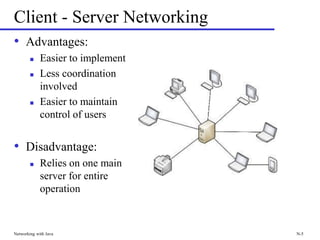
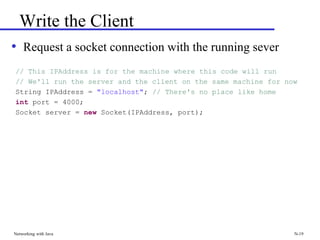
The document discusses networking concepts in Java including client-server and peer-to-peer models. It describes how sockets and streams allow Java programs on different computers to communicate by sending serialized objects over the network. The key classes for networking in Java are ServerSocket, which listens for new connections, and Socket, which represents a connection between two endpoints. Examples are provided to illustrate how to build both a server and client that can transfer objects between each other using input and output streams of a Socket.