The document provides an overview of loops in programming, specifically in C#. It covers various types of loops such as while loops, do-while loops, for loops, and foreach loops, along with their syntax, usage, and examples. Additionally, it discusses loop control operators like break and continue, nested loops, and practical examples of loop implementations.






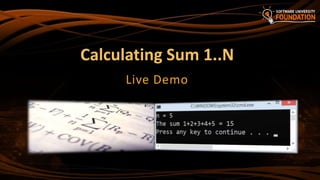








![22
Calculating the product of all numbers in the interval [n..m]:
Product of Numbers [N..M] – Example
int n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int m = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int number = n;
decimal product = 1;
do
{
product *= number;
number++;
}
while (number <= m);
Console.WriteLine("product[{0}..{1}] = {2}", n, m, product);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-22-320.jpg)
![Product of the Numbers
in the Interval [n..m]
Live Demo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-23-320.jpg)









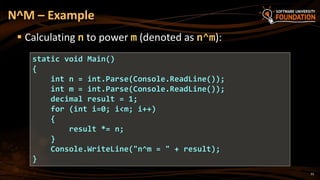

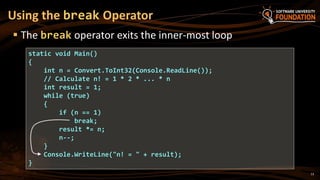
![ continue bypasses the iteration of the inner-most loop
Example: sum all odd numbers in [1…n], not divisors of 7:
Using the continue Operator
int n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2)
{
if (i % 7 == 0)
{
continue;
}
sum += i;
}
Console.WriteLine("sum = {0}", sum);
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-35-320.jpg)


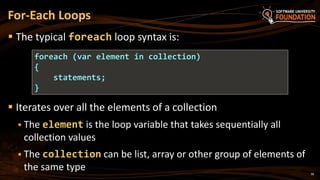
![ Example of foreach loop:
The loop iterates over the array of day names
The variable day takes all its values
Inside a foreach loop we cannot modify the current item
foreach Loop – Example
string[] days = {
"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday",
"Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday" };
foreach (var day in days)
{
Console.WriteLine(day);
}
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-39-320.jpg)




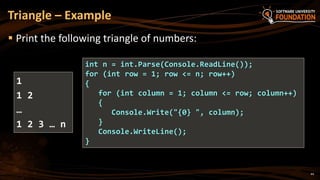

![Primes in the Range [N … M] – Example
int n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int m = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
for (int number = n; number <= m; number++)
{
bool prime = true;
int divider = 2;
int maxDivider = Math.Sqrt(number);
while (divider <= maxDivider)
{
if (number % divider == 0)
{
prime = false;
break;
}
divider++;
}
if (prime)
Console.Write("{0} ", number);
}
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-46-320.jpg)
![Primes in the Range [n, m]
Live Demo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-200318130538/85/06-Loops-47-320.jpg)