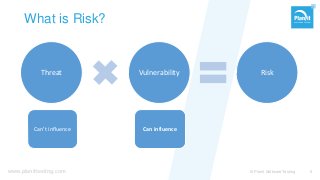
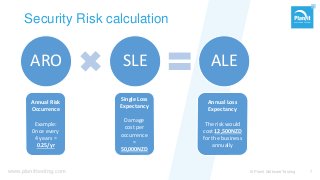
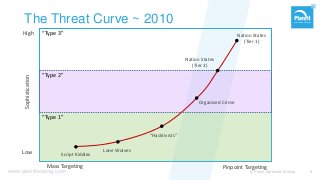
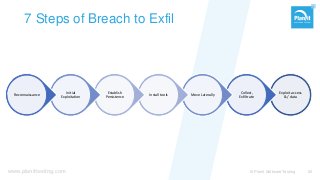
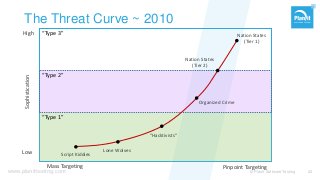
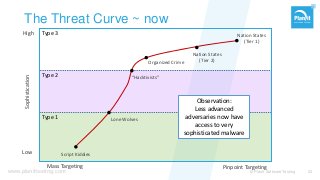
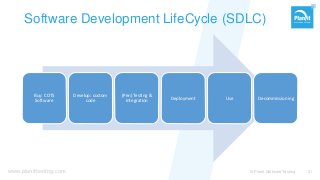
From stand-alone systems to the cloud, “security” is expected to be everywhere. It is the implied requirement, almost never explicitly specified. Just hire a pen-tester before your go-live, and check that box? As with everything, the approach defines if and how you reach your goal.
Ferdinand will walk you through the current approach, the risks involved, and how to improve.
For more information about our Security Testing services visit our website:
https://www.planittesting.com/Services/Security-Testing