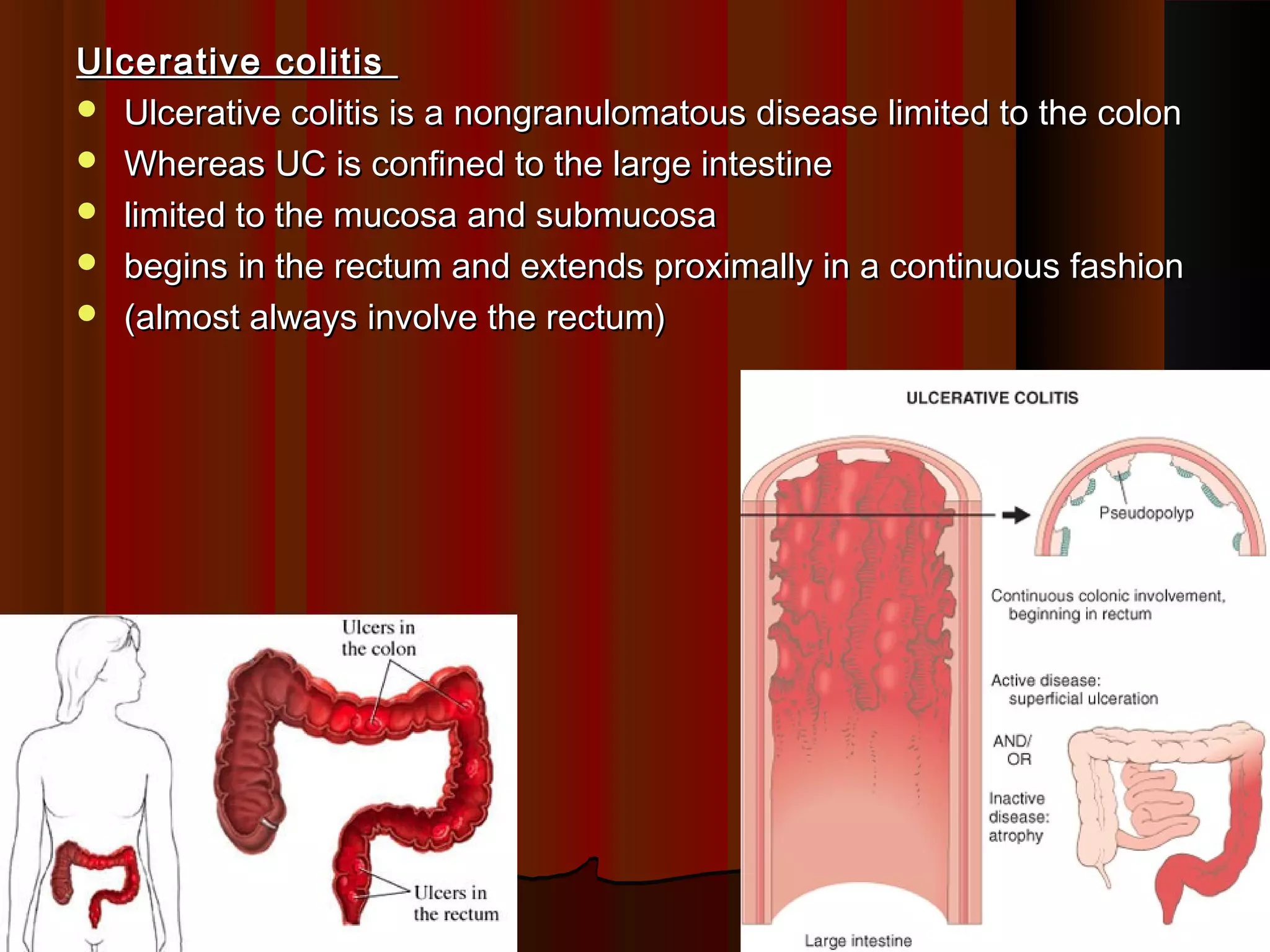
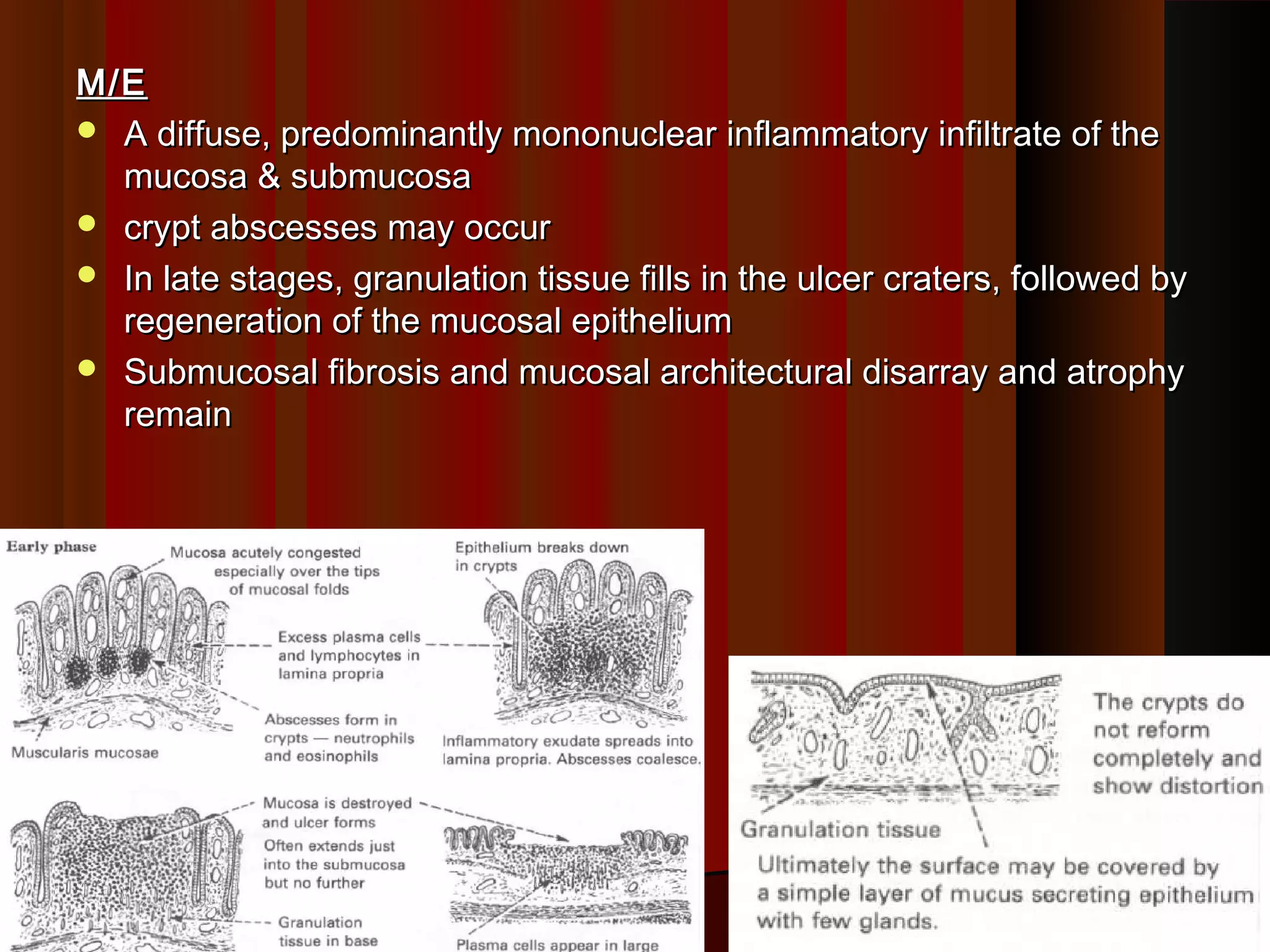
This document summarizes inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), specifically ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. IBD results from an abnormal immune response in the gastrointestinal tract against gut bacteria and antigens. Ulcerative colitis is limited to inflammation of the colon mucosa, while Crohn's disease can impact any part of the GI tract and causes transmural inflammation. The causes of IBD are unknown but involve genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers like infections. Histologically, ulcerative colitis shows diffuse mucosal inflammation and crypt abscesses, while Crohn's disease features non-caseating granulomas and deep ulcers with fibrosis.