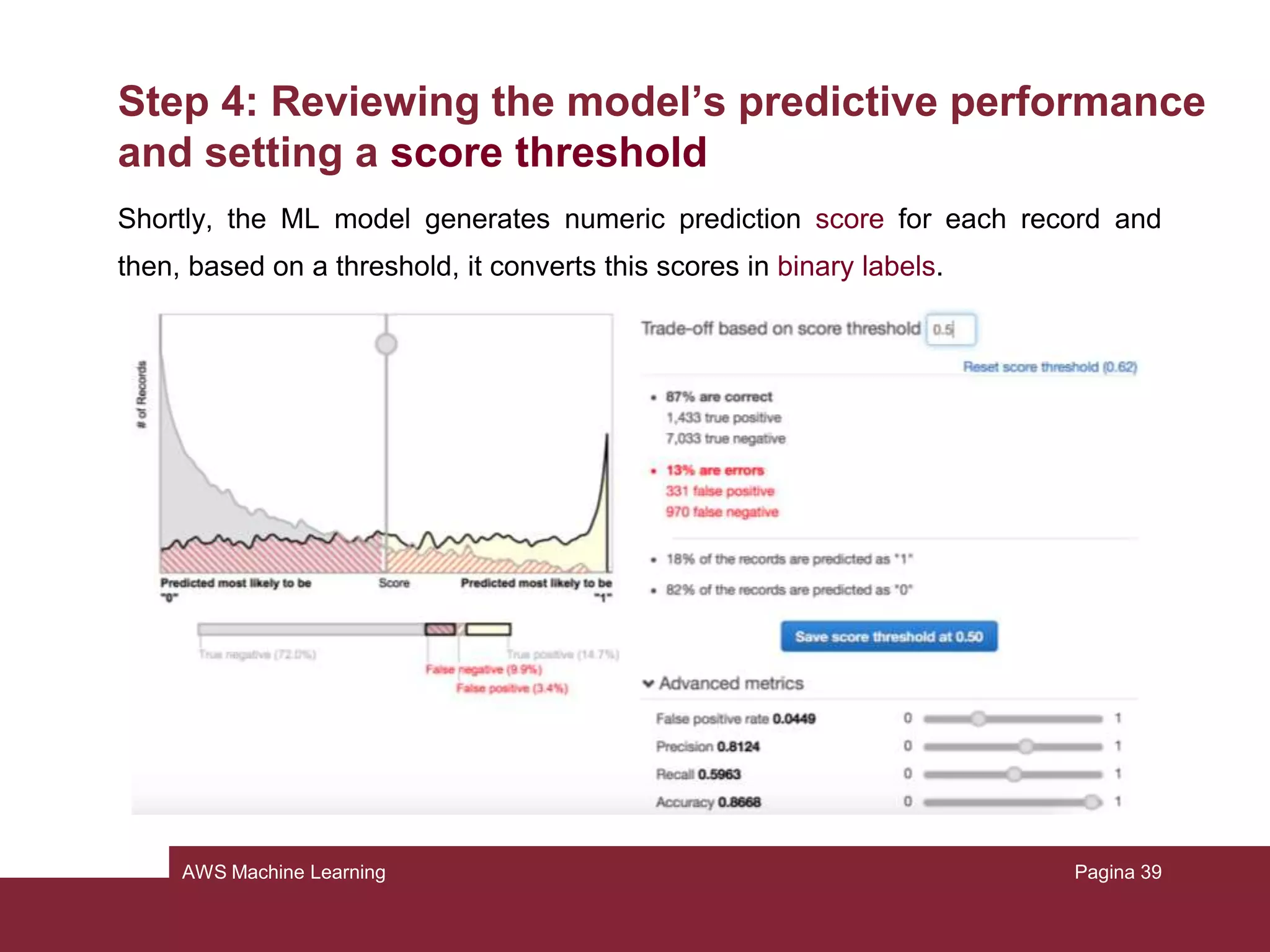
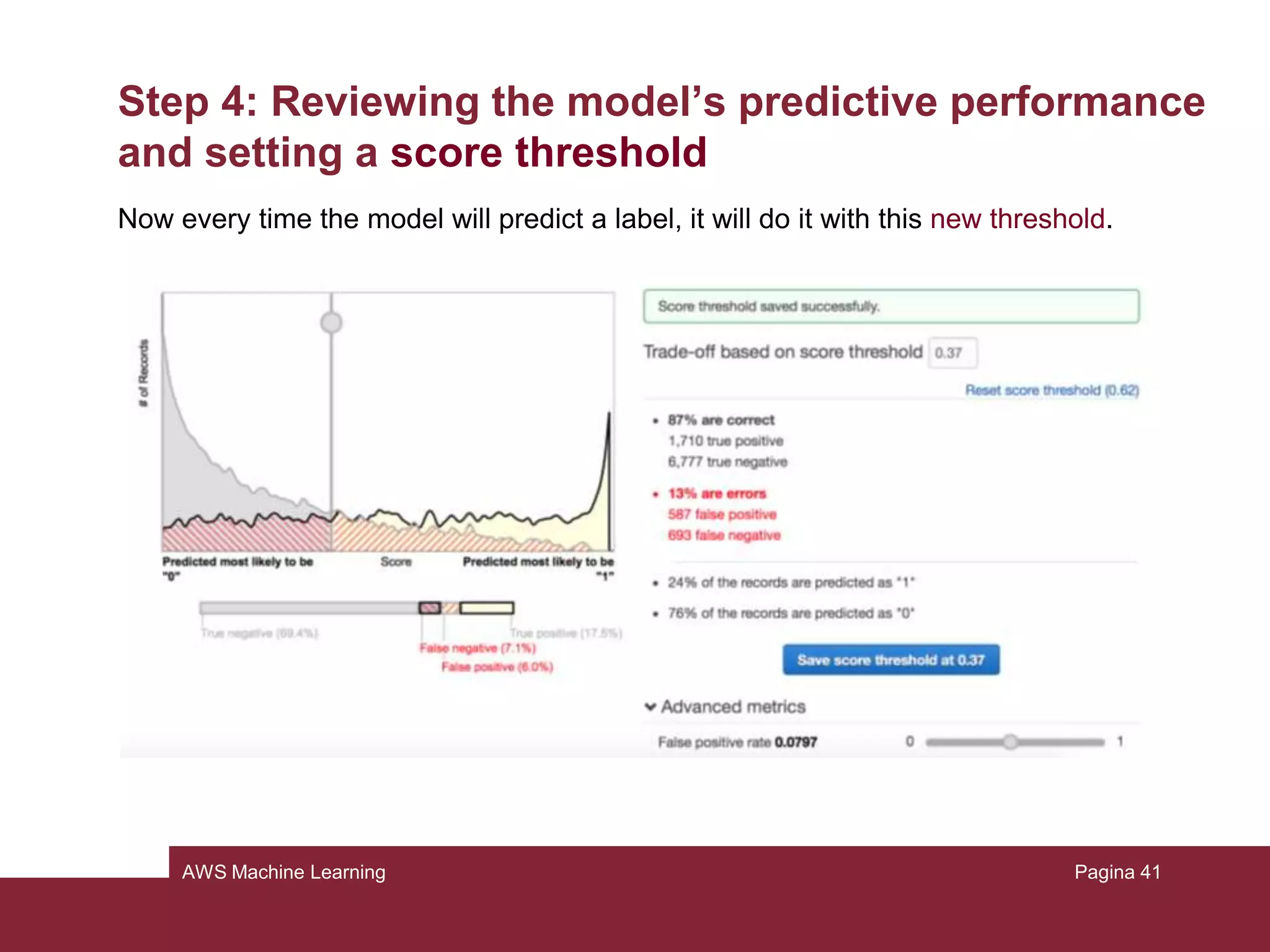
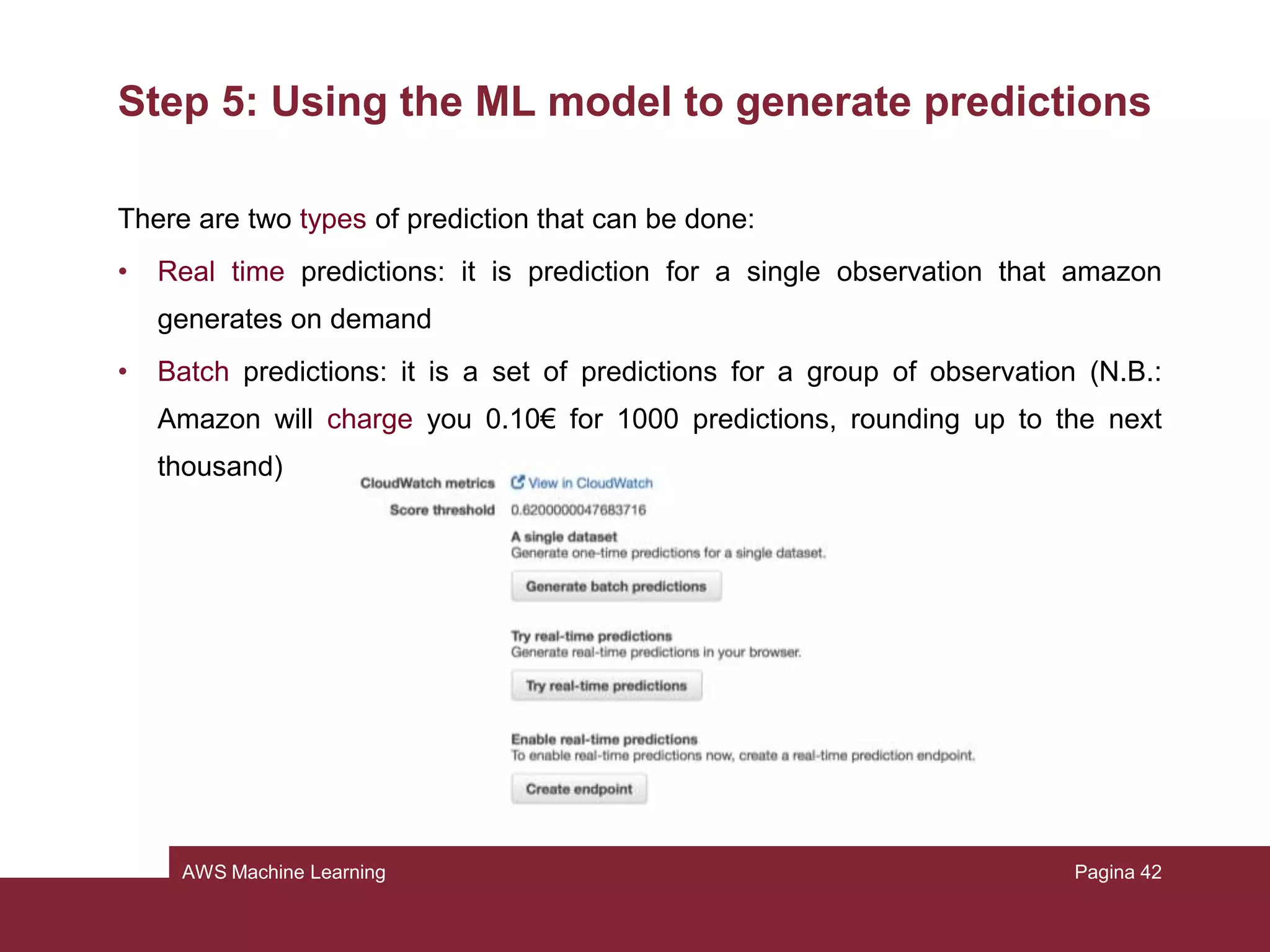
This document provides an overview of a tutorial on using Amazon Machine Learning (ML) to build a predictive model. The tutorial involves the following key steps: 1) Preparing training data from the UCI Census dataset, 2) Creating an ML training datasource, 3) Creating and training an ML model, 4) Reviewing the model's performance and setting a prediction threshold, 5) Using the model to generate predictions, and 6) Cleaning up resources. The homework assignment asks students to repeat steps 1-4 and then write a Python script to generate real-time and batch predictions using the Amazon ML APIs instead of the graphical interface.








































![AWS Machine Learning
Homework Assignment – Exercise 1
Generate real-time predictions: in a new file, store 10 records of the “census-
batch.csv” file. Generate one real-time prediction per record and print the results.
You can make use of the following function:
from boto3.session import Session #install library boto3 first
MODEL_ID = 'the id of the model you have created'
ID = 'your id'
KEY = 'your key'
session = Session(aws_access_key_id=ID, aws_secret_access_key=KEY)
client = session.client('machinelearning', region_name='eu-west-1')
prediction_endpoint = "https://realtime.machinelearning.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com"
fields=["age", "work class", "fnlwgt", "education", "education-num", "marital-status", "occupation", "relationship", "race", "sex",
"capital-gain", "capital-loss", "hours-per-week", "native-country"]
def real_time_prediction(line) : # line = one line of the csv file
record = dict()
for index, val in enumerate(line.split(',')):
record[fields[index]] = val
response = client.predict(MLModelId=MODEL_ID, Record=record, PredictEndpoint=prediction_endpoint)
return response.get('Prediction')
Pagina 57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentazione-tutorial-161211105120/75/Presentazione-tutorial-57-2048.jpg)
![AWS Machine Learning
Homework Assignment – Exercise 2
Generate batch predictions: use the “census-batch.csv” file that you’ve uploaded
and then check the results on S3.
You can make use of the following function:
from boto3.session import Session #install library boto3 first
ID = 'your id'
KEY = 'your key'
MODEL_ID = 'the id of the model you have created'
DATASOURCE_ID = 'the id of the data source you have created (the one related to census-batch.csv)'
PREDICTION_ID = "batch_prediction_0001" # must be unique
PREDICTION_NAME = "bp_0001"
OUTPUT_URI = "s3://your_bucket/dir_batch_0001"
session = Session(aws_access_key_id=ID, aws_secret_access_key=KEY)
client = session.client('machinelearning', region_name='eu-west-1')
client.create_batch_prediction(BatchPredictionId=PREDICTION_ID, BatchPredictionName=PREDICTION_NAME,
MLModelId=MODEL_ID,
BatchPredictionDataSourceId=DATASOURCE_ID, OutputUri=OUTPUT_URI)
status = "PENDING"
while status != "COMPLETED" and status != "FAILED" :
print(status)
response = client.get_batch_prediction(BatchPredictionId=PREDICTION_ID)
status = response['Status']
time.sleep(3)
print(status)
print(response)
print("Your results are in s3!")
Pagina 58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentazione-tutorial-161211105120/75/Presentazione-tutorial-58-2048.jpg)

