Inverse Functions Lesson
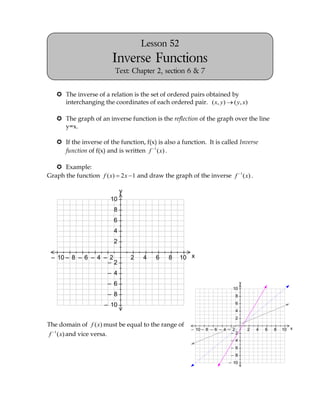
- 1. Lesson 52 Inverse Functions Text: Chapter 2, section 6 & 7 The inverse of a relation is the set of ordered pairs obtained by interchanging the coordinates of each ordered pair. ( x, y) ( y, x) The graph of an inverse function is the reflection of the graph over the line y=x. 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 If the inverse of the function, f(x) is also a function. It is called Inverse function of f(x) and is written f 1 ( x) . Example: Graph the function f ( x) 2 x 1 and draw the graph of the inverse f 1 ( x) . y 10 8 6 4 2 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 – 10 – 8 – 6 – 4 – 2 2 4 6 8 10 x – 2 – 4 – 6 y 10 – 8 8 – 10 6 4 2 The domain of f ( x) must be equal to the range of – 10 – 8 – 6 – 4 – 2 2 4 6 8 10 x f 1 ( x) and vice versa. – 2 – 4 – 6 – 8 – 10
- 2. The inverse of a function algebraically. Example: Find the inverse of f ( x) 2x 1 Steps to follow: 1) Replace f ( x) with y y = 2x - 1 2) Interchange x and y x = 2y – 1 x 1 3) Solve for y y 2 x 1 4) Replace y with f 1 ( x) f 1 ( x) 2 This can be verified by using the composition of functions: x 1 Let f ( x) 2 x 1 and g ( x) 2 f ( g ( x)) g ( f ( x)) x 1 (2 x 1) 1 2 1 2 2 x x Since both compositions produce x, f(x) and g(x) are inverses. Every inverse is not a function. If the original function is one-to-one function then its inverse is also a function. 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 One to one means that each x-value has exactly one unique y-value. And 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2– 2 2– 2 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 each y-value corresponds to exactly one x-value. 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 Applying the horizontal line test will check to see if a function is one to one. y y 10 Not a 1-1 so 10 Is a 1-1 so 8 8 the inverse is the inverse 6 6 4 not a function 4 is a function 2 2 – 10 – 8 – 6 – 4 – 2 2 4 6 8 10 x – 10 – 8 – 6 – 4 – 2 2 4 6 8 10 x – 2 – 2 – 4 – 4 – 6 – 6 – 8 – 8 – 10 – 10