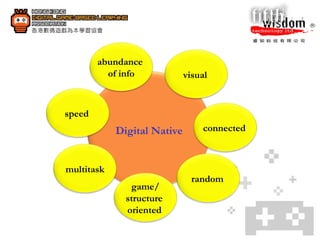
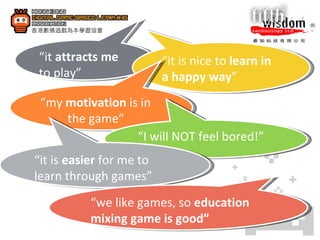
1. Gamifying learning uses gaming mechanics to increase learner engagement, motivation, and enjoyment by having students learn through playing and creating digital games.
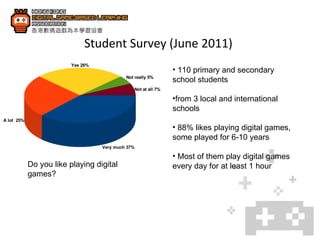
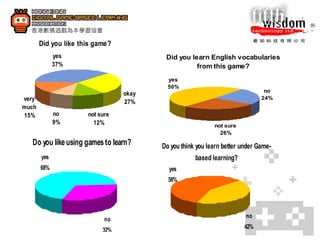
2. Case studies show that students learned English vocabularies faster and were more motivated when learning through a digital game compared to traditional lessons.
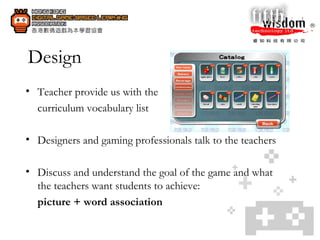
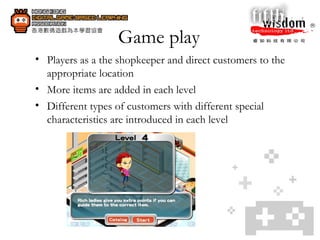
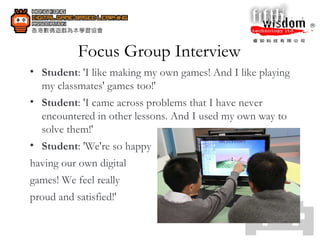
3. When creating their own digital games, students improved skills like programming, creativity, logical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration.

























![Conclusion We seek for advices and improvements while looking for a possible future of digital game-based learning in the Hong Kong classrooms. Thank you! Question or comments? [email_address] www. fifthwisdom.com clara@digitalgameslearning.org www.digitalgameslearning.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18digitalgame-basedlearning-learningandteachingthroughhavingfun-110810044821-phpapp02/85/18-digital-game-based-learning-learning-and-teaching-through-having-fun-34-320.jpg)