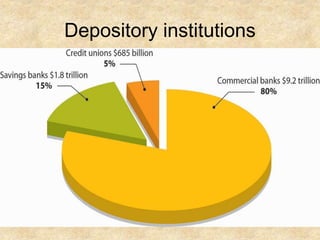
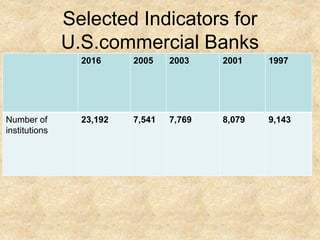
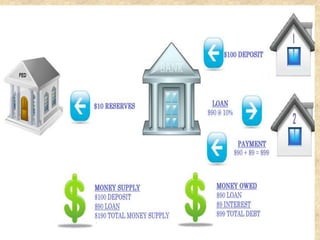
Financial non-depository institutions are financial intermediaries that pool payments from individuals in the form of premiums, contributions, or property used as collateral for pawnshop loans. They include pension funds, securities firms, government agencies, finance companies, insurers, and smaller operations like pawnshops. Insurers may specialize in life insurance, annuities, or other types of coverage. Mutual funds pool investor money to purchase securities, while brokerages assist with stock and investment purchases either online or through branches.