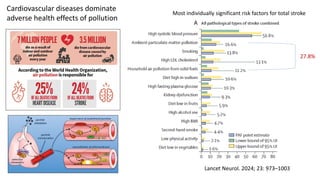
Professor Sir Stephen Holgate highlights the grave impacts of air pollution on human health, noting its role as the leading environmental risk factor and its connection to over 7 million premature deaths worldwide each year. The document discusses various studies linking air pollution to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and cognitive decline, urging for stricter regulations and public awareness to combat this persistent threat. A landmark case has further emphasized the need for action, as air pollution was identified as a contributory factor in the death of a young asthma patient.