My lecture Accu-Calci-Gangrene.pptx
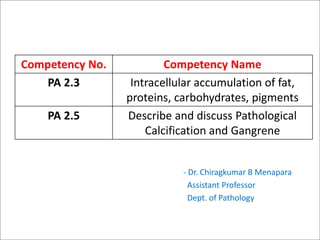
- 1. - Dr. Chiragkumar B Menapara Assistant Professor Dept. of Pathology Competency No. Competency Name PA 2.3 Intracellular accumulation of fat, proteins, carbohydrates, pigments PA 2.5 Describe and discuss Pathological Calcification and Gangrene
- 2. Classify intracellular accumulations Describe Fat accumulation (fatty change) Give examples of conditions in which protein & carbohydrate accumulations occur Describe endogenous (Melanin, Hemoproteins, lipofuscin) & exogenous (inhaled,ingested & injected) pigment accumulations Define pathologic calcification Describe dystrophic & metastatic calcifications Define & describe gangrene.
- 3. Under some circumstances cells may accumulate abnormal amounts of various substances. They may be harmless or associated with varying degrees of injury.
- 4. May be found: in the cytoplasm within organelles (typically lysosomes) in the nucleus Came to the cell through: Synthesis by affected cells Produced elsewhere
- 5. 1. Normal or increased rate of production of a normal substance, but metabolic rate is inadequate to remove it (e.g. fatty change in liver)
- 6. 2. A normal or an abnormal endogenous substance accumulates because of genetic or acquired defects in its folding, packaging, transport, or secretion. e.g. In α-1antitrypsin deficiency, α1at accumulates in the liver causing cirrhosis)
- 7. 3. An inherited defect in an enzyme may result in failure to degrade a metabolite. The resulting disorders are called storage diseases.
- 8. 4. An abnormal exogenous substance is deposited and accumulates because the cell has neither the enzymatic machinery to degrade the substance nor the ability to transport it to other sites. (e.g. Accumulations of carbon or silica particles)
- 10. Fatty change refers to any abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells. Site: liver, most common site It may also occur in heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, and other organs.
- 11. Toxins (most importantly: Alcohol abuse) Diabetes mellitus Protein malnutrition (starvation) Obesity Anoxia
- 13. Gross: With increasing accumulation, the organ enlarges and becomes progressively yellow, soft, and greasy.
- 15. Early: small fat vacuoles in the cytoplasm around the nucleus. Later stages: the vacuoles coalesce to create cleared spaces that displace the nucleus to the cell periphery Occasionally contiguous cells rupture (fatty cysts)
- 18. These macrophages may be filled with minute, membrane-bound vacuoles of lipid, imparting a foamy appearance to their cytoplasm (foam cells).
- 19. 2. Atherosclerosis: Smooth muscle cells and macrophages are filled with lipid vacuoles composed of cholesterol and cholesteryl esters
- 20. 3. In hereditary and acquired hyperlipidemic syndromes, macrophages accumulate intracellular cholesterol 4. Xanthomas: clusters of foamy macrophages present in the subepithelial connective tissue of skin or in tendons
- 21. Morphologically visible protein accumulations are much less common than lipid accumulations They may occur because excesses are presented to the cells or because the cells synthesize excessive amounts
- 22. 1. Nephrotic syndrome: In the kidney trace amounts of albumin filtered through the glomerulus are normally reabsorbed by pinocytosis in the proximal convoluted tubules After heavy protein leakage, pinocytic vesicles containing this protein fuse with lysosomes, resulting in the histologic appearance of pink, hyaline cytoplasmic droplets
- 23. The process is reversible; if the proteinuria abates, the protein droplets are metabolized and disappear.
- 24. 2. Marked accumulation of newly synthesized immunoglobulins that may occur in the RER of some plasma cells, forming rounded, eosinophilic Russell bodies.
- 25. 3. Mallory body, or "alcoholic hyaline," is an eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion in liver cells that is highly characteristic of alcoholic liver disease These inclusions are composed predominantly of aggregated intermediate filaments
- 26. 4. The neurofibrillary tangle found in the brain in Alzheimer disease is an aggregated protein inclusion that contains microtubule-associated proteins
- 27. Associated with abnormalities in the metabolism of either glucose or glycogen. Examples: 1. In poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, glycogen accumulates in renal tubular epithelium, cardiac myocytes, and β cells of the islets of Langerhans.
- 28. 2. Glycogen accumulates within cells in a group of closely related genetic disorders collectively referred to as glycogen storage diseases, or glycogenoses In these diseases, enzymatic defects in the synthesis or breakdown of glycogen result in massive stockpiling, with secondary injury and cell death.
- 29. Pigments are colored substances in the organism or environment. Exogenous : coming from outside the body Endogenous: synthesized within the body itself.
- 30. (1) Inhaled: - Carbon or coal dust - Silica or stone dust - Iron or Iron oxide - Asbestos
- 31. (1) Inhaled: - Carbon or coal dust - The most common exogenous pigment - Picked up by alveolar macrophages - Causes blackening of the tissues of lung (Anthracosis) - Anthracosis + fibroblastic reaction = Coal workers pneumoconiosis
- 34. (1) Inhaled: Silica or stone dust
- 35. (1) Inhaled: Asbestos Asbestos bodies
- 36. (2) Ingested: - Lead: Chronic lead poisoning, Blue line on gum - Silver compounds: Argyria - Certain cathartics: Melanosis coli - Carrot: Carotenemia, Yellow-red coloration of skin
- 39. (3) Inoculated/ Injected: Tattooing – India ink, cinnabar or carbon are injected into the dermis
- 42. Generalised hyperpigmentation: - Genetic - Radiation ( UV ) - Addison’s disease - Cushing’s syndrome/ ACTH production - Acromegaly - Certain drugs - Malabsorption & Biliary cirrhosis
- 43. Focal/Patchy hyperpigmentation: - Freckles - Solar lentigo - Chloasma/Melasma - Post inflammatory pigmentation - Acanthosis nigricans - Café au lait spots in neurofibromatosis and Albright’s synd - Peri oral pigmentation in peutz-jeghers synd. - Melanotic tumor- naevi & melanoma
- 46. Black pigment Autosomal recessive Deficiency of homogentisic oxidase Homogentisic acid accumulates in tissue (ochronosis) & excreated in urine (Alkaptonuria) Ochronosis Black pigment deposit in skin, connective tissues, cartilage, capsules of joints etc.
- 47. Insoluble brownish-yellow granular pigment accumulates near nucleus Inclusions of lipid peroxides, phosphates, proteins Accumulates in liver, heart, brain from normal “wear and tear” Sign of free radical damage Indicative of age, oxidative damage Does not stain blue with Prussian blue or Perl’s iron When present in large amounts, imparts an appearance to the tissue that is called brown atrophy
- 49. Formed by aggregates of ferritin Golden-yellow to brown granular pigment Prussian blue reaction Mononuclear phagocytes of the bone marrow, liver, spleen.
- 50. Develops whenever hemorrhage into the tissue The changing colors of a bruise or a black eye Brown induration of lung: mitral stenosis, left ventricular failure Oxyhemoglobin Deoxyhemoglobin Biliverdin Bilirubin Hemosiderin
- 51. Systemic overload of iron may result in two types of patterns: (1) Parenchymatous deposition: Liver, pancreas, kidney, heart - Excessive intake of dietary iron - Excessive intestinal absorption of iron - Increased erythropoietic activity - Impaired utilization of iron (2) Reticuloendothelial deposition - Repeated blood transfusion - Parenteral iron therapy
- 52. Autosomal dominant disease Excessive absorption of iron Triad of - Pigmentary liver cirrhosis - Pancreatic damage leads to DM - Skin pigmentation
- 53. The iron can be unambiguously identified by the Prussian blue histochemical reaction
- 54. Brown colored pigment containing haem iron in ferric form Formed by oxidation of Hb. Can’t be stained by prussian blue reaction Chronic malaria, mismatched blood transfusion
- 55. Non-iron containing yellow colored pigment Bilirubin build-up in tissues (Jaundice) Prehepatic or hemolytic: due to excessive hemolysis build-up of unconjugated bilirubin Hepatic or hepatocellular: due to failure of at least 80% of liver function both conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin accumulates Posthepatic or obstructive: due to failure of bile to drain into GI Conjugated bilirubin accumulates
- 57. Porphyra = purple Purple discolouration of feces and urine when exposed to light Porphyrins are tetrapyrroles, are intermediates of heme synthesis Porphyrias result from genetic deficiency of one of the enzymes required for the synthesis of heme, so that there is excessive production of porphyrins Two types: 1. Erythropoietic porphyrias 2. Hepatic porphyrias
- 58. Deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than osteoid or enamel is called pathologic or heterotopic calcification.
- 59. Dystrophic calcification: When the deposition occurs in dead or degenerated tissues It occurs with normal calcium metabolism and normal serum calcium level. Metastatic calcification: The deposition of calcium salts in normal tissues It almost always reflects some derangement in calcium metabolism (hypercalcemia).
- 60. Gross: Only be detected grossly if extensive. If grossly evident, calcification appears as pale chalky areas (granules or clumps) in the tissues. Even if not visible, calcification can sometimes be detected by the coarse gritty feel of the tissues when scraped or incised with a knife or scalpel blade. Sometimes a tuberculous lymph node is essentially converted to radio-opaque stone.
- 61. Histologically Calcification appears as intracellular and/or extracellular deeply basophilic, irregular and granular clumps. In larger deposits, only the rim stains basophilic while the bulk of the internal core is eosinophilic (pink). Sometimes, single necrotic cells act like little grains of sand around which a “pearl” of calcium is deposited. This is called a psammoma body Confirmed by special stains: - silver impregnation method of von-Kossa producing black colour - alizarin red S produces red staining.
- 63. Etiology: - In Dead tissue 1) Caseous necrosis: the most common site for dystrophic ca. 2) Liquefaction necrosis in chronic abscesses 3) Fat necrosis (acute pancreatitis or traumatic) 4) Infarct 5) Gamna-Gandy bodies: calcific deposits admixed with haemosiderin on fibrous tissue. 6) Thrombi especially in the veins, may produce phleboliths. 7) Hematomas (esp. in the vicinity of bones) 8) Dead parasites: hydatid cyst, Schistosoma eggs, and cysticercosis 9) Foreign substances: Asbestosis- calcium and iron salts gather about long slender spicules of asbestos 10) Calcification in breast ca. 11) Congenital Toxoplasmosis
- 65. Etiology: - In degenerated tissue 1) Dense old scars: hyaline degeneration f/b calcifications 2) Atheroma 3) Monckeberg’ sclerosis 4) Stroma of tumors: uterine fibroids, breast cancer, thyroid adenoma, goitre 5) Cysts of long duration: epidermal and pilar cysts. 6) Calcinosis cutis: irregular nodular deposits of calcium salts in the skin and subcutaneous tissue 7) Senile degenerative changes: costal cartilages, tracheal or bronchial cartilages, and pineal gland 8) Psammoma bodies
- 68. Etiology: Excessive mobilisation of calcium from the bone. Excessive absorption of calcium from the gut.
- 69. Etiology: Excessive mobilisation of calcium from the bone - Hyperparathyroidism - Bony destructive lesions - Hypercalcaemia as a part of paraneoplastic syndrome - Prolonged immobilisation: disuse atrophy of the bones and hypercalcaemia.
- 70. Etiology: Excessive absorption of calcium from the gut - Hypervitaminosis D: Excess vit D intake (overdose) or sarcoidosis - Milk-alkali syndrome - Idiopathic hypercalcaemia of infancy (Williams syndrome) - Renal causes such as in renal tubular acidosis
- 71. Metastatic calcification can occur widely throughout the body but principally affects the interstitial tissues of the vasculature (systemic arteries, and pulmonary Veins), kidneys, lungs, and gastric mucosa, cornea, synovium All these tissue excrete acid and therefore have internal alkaline compartment that predispose them to metastatic calcification. Calcium binds with phosphate, this leads to precipitates of calcium phosphate at the preferential sites Metastatic calcification is reversible upon correction of underlying metabolic disorder.
- 72. The calcium deposits morphologically resemble those described in dystrophic calcification. Kidneys: basement membrane of tubular epithelium and in the tubular lumina causing nephrocalcinosis Lungs: in the alveolar walls. Stomach: on the acid-secreting fundal glands. Blood vessels: on the internal elastic lamina.
- 73.
- 75. Definition: Necrosis of tissue associated with superadded putrefaction Three forms - Dry Gangrene - Wet Gangrene - Gas Gangrene
- 76. Dry Gangrene Site: Distal part of a limb Causes: arteriosclerosis, TAO, Burger’dis, Raynaud’ dis. ,trauma, ergot poisoning Line of separation Pathological changes: - Gross: dry, shrunken and dark black, resembling the foot of a mummy - M/E: Coagulative necrosis with smudging of tissue. The line of separation consists of inflammatory granulation tissue
- 77. Wet Gangrene Site: In naturally moist tissues and organs such as the bowel, lung, mouth, cervix, vulva. Diabetic foot due to high glucose content. Bed sores in a bed-ridden patient Causes: Blockage of both venous return as well as arterial blood flow Toxic products….. No line of separation Pathological changes: - Gross: soft, swollen, putrid, rotten and dark - M/E: coagulative necrosis with stuffing of affected part with blood. Intense acute inflammatory exudates
- 78. Gas Gangrene – form of wet gangrene caused by gas forming clostridia Cause: clostridia (gram-positive anaerobic bacteria) Site: open contaminated wounds, as a complication of operation on colon Pathological changes: - Gross: swollen, oedematous, painful and crepitant due to accumulation of gas bubbles - M/E: coagulative necrosis with liquefaction, Large number of gram-positive bacilli, leucocytic infiltration, oedema and congestion