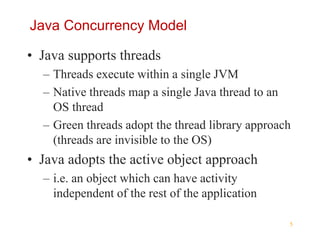
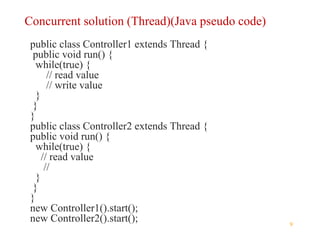
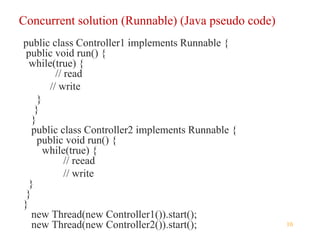
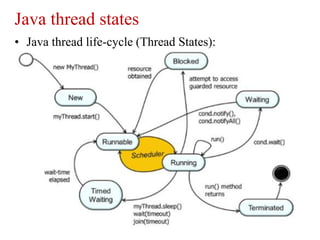
Multithreading in Java allows expressing potentially parallel code through threads. A thread represents concurrently executable code as a Runnable or by overriding the run() method in a Thread subclass. Starting a Thread object via its start() method executes the run() method concurrently. Threads run independently until completing run() or being blocked by operations like sleeping, locking, waiting or joining with other threads.