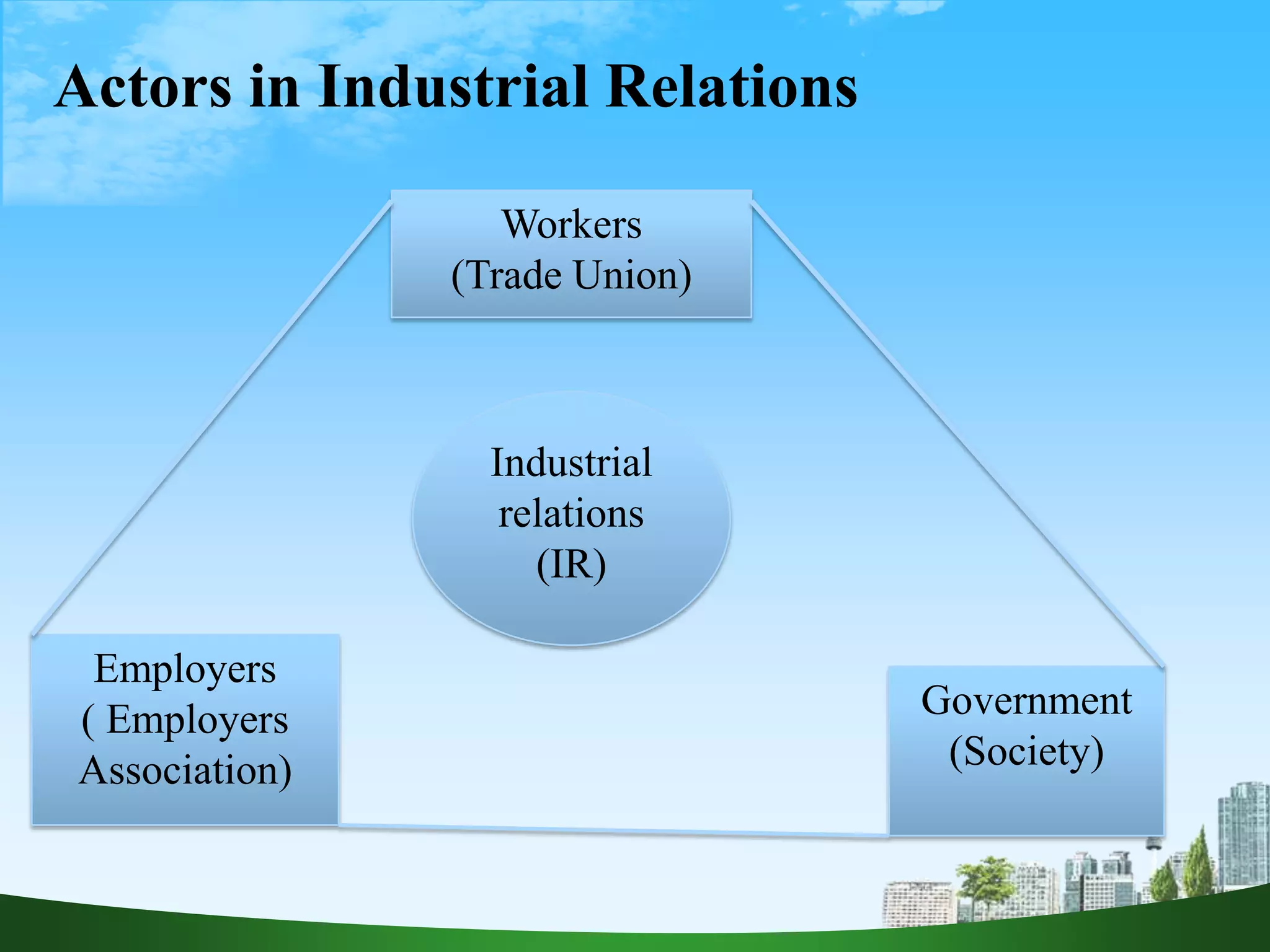
Industrial relations deal with the relationships between workers, employers, and the government. The main aspects are how proceeds from work are divided as wages between different levels of employees. The objectives of industrial relations are to safeguard interests, avoid conflicts, establish growth, raise productivity, and have government control. The main actors in industrial relations are workers represented by trade unions, employers represented by employer associations, and the government representing society. In Nepal, there is mutual hostility between these groups, and disputes are often resolved through strikes with unacceptable labor practices still occurring and disputes handled through power rather than transparency.