitation relies on collisions. Rain, snow, sleet, glaze and hail are different forms of precipitation.