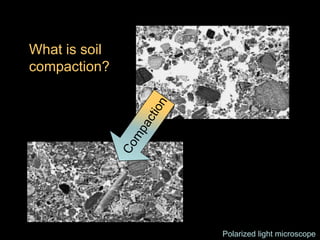
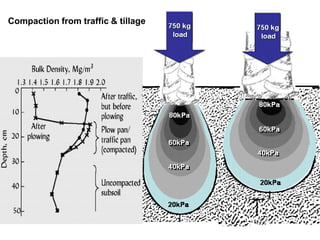
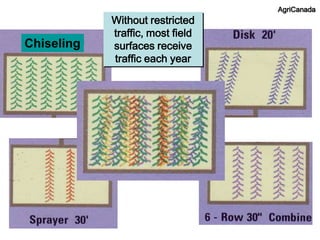
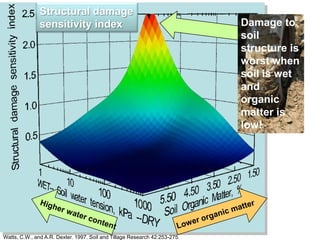
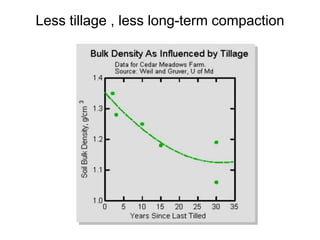
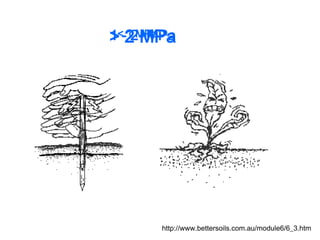
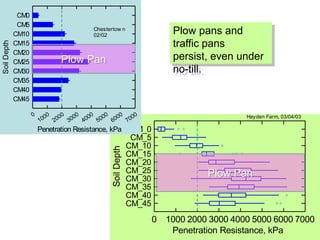
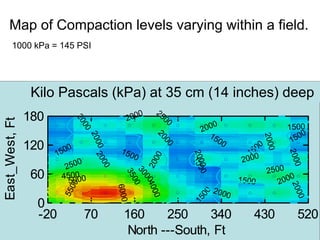
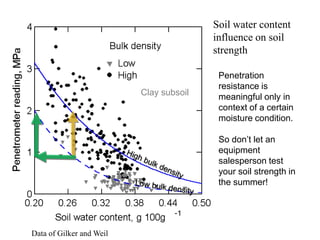
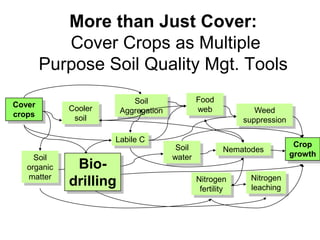
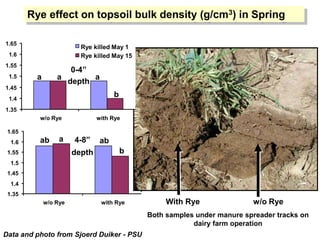
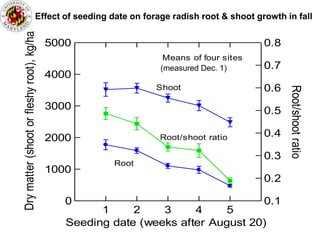
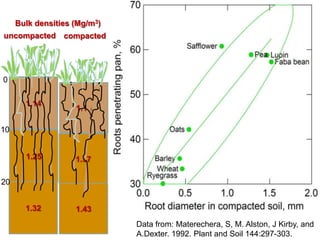
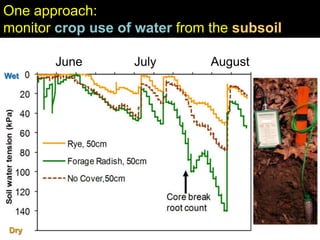
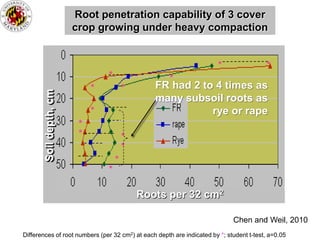
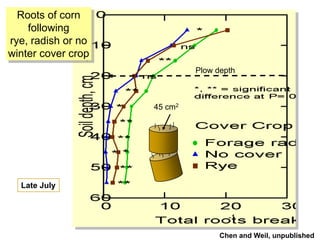
This document discusses soil compaction, its causes and impacts, and strategies for mitigating compaction through reduced tillage and the use of cover crops. It notes that soil compaction physically impedes root growth, limits water and nutrient uptake, reduces infiltration and aeration, and increases risks of stress, disease and poor fertilizer efficiency for crops. Cover crops like rye and forage radishes are presented as tools to alleviate compaction through their root systems. Research shows that forage radishes in particular have a large, deep taproot capable of penetrating compacted subsoil layers and improving soil structure. The document emphasizes the importance of cover crop root systems and provides evidence from studies using imaging and root counting methods.