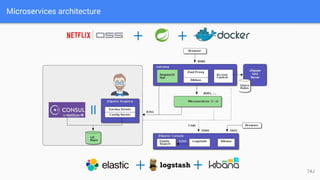
The document provides a comprehensive overview of JHipster, a development platform that combines Spring Boot and AngularJS to create modern web applications. It covers installation, application generation, client and server-side frameworks, as well as advanced features and tools for developers including database support, security options, testing, and deployment methods. Key highlights include entity creation, Docker integration, and management of application environments, showcasing JHipster's functionalities and the community involved in its development.