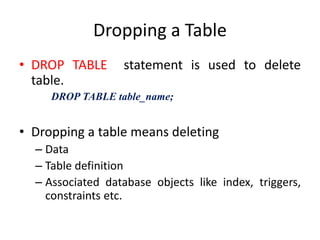
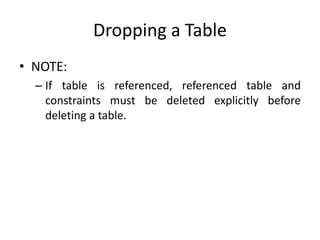
This document discusses how to manage tables in a database including creating, modifying, and dropping tables. The key points are:
1. A table stores data in rows and columns and is created using the CREATE TABLE statement.
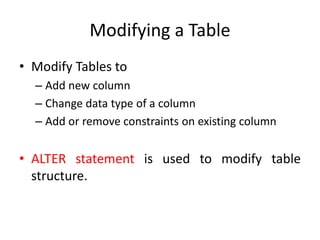
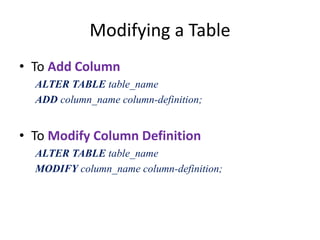
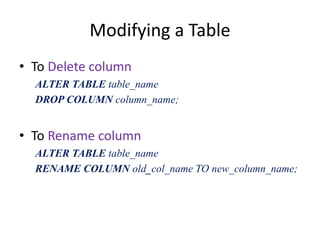
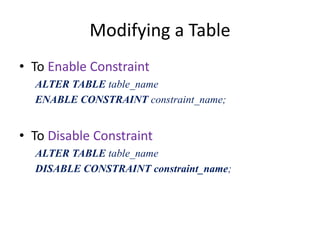
2. Tables can be modified using the ALTER TABLE statement to add, modify, or drop columns and constraints.
3. Integrity constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, checks and defaults are applied to tables to maintain data integrity.
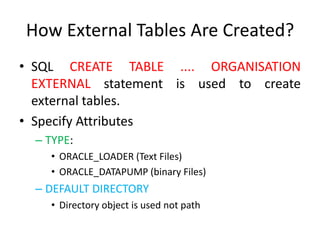
4. External tables allow querying data stored outside the database in flat files and are created using the CREATE TABLE statement with the ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL clause.


![1.2 CREATING A TABLE
CREATE TABLE tablename
(
column1 datatype (size) [DEFAULT expression]
[CONSTRAINT constraint_name constraint_type]
,
column2 datatype (size) [DEFAULT expression]
[CONSTRAINT constraintname constrainttype ],
....
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-4-320.jpg)

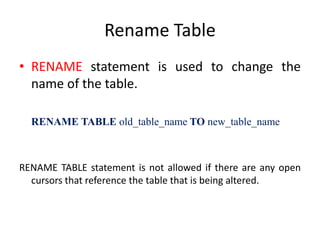





![Applying Constraint - UNIQUE
• Use to enforce uniqueness (entity integrity) on
non-primary columns.
• It ensures no two rows of a table have duplicate
values in a specified column(s).
CREATE TABLE tablename
( column1 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraint_name]
UNIQUE,
column2 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraintname]
UNIQUE], ....
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-18-320.jpg)
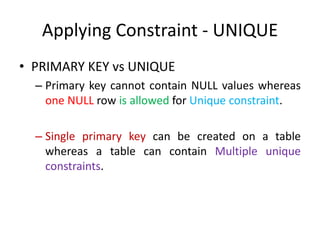
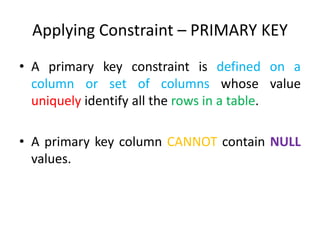
![Applying Constraint – PRIMARY KEY
• Applying Primary Key while creating table
CREATE TABLE tablename
( column1 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT
constraint_name] PRIMARY KEY ,
column2 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT
constraintname constraint_name], .... )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-21-320.jpg)

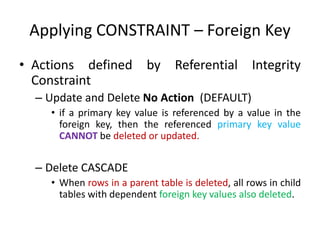
![Applying CONSTRAINT – Foreign Key
• Syntax
CREATE TABLE tablename
( column1 datatype (size) REFERENCES tablename
(columnname) [DELETE CASCADE | DELETE
SET NULL],
column2 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraintname
constraint_name], .... )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-23-320.jpg)

![Applying CONSTRAINT - CHECK
• CHECK constraint enforce domain integrity by
restricting values to be inserted in a column.
CREATE TABLE tablename
( column1 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraint_name]
CHECK (coulumn name check condition), ...... )
• Multiple CHECK constraint can be defined on a
single column.
Expression include elements such as arithmetic
operators, relational operators, keyword such as IN, LIKE
and BETWEEN.
Condition Limitations
• It must be a Boolean expression evaluated using the
values in the row being inserted or updated
•
• It cannot contain subqueries; sequences; the SQL
functions SYSDATE, UID, USER, or USERENV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-26-320.jpg)

![Applying Constraint - DEFAULT
• DEFAULT constraint is used to assign constant
value to a column.
• One DEFAULT constraint can be created for a
column.
CREATE TABLE tablename
( column1 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraint_name]
DEFAULT (constant expression | NULL),
column2 datatype (size) [CONSTRAINT constraintname]
DEFAULT (constant expression | NULL], ....
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-170206105858/85/3-ddl-create-28-320.jpg)