Gout and pseudo gout
- 1. Gout and Pseudogout By: Dr Sabir kumar khadka Jr2,Orthopedics,BPKIHS 2020/06/21 Moderator:Dr Rosan Psd Kalawar1
- 2. References • Kelley and Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology vol II,10th edition . • Apley and Solomon’s System of Orthopedics and Trauma , 10th edition. • Medscape 2
- 3. GOUT • History • Introduction • Epidemiology • Classification • Etiology • Purine and Uric acid metabolism • Pathogenesis • Pathology • Clinical Features and stages of Gout • Laboratory investigations • Imaging • Diagnosis • Treatment 3
- 4. PSEUDOGOUT • Crystal deposition diseases • Pathogenesis • Clinical Features • Investigations • Imaging • Diagnosis • Treatment • Differences between Gout and Pseudogout 4
- 5. Introduction • Gout represents a heterogeneous group of disorders of purine metabolism characterized by : – Hyperuricemia – Recurrent attacks of acute arthritis – Deposition of Monosodium urate monohydrate crystals ( tophi) in and around the joints – Renal disease – Uric acid nephrolithiasis 5
- 6. Reference range of uric acid • Men: 2.5 – 8 mg/dl • Women: 1.9 - 7.5 mg/dl • Children: 3 – 4 mg/dl • A serum urate of less than 6mg/dl is the target of therapy. 6
- 7. Epidemiology • Prevalence: 2.6 % – 47.2 % • Males involved much more ( 2:1 to 7:1) • Females more commonly affected after menopause • Age of onset : 35-45 year 7
- 8. Classification • Primary ( 95%) Absence of any obvious cause – Underexcretion ( 90 %) – Overproduction ( 10 %) • Secondary ( 5 %) – Renal Causes – Diuretics or Drug induced – Metabolic – Myeloproliferative Diseases 8
- 9. Etiology • Unknown • Proposed factors : 1. Genetics : – Familial incidence : 11 – 80 % 9
- 10. Etiology 2. Obesity – Hyperuricemia 3 times more common in people with bodyweight > 80th percentile – Hypertriglyceridemia > 80 % of patients with Hyperuricemia 3. Alcohol . 4. Diabetes Mellitus 5. Adrenal Cortex activity . 10
- 11. Etiology 6. Vascular Changes 7. Disturbed Electrolyte equilibrium 8. Decreased urinary 17 ketosteroids : < 3mg/24 hrs 9. Hypertension and Coronary artery disease : have predictive relationship with Hyperuricemia 11
- 12. 12
- 13. Natural history of gout • Hyperuricemia – common 2.3-41.4 %,. • Level of the urate level determines the risk of the gouty attack – level >9 mg/dl -4.9 % ,7- 8.9mg/dl -0.5%, <7mg/dl -0.1% . • Second attack –generally 6 months to 2 years • Chronic tophacious gout –average 11.6 years ,50 % of patient free of obviuos tophi after 10 years ,slowly declines to 28 % in 20 years . 13
- 14. Clinical Features • Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia • Acute Gouty arthritis • Inter critical gout • Chronic gouty / tophaceous arthritis 14
- 15. Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia • Serum urate levels are high • > 7mg/dl in males and > 6 mg/dl in females • No manifestations of gout noted • Most people with hyperuricemia remain asymptomatic • Usually sustained for first 10-20 years of illness • Phase ends with first attack of gout 15
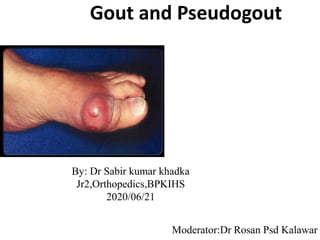
- 16. Acute Gouty arthritis • First attack : – Usually between 40-60 years (males) or >60 (females) – Monoarticular – Not associated with many constitutional symptoms – Usually 1st metatarsophalangeal joint – Explosive suddenness – Commonly begins at night – Joint becomes hot , dusky red , swollen and extremely tender – May resolve within hrs to days 16
- 18. Acute Gouty arthritis • Later on : – Skin may desquamate – More than one site involved • Other sites : – Ankle – Finger joints – Olecranon – Heels ,knees , wrists – Prepatellar /Olecranon bursa – Ear 18
- 19. Acute Gouty arthritis • Precipitating factors : – Alcohol – Surgery – Excess diet – Glucocorticoid withdrawl – Trauma – CVA / MI – Infection – Drugs : Antihyperuricemic therapy , Cyclosporine , Heparin , Diuretics 19
- 20. Acute Gouty arthritis • When to label the condition as acute gout : 1. Triad of 1. Acute monoarticular arthritis 2. Hyperuricemia 3. Dramatic response to colchicine therapy 2. Criteria for classification of Acute gouty arthritis 1. Presence of characteristic urate crystals in the joint fluid OR 2. Tophus proved to contain urate crystals by chemical or polarised light OR 20
- 21. Acute Gouty arthritis • When to label the condition as acute gout : 3. Presence of atleast 6 of the following: – More than one attack of acute arthritis – Maximum inflammation within 1 day – Attack of monoarticular arthritis – Joint redness – 1st MTP joint swollen/inflammed – Unilateral attack involving 1st MTP joint – Unilateral attack involving tarsal joint – Suspected tophus contd … 21
- 22. Acute Gouty arthritis • When to label the condition as acute gout : 3. Presence of atleast 6 of the following: – Hyperuricemia . – Asymmetric swelling within a joint ( XRay) – Subcortical cyst without erosion ( XRay) – Negative culture of joint fluid for micro-organism during attack of acute inflammation 22
- 23. Inter-critical Gout ( Interval Gout) • Some patients never have a second attack • Second attack usually follow 6 months to 2 years later • Frequency of attack increases with time • Later attacks have a – Less explosive onset – Polyarticular – More severe – Last longer – Take longer to subside 23
- 24. Inter-critical Gout ( Interval Gout) • X ray changes may occur in between without evidence of tophi in intervals • Diagnosis tests on joint aspiration only 24
- 25. Chronic Tophaceous Gout • No pain free intercritical periods • Interval between 1st attack and chronic gout may last from 3 – 42 years • Rate of formation of tophi depends on both intensity and duration of hyperuricemia • Irregular asymmetric moderately discrete tumescence of fingers , hands , knees or feet • Usually painless but may be accompanied by periods of painful inflammation 25
- 27. Chronic Tophaceous Gout • Other sites include : – Ulnar surfaces of forearm – Antihelix of ear – Fusiform enlargement of Achilles tendon – Saccular distensions of olecranon bursa • Eventually extensive destruction of joint occurs • Deformities and progressive crippling • Tense shiny thin skin over tophi may ulcerate • White, chalky or pasty material extruded 27
- 28. Chronic Tophaceous Gout • May lead to marked limitation of joint by : – Involvement of joint directly – Involvement of tendon • Acute gouty spondylitis rare • Nerve / spinal cord compression rare 28
- 33. Investigations • Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia : – Serum urate levels high • Acute Gouty Arthritis : – Aspiration of joint and identification of intracellular needle shaped crystals – Crystals have negative birefringence on polarized microscopy – Crystals : rod shaped , blunt ended and digested by uricase – Serum urate levels high 33
- 34. • Definitive diagnosis only possible by aspirating and inspecting synovial fluid or tophaceous material and demonstrating MSU crystals • Polarized microscopy, the crystals appear as bright birefringent crystals that are yellow (negatively birefringent) 34
- 35. Investigations • Murexide Test : – Few drops of nitric acid are added to substance and mixture evaporated to dryness. Ammonium hydroxide added. If uric acid present : purple colour occurs 35
- 36. Synovial Fluid Findings • Needle shaped crystals of monosodium urate monohydrate that have been engulfed by neutrophils 36
- 37. Imaging • Acute attacks : only soft tissue swelling • Chronic : – Joint space narrowing – Juxta articular osteoporosis – Secondary Osteoarthritis – Tophi : punched out cysts or deep erosions in para-articular bone ends ( Martel’s Sign) – Erosions with sclerotic margins and overhanging margins 37
- 38. Imaging A large tophus is replacing much of the fifth left metatarsal Classical ‘punched-out’ para-articular erosion with a sclerotic margin of the proximal phalanx 38
- 39. Imaging 39
- 40. Imaging 40
- 41. Imaging 41
- 42. Diagnosis • Family history of gouty arthritis • Repeated attacks with intervals of freedom from pain • Renal disturbance or urate calculus • Hyperuricemia • Response to colchicine 42
- 43. Differential Diagnosis • Trauma • Infections – septic arthritis, gonococcal arthritis, cellulitis • Inflammatory – Rheumatic arthritis, Reiter’s syndrome, Psoriatic arthritis • Metabolic – pseudogout • Miscellaneous – Osteoarthrtis 43
- 44. Treatment • Therapeutic Aims : – Terminate attack of acute gout promptly and gently – Prevent recurrence of acute gouty arthritis – Prevent or reverse complications of disease resulting from deposition of urate – Prevent or Reverse associated illness like obesity , hypertension , hypertriglyceridemia 44
- 45. Treatment : Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia • Hyperuricemia alone not an indication of starting anti hyperuricemic therapy • Cause of hyperuricemia if any to be found • Therapy to be started only if metabolic/ inherited causes • Obesity , Hypertension , Hypertriglyceridemia need attention • Lifestyle modifications 45
- 46. Treatment : Acute Gout • Termination of attack may require – NSAIDs (sure diagnosis) – Colchicine ( unconfirmed diagnosis) – Glucocorticoid preparation ( elderly ) – Ice packs • Colchicine : – Oral : 0.5 /0.6 mg tablet started ,taken every hour till : • Nausea , vomiting or diarrhea occurs • Joint symptoms eased • Maximum 10 doses taken 46
- 47. Treatment : Acute Gout • Colchicine : – Side effects : • Increased peristalsis • Cramping abdominal pain • Diarrhea , nausea , vomiting – The 2012 ACR guidelines recommend starting 1.2mg, followed by 0.6mg 1 hr later, and then 0.6 mg every 12 hrs until the attack has subsided. – The regimen can then be followed by 0.6mg once or twice daily for prophylaxis as needed. – For severe renal insufficiency:0.3mg/day 47
- 48. Treatment : Acute Gout • Colchicine : – Acts by inhibiting E selectin mediated adhesiveness for neutrophils – Decreases • neutrophil L selectin expression • Random motility of neutrophils • Chemotaxis • PLA 2 acivation • IL 1 expression • Mast cell histamine release • Endothelial cell ICAM 1 expression – Downregulates TNFα receptors on macrophages 48
- 49. Treatment : Acute Gout • Non Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs : – Effective in 90% of patients and the resolution of signs and symptoms usually occurs in 5 to 7 days – Indomethacin : NSAID of choice – 50-75 mg is initial dose followed by 50 mg every 6 to 8 hrs – With a maximum of 200mg in 1st 24 hrs – Taper by 50 mg every 8 hrs for next 2 days – Steady dose of 50 – 75 mg /day – Ibuprofen : 800 mg tid or Diclofenac 50 mg tid – Naproxen : very good results – Sulindac , Piroxicam , Ketoprofen , COX 2 inhibitors 49
- 50. Treatment : Acute Gout • Glucocorticoids : – Intra – articular glucocorticoids useful in treatment of single joint or bursa – A single intravenous dose of methylprednisolone or – 7 mg of betametasone or – 20 to 40 mg of intraarticular triamcinolone acetonide – ACTH as an intramuscular injection of 25 to 80 IU in a single dose or every 12 h for 1 to 2 days is effective in patients with acute polyarticular refractory gout or with a contraindication for using colchicine or NSAIDs – Oral glucocorticoids such as prednisone, 20 to 60 mg/d as the initial dose and tapered over 5 to 7 days equally effective 50
- 51. : IL-1 inhibition • Canakinumab • single s/c injection 150mg • For NSAID’s,colchine contraindicated patient 51
- 52. Recommendations for low purine diet • Beverages: carbonated drinks, fruit juice • Dairy products: milk, cream,butter,cheese • Cereals: all grains, bread, pasta , cakes • Vegetables: lettuce, tomatos, vegetables except peas, beans, lentils and spinach • Fruite all kind, cherries • Nuts: all kind • Eggs, vitamin C 52
- 53. Foods to be avoided • Tea, coffee and chocolate, high fructose corn syrup • Animal based proteins: meats, poultry, sea foods, meat extracts, liver, kidney, heart, gizzard, sweet breads • Vegetables: peas, beans, spinach, lentils • Beverages: alcohol, beer and beer products 53
- 56. prophylaxis • Continued till serum uric acid normal and no acute attacks for 3 to 6 months. • 2012 ACR guidelines recommend prophylaxis for 6 months, or 3months after achieving target serum urate for patients w/o tophi or • 6 months after acheving target serum urate with resolution of tophi. 56
- 57. Treatment : Intercritcial Gout • Prophylaxis : – 0.6 mg of Cochicine once to thrice daily to prevent attacks – May produce axonal neuromyopathy – Indomethacin 25 mg TDS also effective • Antihyperuricemic therapy : – Usually started after 1st attack in a patient of hyperuricemia – Need definite if existent hypertension – Lifelong continuation usually required 57
- 58. Anti hyperuricemic therapy 1. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor ( Allopurinol) 2. Uricosurics • Lower the serum uric acid level , faster the reduction in its deposition • Should never be given during an acute attack • Target to reduce Serum uric acid to < 6 mg/dl • Helpful in prevention of renal deterioration 58
- 59. Anti hyperuricemic therapy Xanthine oxidase inhibitor ( Allopurinol, febuxostat ) • Indications : 1. Hyperuricemia with increased uric acid production : – Urinary uric acid excretion of > 1000 mg / 24 hrs – Hyperuricemia with HPRT deficiency or PRPP synthetase hyperactivity – Uric acid nephropathy – Nephrolithiasis – Prophylaxis before cytolytic therapy 59
- 60. Anti hyperuricemic therapy Xanthine oxidase inhibitor ( Allopurinol , febuxostat) • Indications : 2. Intolerance or reduced efficacy of uricosurics : – Gout with renal insufficiency ( GFR < 60 ml/min ) – Allergy to uricosurics 60
- 61. Anti hyperuricemic therapy Xanthine oxidase inhibitor ( Allopurinol) • Substrate for Xanthine oxidase which oxidises to Oxypurinol which inhibits Xanthine oxidase • The starting dose is usually 100mg/day but 50 mg or even 50mg on alternate day for elderly or with renal impairment. • 4 weeks before starting Allopurinol , NSAID or Colchicine should be started • Most important side effect : Allpurinol Hypersensitivity syndrome : skin rash , fever , esophilia , hepatitis , renal impairment • Others : GI intolerance , TEN , Alopecia , Rashes , Bone marrow suppression 61
- 62. Anti hyperuricemic therapy Uricosurics : • Increase the rate of uric acid excretion • Uricosuric drugs present in the lumen and competitively inhibit urate for the transporter • Probenecid , Sulfinpyrazone , Benzbromarone, lesinurad ) • Probenecid : – Maintaince dose of 500 mg – 3gm /day in 2 or 3 divided doses – High drug interaction 62
- 64. Anti hyperuricemic therapy Uricosurics : • Ideal candidate : – < 60 years – Normal renal function – Uric acid excretion of < 800 mg /24 hrs – No history of renal caliculi – Not taking inflammatory doses of salicylates 64
- 65. Newer Therapies • Uricase – Enzyme that oxidizes uric acid to a more soluble form – Natural Uricase from Aspergillus flavus and Candida utilis under investigation – Pegloticase for refractory tophaceous gout. • Febuxostat – New class of Xanthine Oxidase inhibitor – More selective than allopurinol – Little dependence on renal excretion – Initial dose: 40 mg po od, can be increased upto 80mg • Losartan • Fenofibrate – Studies note when used in combo with Allopurinol produced additional lowering of the urate 65
- 66. Surgical Procedures • Immobilization of joint will lessen the degree of destruction • Large tophi that interfere with joint movement may need removal • Surgery requires following precautions : – Avoidance of local anesthesia – Incision parallel with course of blood vessels – Sharp dissection – Loose suturing to allow escape of liquefied deposits – Pressure dressing – Avoidance of prolonged splintage 66
- 67. Other Crystal Deposition disorders Calcium Pyrophosphate dehydrate deposition : • Chondrocalcinosis • Pseudogout • Chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy Calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disorders ( Basic Calcium phosphate deposition disorders) 67
- 68. Associations of CPPD • Ageing • Disease-associated • Primary hyperparathyroidism • Hemochromatosis • Hypophosphatasia • Hypomagnesemia • Chronic tophaceous gout • Postmeniscectomy • Epiphyseal dysplasias • Hereditary • Wilson’s Syndrome 68
- 69. Clinical features (CPPD) • > 60 years • Asymptomatic Chondrocalcinosis : – Calcification of the menisci asymptomatic – Hemarthrosis • Acute Synovitis ( Pseudo gout ) – Typically involve one large joint – Most often knee ; 1st MTP involved very rarely – Sudden onset – Excruciatingly painful 69
- 70. Clinical features (CPPD) • Acute Synovitis ( Pseudogout ) – Periarticular swelling, warmth and edema – Attacks last for 7 -10 days usually – Associated with fever and chills – Leukocytosis • Chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy : – Mimics osteoarthritis – Pain , stiffness , swelling , crepitus , loss of movement – Seen in shoulders , hips , knees , wrists 70
- 71. Clinical Features ( CPPD ) 71
- 72. Clinical Features (CPPD) • Provocative factors : – Direct trauma to joint – Intercurrent medical illness – Surgery ( especially parathyroidectomy) – Blood transfusion – Thyroxine replacement therapy – Joint lavage – Arthroscopy – Hyaluronic acid injection 72
- 73. Clinical Features ( HA ) • Acute / Subacute Periarthritis : – Commonest form of HA crystal deposition – Adult between 30-50 yrs – Pain near one of the larger joints : eg. knee /shoulder – Seen most commonly in rotator cuff lesions of shoulder – Preceded usually by minor trauma – Symptoms subside themselves within few weeks – May reveal tense globule of creamy material oozing from between frayed fibres of tendon /ligament 73
- 74. Clinical Features ( HA ) • Chronic Destructive arthritis : – Shoulder ( Milwaukee Shoulder ) : bilateral , worse on the side of dominant hand – Synovial fluid is blood stained – May also involve knee 74
- 75. Investigations • Leukocytosis ( > 20,000 /mm3) • ESR increased • Presence of CPPD crystals in synovial fluid • Crystals are weakly birefringent , rhomboid • HA crystals : nonbirefringent globular clumps • HA crystals stain with Alizarin red 75
- 76. Imaging • Calcification seen in and around : – Knees , wrists , shoulder , hips , Pubic symphysis • Heavy punctate and linear calcification • Radiocarpal or patellofemoral joint space narrowing • Patella wrapped around femur • Scaphoid lunate widening • Femoral cortical erosion superior to patella • Metacarpal squaring with beak like osteophytes and subchondral cyst • Tendon calcification 76
- 77. Imaging 77
- 78. Imaging 78
- 79. Imaging 79
- 80. Imaging 80
- 81. Imaging (Hydroxyapatite) • Calcification seen in tendons and ligaments close to joints • Most commonly calcification in shoulder • No calcification in fibrocartilagenous structures • Loose bodies seen in synovial joints • Loss of articular space • Little / No sclerosis or osteophyte formation • Subchondral bone eroded in later stages 81
- 82. Diagnosis of CPPD Criteria : 1. Demonstration of CPPD crystals obtained by biopsy or aspirated synovial fluid 2. Identification of monoclinic or triclinic crystals showing weakly positive birefringence by polarized light microscopy 3. Presence of typical calcifications in radiographs , punctate and linear calcifications , especially if bilaterally symmetrical 4. Acute arthritis especially of knee or other large joints 5. Chronic arthritis accompanied by acute exacerbations of elbow , shoulder , MCP joints 82
- 83. Diagnosis of CPPD Diagnostic Categories : • Definite : Criteria 1 or 2 • Probable : Criteria 2 or 3 • Possible : Criteria 4 or 5 83
- 84. Treatment • Rest • High dosage NSAIDs • Joint aspiration • Intra-articular glucocorticoid therapy • Low dose colchicine orally only for prophylaxis • Possible benefits of Magnesium , Hydroxy chloroquine • Colchicine intravenously not recommended 84
- 85. Treatment ( Hydroxyapatite) • NSAIDs especially COX 2 inhibitors • Local Corticosteroid injection • Local irrigation • Surgical removal of calcific deposits 85
- 86. GOUT and PSEUDOGOUT GOUT PSEUDOGOUT Mainly involves 40-60 yrs > 60 yrs Smaller joints involved ( esp 1st MTP ) Larger joints involved ( esp knee) Pain is intense Pain moderate Joint inflamed Joint swollen Hyperuricemia Chondrocalcinosis Negatively birefringent crystals , rod shaped Positively birefringent crystals , rhomboid shaped Crystals digested by uricase Not digestable by uricase XRay : No calcification , erosion characteristic Calcification seen , erosion degenerative 86
- 87. 87
