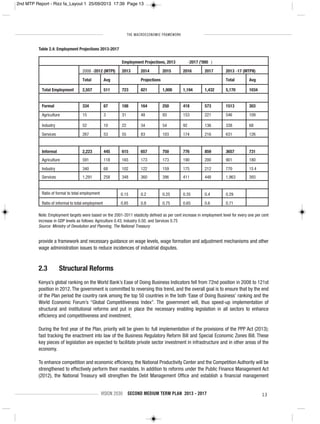
This document outlines Kenya's Second Medium Term Plan from 2013 to 2017. Some key points:
- It aims to accelerate economic growth and achieve a double digit GDP growth rate to reduce poverty, unemployment and inequality.
- Priority sectors for investment and growth include infrastructure, agriculture, livestock, fisheries, manufacturing, oil and mineral resources.
- It emphasizes implementing devolution, training youth, and commercializing agriculture to increase incomes and food security.
- Reforms are outlined in areas like public sector, land, science and technology, and establishing national values and ethics.

































































































![VISION 2030 SECOND MEDIUM TERM PLAN 2013 - 201792
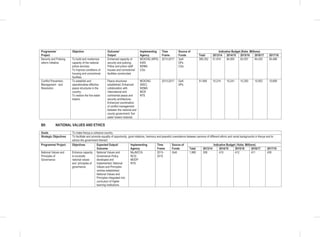
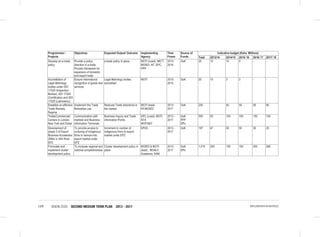
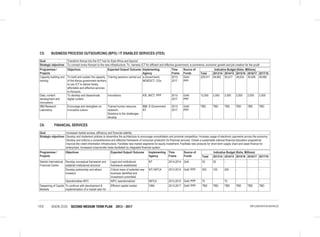
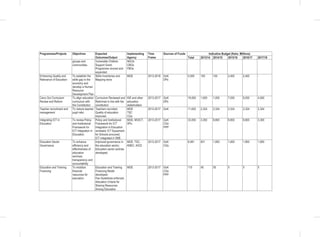
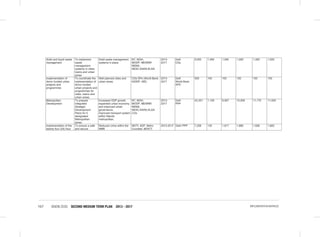
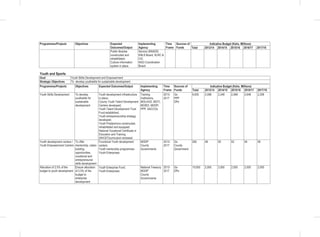
THE SOCIAL PILLAR
disaggregated data to update the gender development index;
• Establishment of Gender Research and Documentation Centre: The sub-sector will establish and equip the centre
with requisite resources;
• Establishment of integrated one stop sexual and gender based violence response centers in all healthcare facilities
in Kenya. The proposed centers will offer medical, legal and psychosocial support to victims of SGBV;
• Public awareness campaign against FGM, early and forced marriages: The sub-sector will develop and implement
a national sexual and gender based violence policy and operationalize the FGM Act 2011.The sub-sector will work
closely with the National Gender and Equality commission to issue sanctions and recommend prosecution on
gender discrimination cases.
Women’s Empowerment: The following specific interventions will be undertaken:
• Implementation of the 30 percent public procurement preference for women entrepreneurs: The sub-sector will
carry out a public awareness campaign on the provisions of the Public Procurement and Disposable [Preference
and Reservation] Regulations 2013 for women;
• Implementation of the Uwezo Fund; the sub-sector will seek to expand access to finances and promote women led
enterprises at the constituency level through the Uwezo Fund;
• Women Enterprise Fund:The sub-sector will seek to review the funds product and services, re-brand and re-launch
the Women Enterprise Fund.
Vulnerable Groups
Consolidated Social Protection Fund
• Establishment of the single registry for all CSPF Initiatives;
• Support to Persons with Albinism (PWA); and
• Establishment of National Safety Nets Program.
Scale up the National Development Fund for PWDs: This fund will provide assistance to persons with disabilities for
their socio-economic empowerment. It will also support infrastructure improvement to institutions providing services to
PWDs and capacity building for disabled persons’ organizations.
Implementation of the 30 percent public procurement preference for Person With Disability: The sub-sector will
carry out a public awareness campaign on the provisions of the Public Procurement and Disposable [Preference and
Reservation] Regulations 2013 for PWD’s.
Disability Mainstreaming (inclusion and accessibility): This will ensure that issues that directly affect PWDs
are adequately addressed in policies and legal frameworks, programmes and projects.
Child Protection Programmes: Under this flagship project the following interventions will be undertaken:-
• Establishment of Child Protection Centres;
• Development of Integrated Data Management System for children;
• Implementation of Children Rehabilitation Programmes;
• Facilitating alternative family care services (Adoption, foster care and guardianship); and
• Finalize and implement the National Community Development Policy.
Other Programmes
• Public awareness on the needs, aspirations and capacities of vulnerable persons;
• Review Child participation Guidelines (2006);
• Support Children Assemblies; and
• Child helpline (116)
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1secondmediumtermplan2013-2017-150113065022-conversion-gate01/85/1-second-medium-term-plan-2013-2017-107-320.jpg)
![VISION 2030 SECOND MEDIUM TERM PLAN 2013 - 2017 93
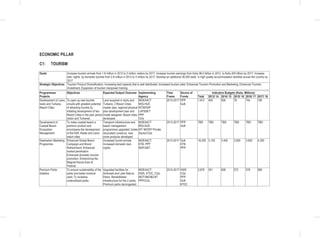
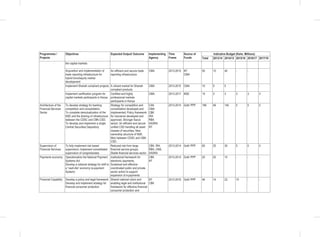
THE SOCIAL PILLAR
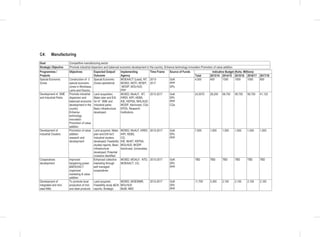
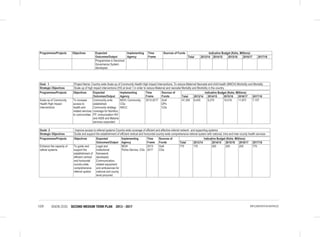
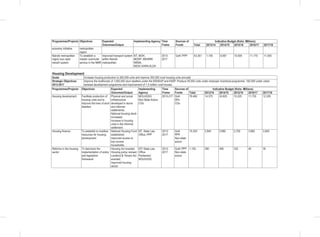
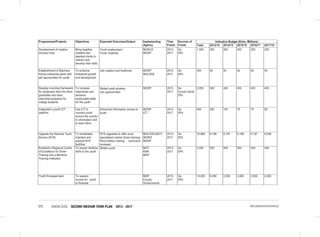
Youth
Flagship Projects
Youth Skills Development: Among the specific interventions under this flagship will be the following;-
• Establishment of youth development centers, offering mentorship, nation-building, value building opportunities,
vocational and entrepreneurial skills development.
• Ensure allocation of 2.5% of the budget to youth development.
• Development of creative industry hubs.
• Establishment of Biashara Kenya enterprise parks with job opportunities for the youth.
• Develop incentive framework for employers who hire fresh graduates and have internship programs for college
students.
• Integrated e-youth ICT platform. The sub-sector will establish a youth portal to enhance information access to the
youth
• Upgrade the National Youth Service (NYS) with projected annual youth recruitment of more than ten thousand
recruits.
• Establish a Regional Centre of Excellence for Driver Training and a Maritime Training Institution
Youth Empowerment: Among the specific interventions under this flagship will be the following;
• Implementation of the 30 percent public procurement preference for all youth in all MDAs:The sub-sector will carry
out a public awareness campaign on the provisions of the Public Procurement and Disposable [Preference and
Reservation] Regulations 2013 for youth
• Implementation of the Uwezo Fund; The sub-sector will seek to expand access to finances and promote youth led
enterprises at the constituency level through the Uwezo Fund.
• Youth Enterprise Fund: The sub-sector will seek to review the funds product and services, re-brand and re-launch
the Youth Enterprise Fund.
• Development and implementation of Youth leadership and entrepreneurship strategy
5.5.4 Policy, Legal and Institutional Reforms
Gender
• Development and Enactment of the WEF Bill
• Develop and Implement the National Equality Bill;
• Develop and Implement the Sexual and Gender Based Violence Policy; and
• Finalize and Implement the National Affirmative Action Policy
• Review the National Gender and Development Policy
• Develop and Implement the Public Financial Management (Uwezo Fund) Regulations 2013.
• Implementation of Public Procurement and Disposable [Preference and Reservation] Regulations 2013 for women.
Vulnerable Groups
• Establishment of National Safety Net Program;
• Finalize and Implement the Disability Act Amendment Bill 2012;
• Finalize and Implement the Affirmative Action Policy on PWDs;
• Develop and Implement the National Disability Mainstreaming Strategy;
• Implementation of Accessibility Action Plan;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1secondmediumtermplan2013-2017-150113065022-conversion-gate01/85/1-second-medium-term-plan-2013-2017-108-320.jpg)
![VISION 2030 SECOND MEDIUM TERM PLAN 2013 - 201794
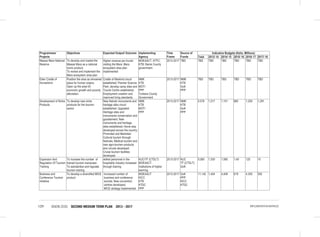
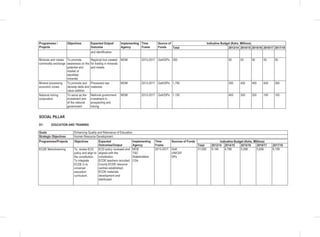
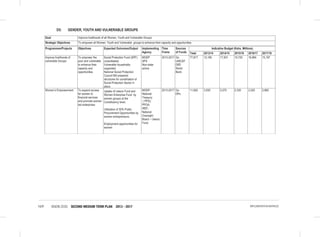
THE SOCIAL PILLAR
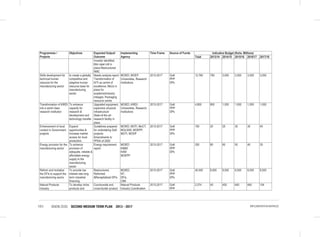
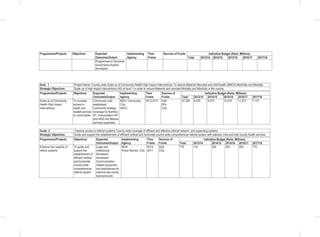
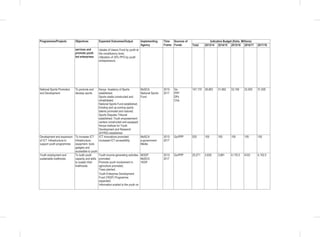
• Finalize and Implement the National Community Development Policy;
• Development of a National volunteerism policy;
• Passing of the Children Amendment Bill into law;
• Revision of child participation guidelines and guidelines on children’s services delivery to take into account amongst
others, Kinship Adoption;
• Development of a National Action Plan on Children for the implementation of the National Children’s Policy;
• Development of a National Social Protection Sessional Paper based on the National Social Protection Policy;
• Establishment of a National Social Protection Council;
• Development of a Social Assistance Bill; and
• Review of various Social Protection components (Social Insurance, Health insurance) policies to be in line with the
National Social Protection Policy.
Youth
• Reviewing the National Youth Policy (2007);
• Review the National Youth Council Act 2009;
• Review National Youth Service Act(1964);
• Develop and Enact the National Youth Enterprise Development Bill;
• Implementation of the National Industrial Training Attachment Policy;
• Develop the National Youth Employment Policy;
• Finalization and implementation of the National Policy on Youth Polytechnics and the Vocational Sector (NPYPVS);
• Develop the Youth Societies Bill;
• Develop the Policy and Framework on Youth Talent, Identification and Nurturing;
• Develop National Youth & Internship Volunteer Policy;
• Implementation the Public Procurement and Disposable [Preference and Reservation] Regulations 2013 for youth;
• Develop and Implement the Public Financial Management (Uwezo Fund) Regulations 2013.
5.6 Sports, Culture and Arts
“Celebrating the Best in Us”
Kenya Vision 2030 recognizes that regulation and effective exploitation of Public Benefits Organisations (PBOs) sector,
positive promotion and effective exploitation of our cultural diversity, preservation and promotion of national heritage,
sports and arts are critical to socio-economic, political and cultural development.
5.6.1 Situation Analysis
The sector has proved to be a major contributor to socio-economic development.Towards this end, a national policy on
heritage and culture was developed aimed at creating an enabling environment for the development of creative cultural
industry with a view to preserve, promote Kenya’s rich cultural heritage and employment creation.
An international sports academy will be set up at the Moi International Sports Centre Kasarani where land has already
been identified for development and the initial concepts, design and bill of quantities developed. The academy will
nurture top level skills development of sports men and women whose talent is tapped from the grassroots level
countrywide as well as train sports administrators, instructors and coaches.
The Kenya National Library Services has increasingly continued to improve access to information and knowledge
sources to all communities. With a network of 59 branch libraries countrywide, 11 million Kenyans visit these library
centres annually to seek information to meet their various needs, this represents a paltry 26% of total population.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1secondmediumtermplan2013-2017-150113065022-conversion-gate01/85/1-second-medium-term-plan-2013-2017-109-320.jpg)