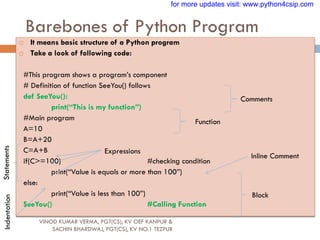
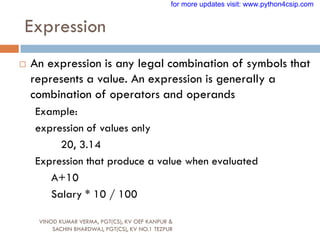
This document provides an overview of Python fundamentals including character sets, tokens, keywords, identifiers, literals, data types, input/output, and type conversions. It describes the basic building blocks of the Python language such as letters, digits, symbols, whitespace, and escape characters that make up character sets. It also defines tokens, keywords, identifiers, literals (string, numeric, boolean, none), and discusses single-line vs. multi-line strings and string operations like length. The document concludes with sections on basic input/output and type conversions.

![Python Character Set
VINOD KUMAR VERMA, PGT(CS), KV OEF KANPUR &
SACHIN BHARDWAJ, PGT(CS), KV NO.1 TEZPUR
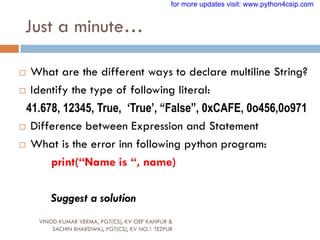
Is a set of valid characters that python can recognize. A
character represent letters, digits or any symbol. Python
support UNICODE encoding standard. Following are the
Python character set
Letters : A-Z, a-z
Digits : 0-9
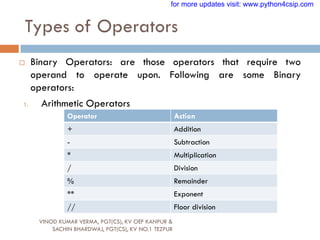
Special symbols :space +-*/()~`!@#$%^ & [{
]};:‟”,<.>/?
White spaces : Blank space, Enter, Tab
Other character : python can process all ASCII and
UNICODE as a part of data or literal
for more updates visit: www.python4csip.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008featuresofpython-230615073053-a9af4c61/85/008-FEATURES-OF-PYTHON-pdf-2-320.jpg)































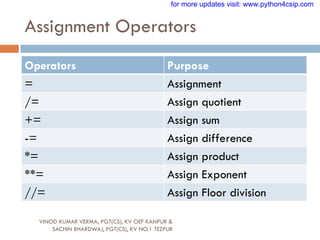

![Punctuators
VINOD KUMAR VERMA, PGT(CS), KV OEF KANPUR &
SACHIN BHARDWAJ, PGT(CS), KV NO.1 TEZPUR
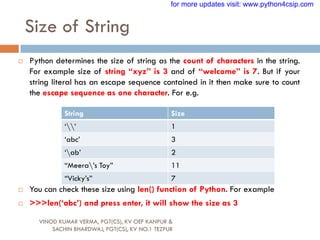
Punctuators are symbols that are used in programming
languages to organize sentence structure, and indicate
the rhythm and emphasis of expressions, statements,
and program structure.
Common punctuators are: „ “ # $ @ []{}=:;(),.
for more updates visit: www.python4csip.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008featuresofpython-230615073053-a9af4c61/85/008-FEATURES-OF-PYTHON-pdf-43-320.jpg)






![Variables
VINOD KUMAR VERMA, PGT(CS), KV OEF KANPUR &
SACHIN BHARDWAJ, PGT(CS), KV NO.1 TEZPUR
Note: Python variables are not storage containers like other
programming language. Let us analyze by example.
In C++, if we declare a variable radius:
radius = 100
[suppose memory address is 41260]
Now we again assign new value to radius
radius = 500
Now the memory address will be still same only value
will change
for more updates visit: www.python4csip.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008featuresofpython-230615073053-a9af4c61/85/008-FEATURES-OF-PYTHON-pdf-53-320.jpg)
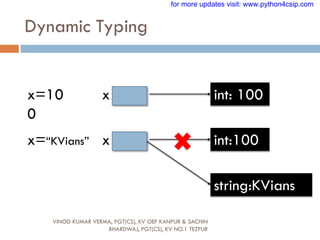
![Variables
VINOD KUMAR VERMA, PGT(CS), KV OEF KANPUR &
SACHIN BHARDWAJ, PGT(CS), KV NO.1 TEZPUR
Now let us take example of Python:
radius = 100 [memory address 3568]
radius = 700 [memory address 8546]
Now you can see that In python, each time you assign new
value to variable it will not use the same memory address
and new memory will be assigned to variable. In python the
location they refer to changes every time their value
change.(This rule is not for all types of variables)
for more updates visit: www.python4csip.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008featuresofpython-230615073053-a9af4c61/85/008-FEATURES-OF-PYTHON-pdf-54-320.jpg)









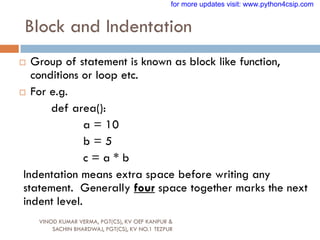
![Output through print()
VINOD KUMAR VERMA, PGT(CS), KV OEF KANPUR &
SACHIN BHARDWAJ, PGT(CS), KV NO.1 TEZPUR
Python allows to display output using print().
Syntax:
print(message_to_print[,sep=“string”,end=“string”])
Example 1
print(“Welcome”)
Example 2
Age=20
print(“Your age is “, Age)
for more updates visit: www.python4csip.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/008featuresofpython-230615073053-a9af4c61/85/008-FEATURES-OF-PYTHON-pdf-65-320.jpg)