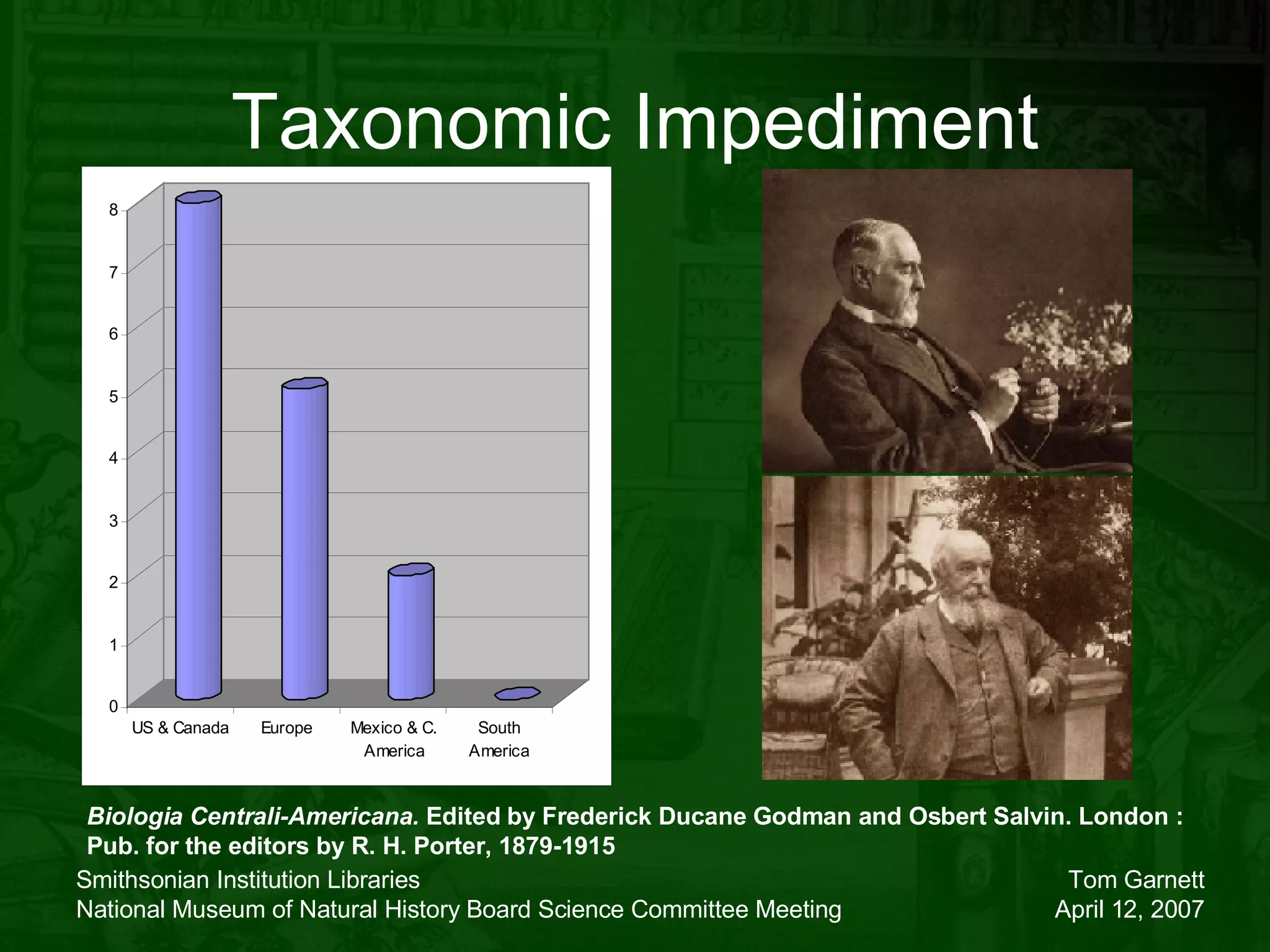
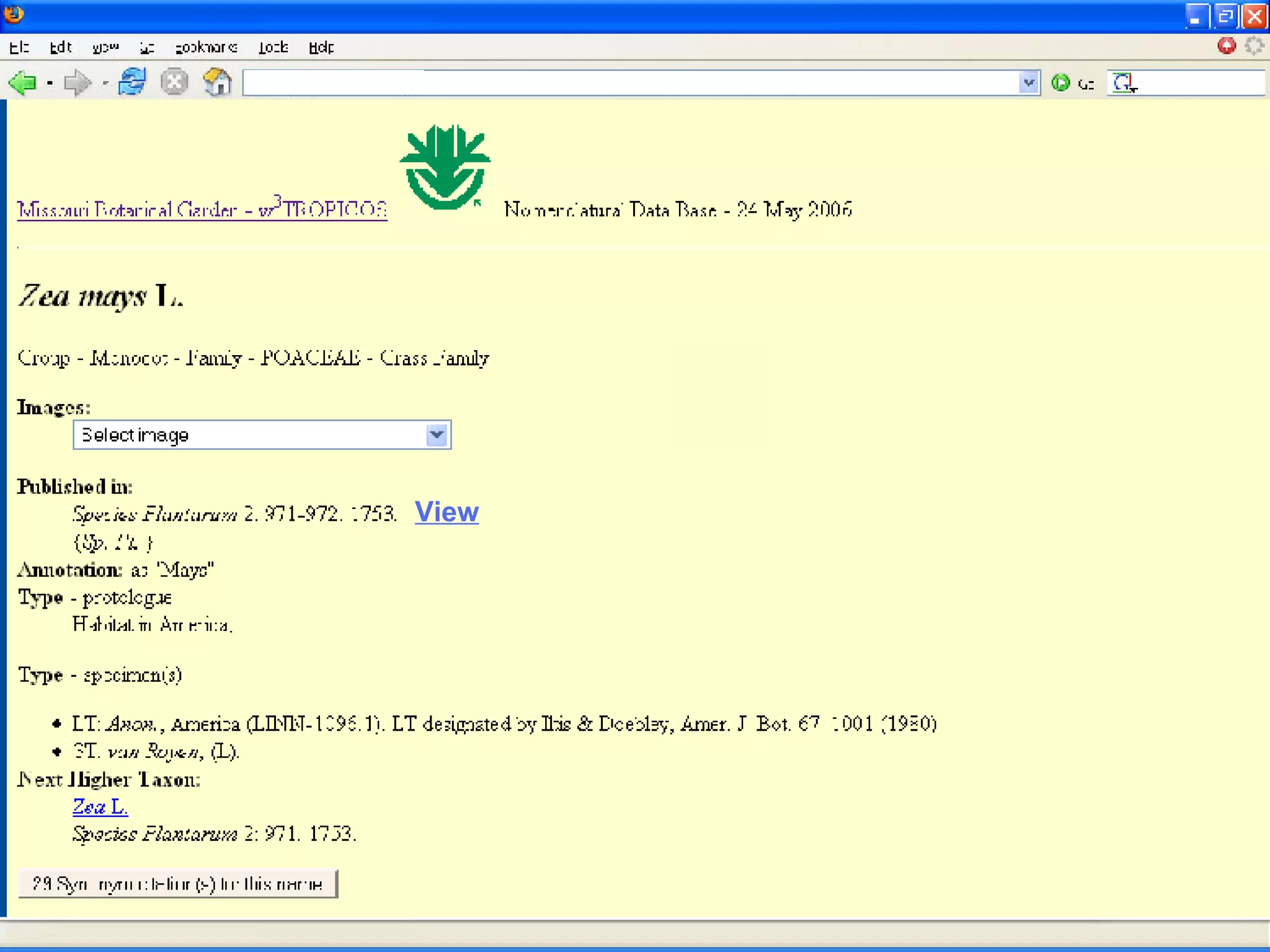
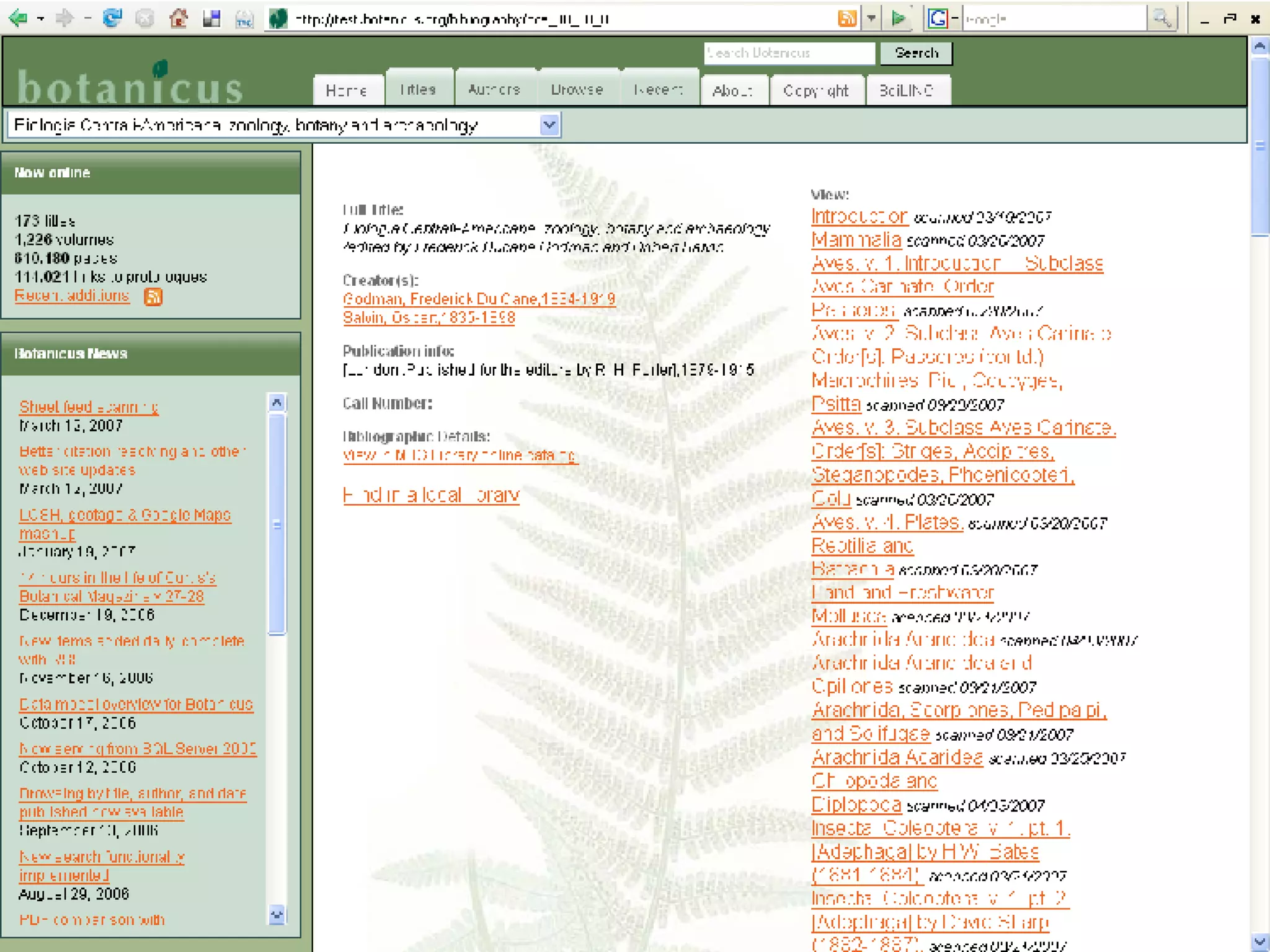
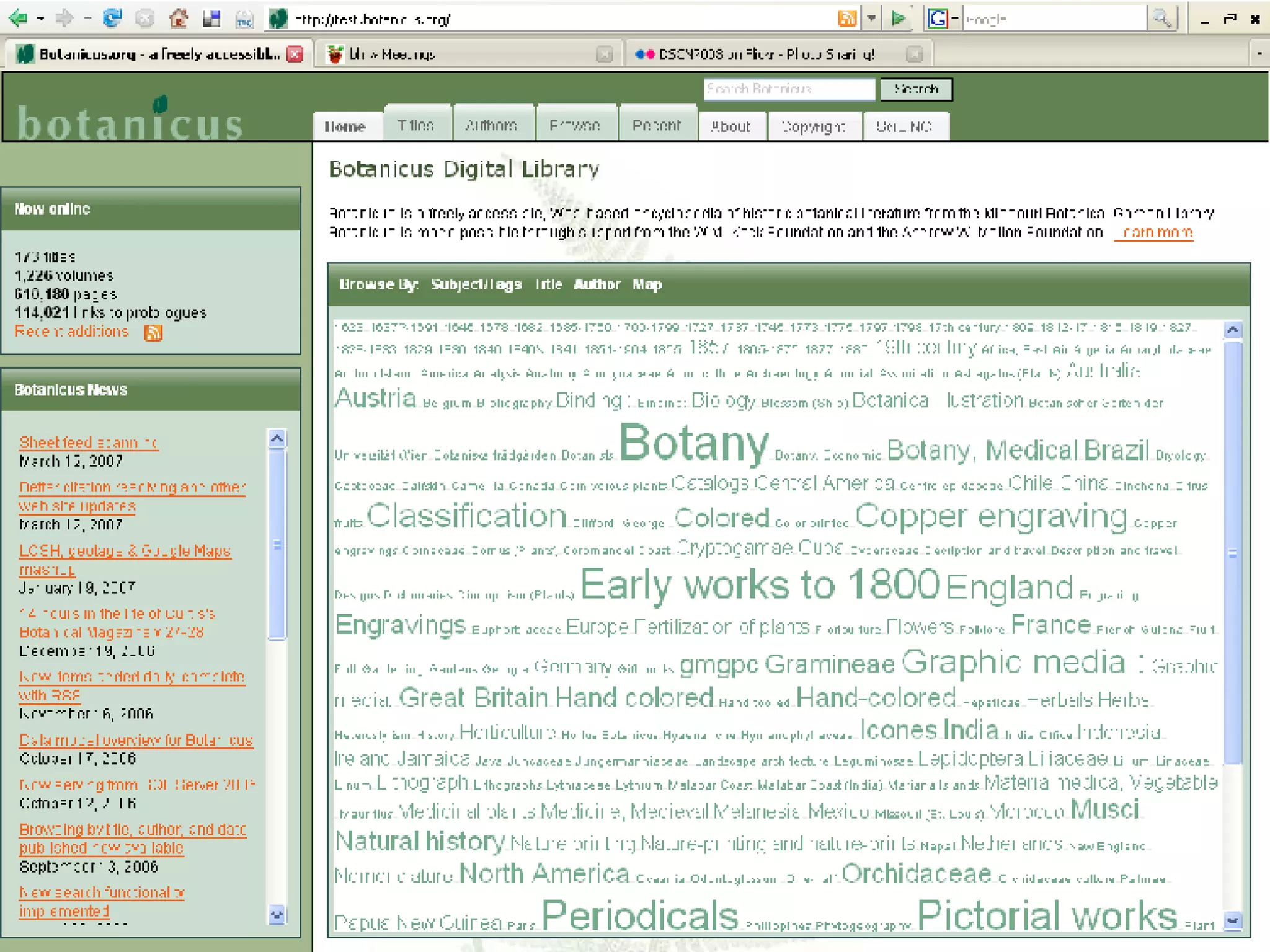
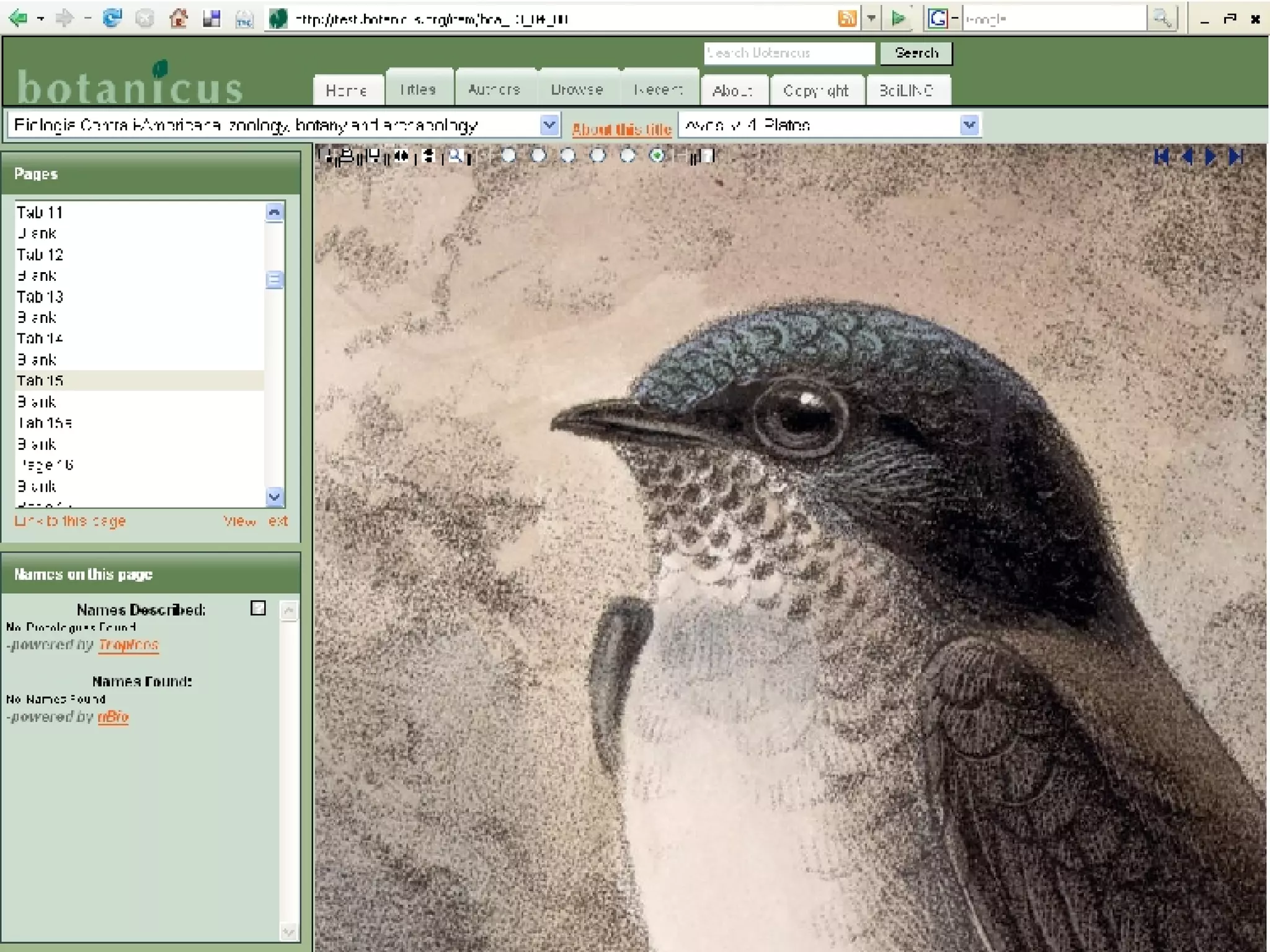
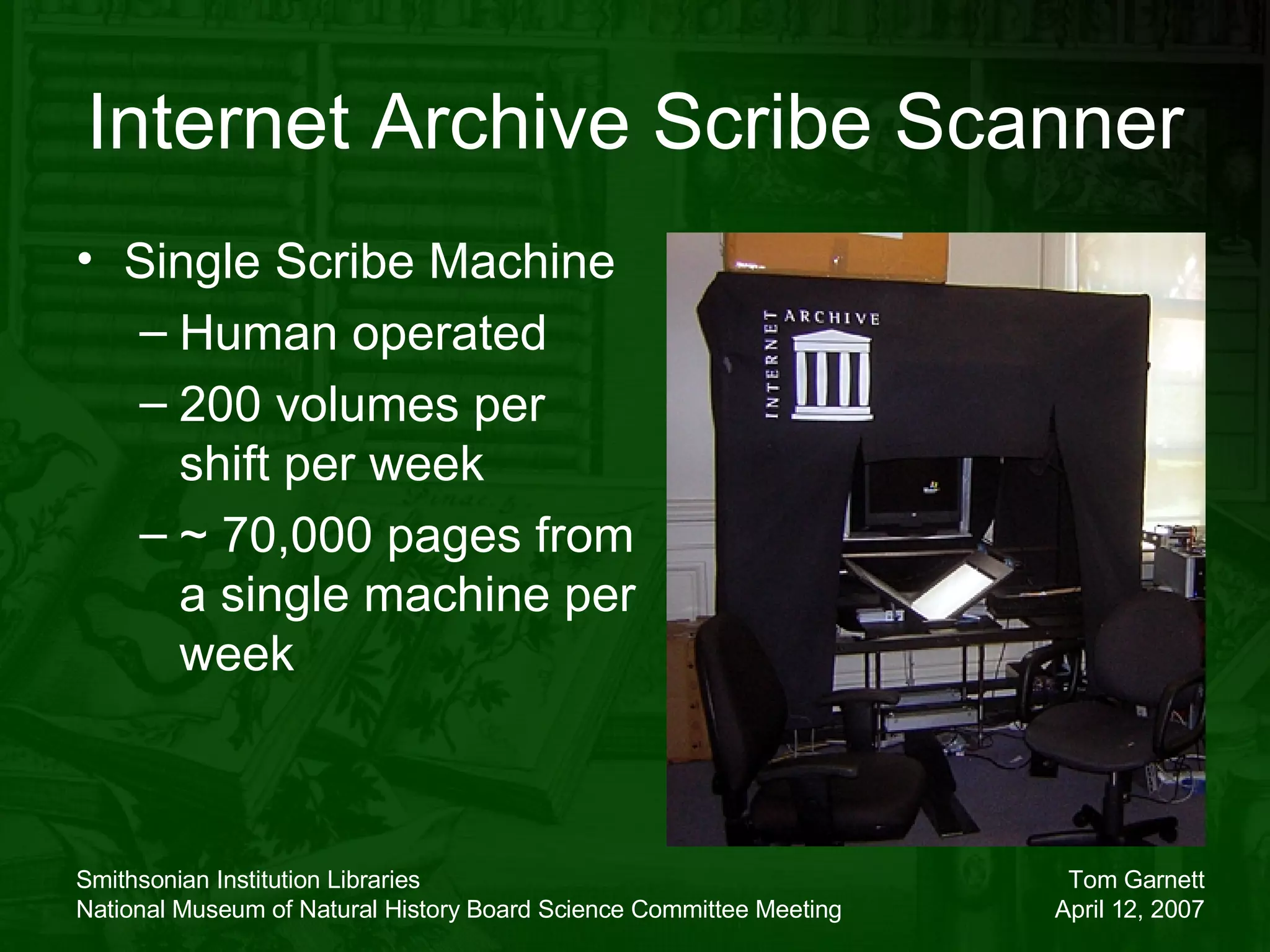
The document discusses the Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL), an open access digital library focused on taxonomic literature from the 18th century onward. It notes that taxonomic literature has a longer half-life of citation than other scientific disciplines. The BHL aims to digitize over 1.4-1.6 million publications, totaling 280-320 million pages, from its partner institutions to make this literature more accessible online. It has already digitized around 400,000 pre-1923 publications totaling 80 million pages.