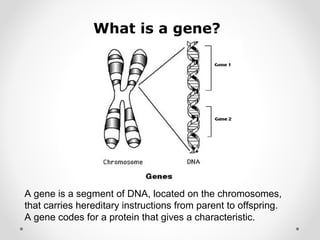
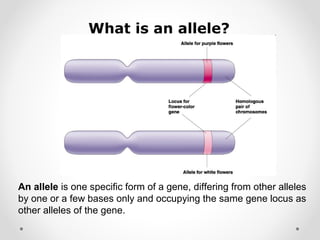
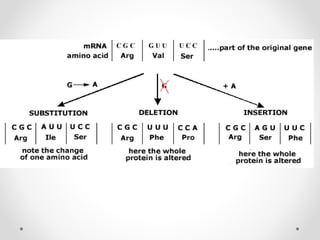
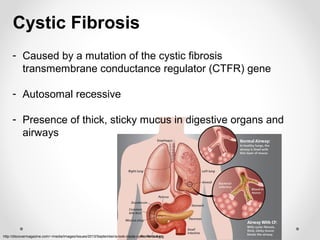
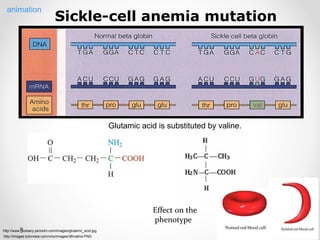
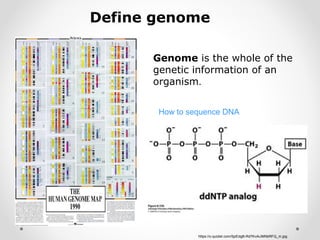
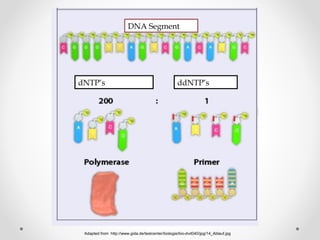
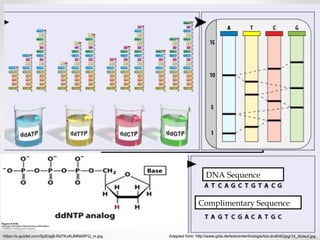
A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein which influences a heritable characteristic. Genes are located on chromosomes at a specific locus and can exist in different alleles that vary in their DNA sequence by one or a few bases. Mutations, or permanent changes in DNA, can occur via mutagens and result in new alleles. The genome is the complete set of genetic material of an organism, such as the human genome which was fully sequenced by the Human Genome Project in 2003.