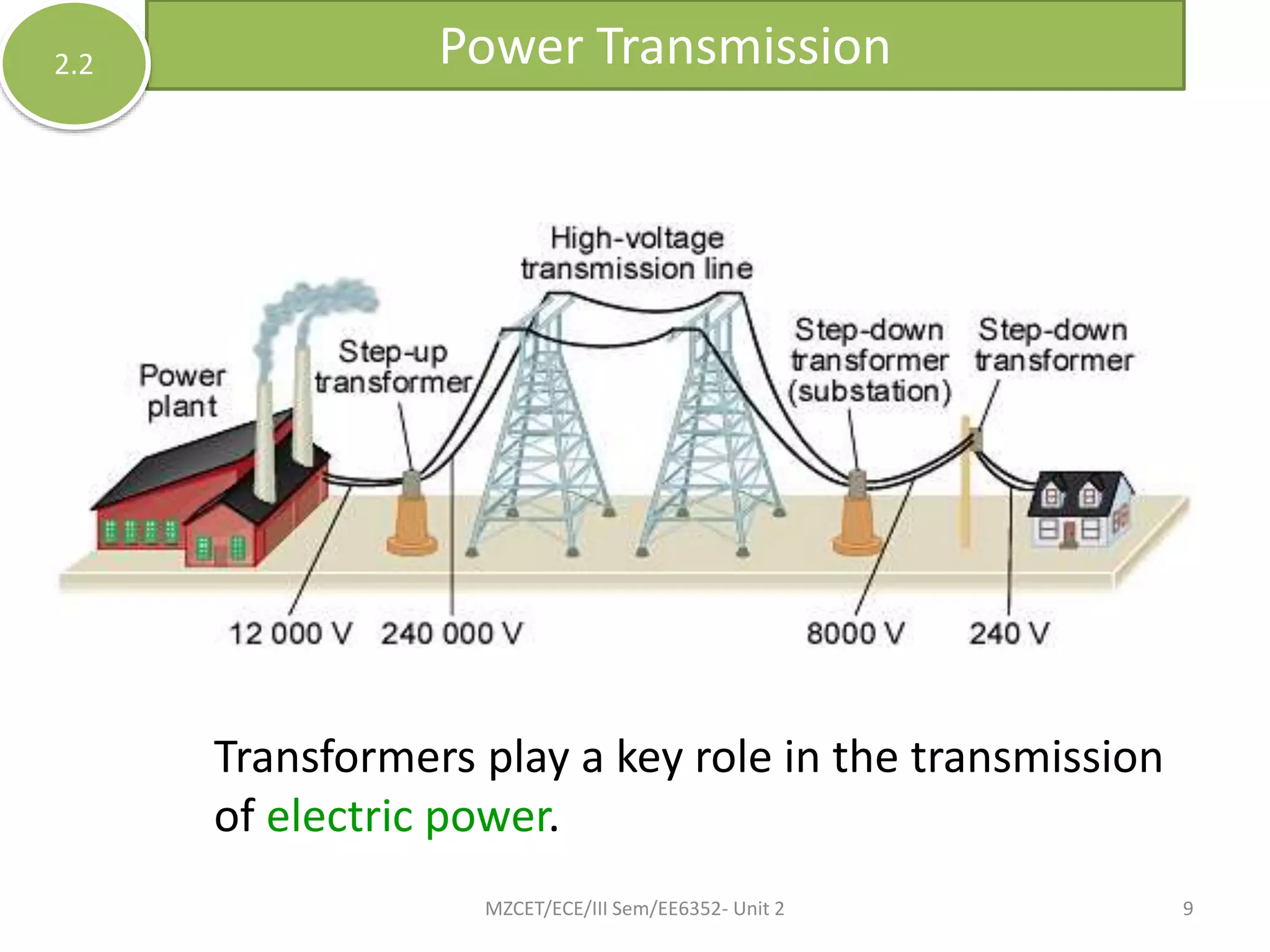
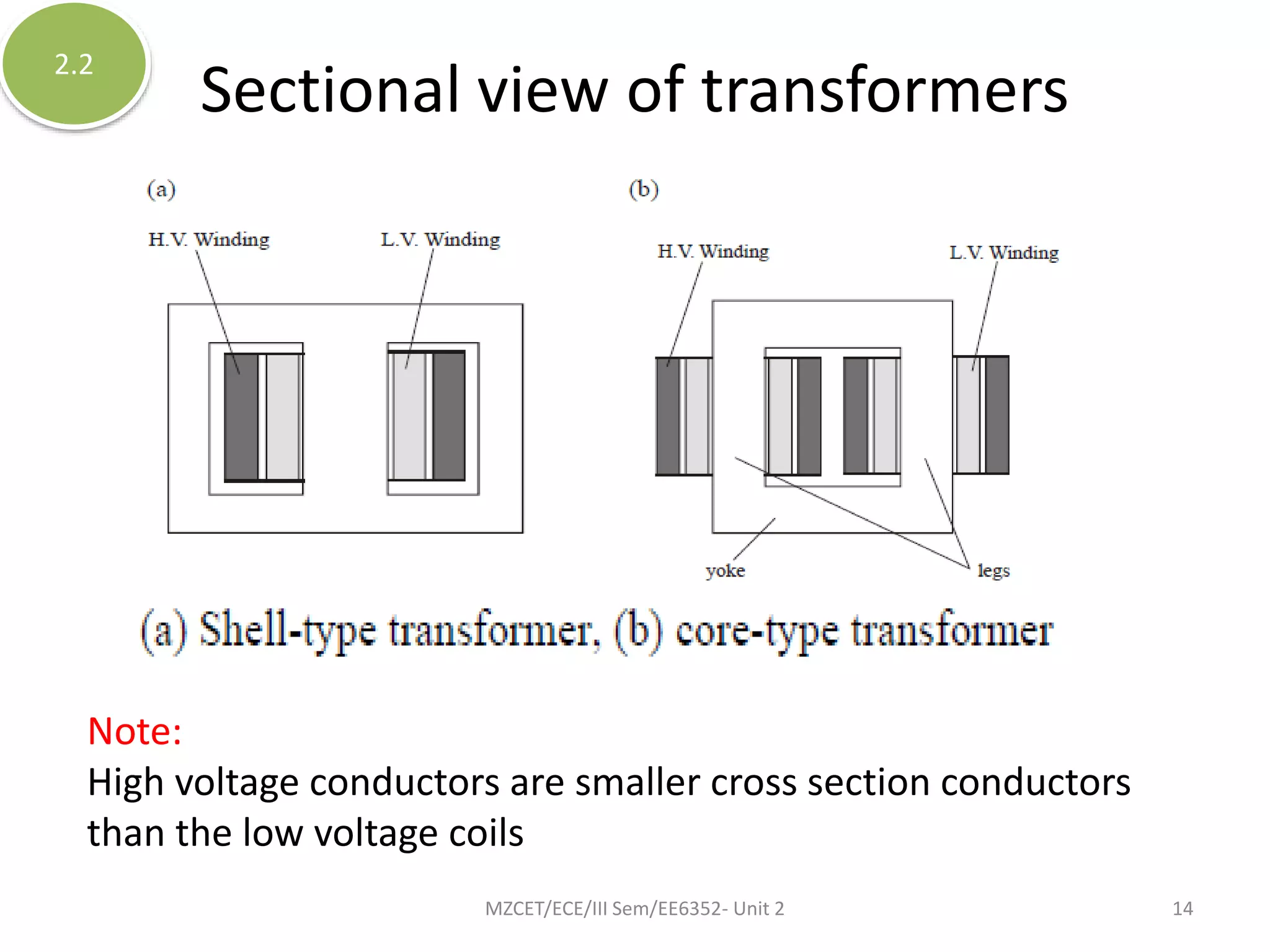
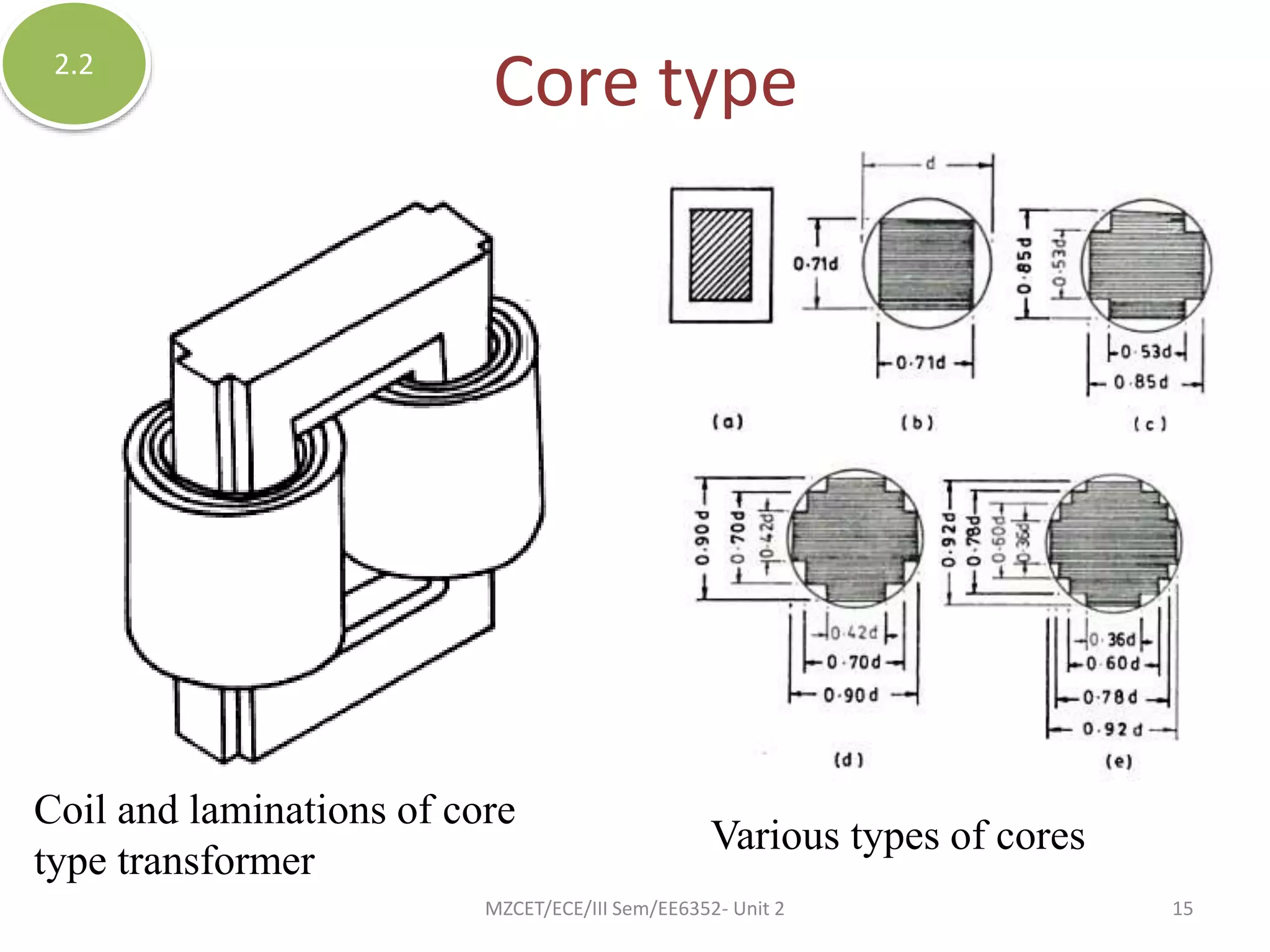
This document discusses the classification and components of transformers. Transformers can be classified by the number of windings (conventional, autotransformer, multi-winding), number of phases (single or three-phase), and voltage level (step-up or step-down). The key components are the core, which is made of laminated steel, and the windings, which can be shell, core, or sandwich type. Transformers work on the principle of mutual induction to transmit power by increasing or decreasing voltages.