Recommended
PDF
Lesson 19: The Mean Value Theorem
PDF
Lesson 5: Continuity (slides)
PPT
Calculus Sections 4.1 and 4.3
PPT
Intermediate Value Theorem
PPT
3.1 Extreme Values of Functions
PPT
PPT
PDF
3.4 Velocity And Other Rates Of Change
PDF
Video Infrastructure_ Streaming Architecture and Delivery Systems.pdf
PDF
Huawei Datacom – How To Pass H12-892 On Your First Try
PDF
Ai In Courts Ai in courts AI in court AI in court
PPTX
Pizza Chain Market Data Scraping for Better Insights Report.pptx
PDF
How Application Performance Monitoring Tools Are Used in Performance Testing
PPTX
Cybersecurity Basics: Understanding Threats, Protection Methods, and Safe Dig...
PDF
The map to conquer linear algebra for IT engineer
PDF
Top Benefits of Using KVM VPS Hosting for Growing Businesses
PDF
Small Business Automation: A Comprehensive Cost and ROI Guide
PDF
Unit 1.2 Components of a Computer System.pdf
PDF
Groq Series A Investment Memo - Chamath Palihapitiya
PDF
IAC 500 Sensor - Humidity Measurement Device
PPT
Information and Communication Technologies and Power
PPT
Carole BirdCarole BirdCarole BirdCarole Bird.ppt
PPTX
Salesforce Spring 26 Release Key .pptx
PPTX
Digital transformation success powered by EPM and NexInfo.pptx
PPTX
Document Reconstruction using AI & Deep Learning
PPT
HDTV and DTV Standards: The United States Opts for a Digital HDTV Standard
PPTX
Corporate AI Training to AI Enable a Company Workforce
PPTX
Compare and contrast types of attacks.pptx
PDF
Artificial Intelligence, Data and Competition – SCHREPEL – June 2024 OECD dis...
PDF
2024 Trend Updates: What Really Works In SEO & Content Marketing
More Related Content
PDF
Lesson 19: The Mean Value Theorem
PDF
Lesson 5: Continuity (slides)
PPT
Calculus Sections 4.1 and 4.3
PPT
Intermediate Value Theorem
PPT
3.1 Extreme Values of Functions
PPT
PPT
PDF
3.4 Velocity And Other Rates Of Change
Recently uploaded
PDF
Video Infrastructure_ Streaming Architecture and Delivery Systems.pdf
PDF
Huawei Datacom – How To Pass H12-892 On Your First Try
PDF
Ai In Courts Ai in courts AI in court AI in court
PPTX
Pizza Chain Market Data Scraping for Better Insights Report.pptx
PDF
How Application Performance Monitoring Tools Are Used in Performance Testing
PPTX
Cybersecurity Basics: Understanding Threats, Protection Methods, and Safe Dig...
PDF
The map to conquer linear algebra for IT engineer
PDF
Top Benefits of Using KVM VPS Hosting for Growing Businesses
PDF
Small Business Automation: A Comprehensive Cost and ROI Guide
PDF
Unit 1.2 Components of a Computer System.pdf
PDF
Groq Series A Investment Memo - Chamath Palihapitiya
PDF
IAC 500 Sensor - Humidity Measurement Device
PPT
Information and Communication Technologies and Power
PPT
Carole BirdCarole BirdCarole BirdCarole Bird.ppt
PPTX
Salesforce Spring 26 Release Key .pptx
PPTX
Digital transformation success powered by EPM and NexInfo.pptx
PPTX
Document Reconstruction using AI & Deep Learning
PPT
HDTV and DTV Standards: The United States Opts for a Digital HDTV Standard
PPTX
Corporate AI Training to AI Enable a Company Workforce
PPTX
Compare and contrast types of attacks.pptx
Featured
PDF
Artificial Intelligence, Data and Competition – SCHREPEL – June 2024 OECD dis...
PDF
2024 Trend Updates: What Really Works In SEO & Content Marketing
PDF
Storytelling For The Web: Integrate Storytelling in your Design Process
PDF
How to Leverage AI to Boost Employee Wellness - Lydia Di Francesco - SocialHR...
PDF
How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health
PDF
Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings
PDF
Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights
PDF
PEPSICO Presentation to CAGNY Conference Feb 2024
PDF
Everything You Need To Know About ChatGPT
PDF
Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)
PDF
PDF
Getting into the tech field. what next
PDF
ChatGPT and the Future of Work - Clark Boyd
PDF
Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent
PDF
How to have difficult conversations
PDF
5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary
PDF
2024 State of Marketing Report – by Hubspot
PDF
Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024
PDF
AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf
PPTX
How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024
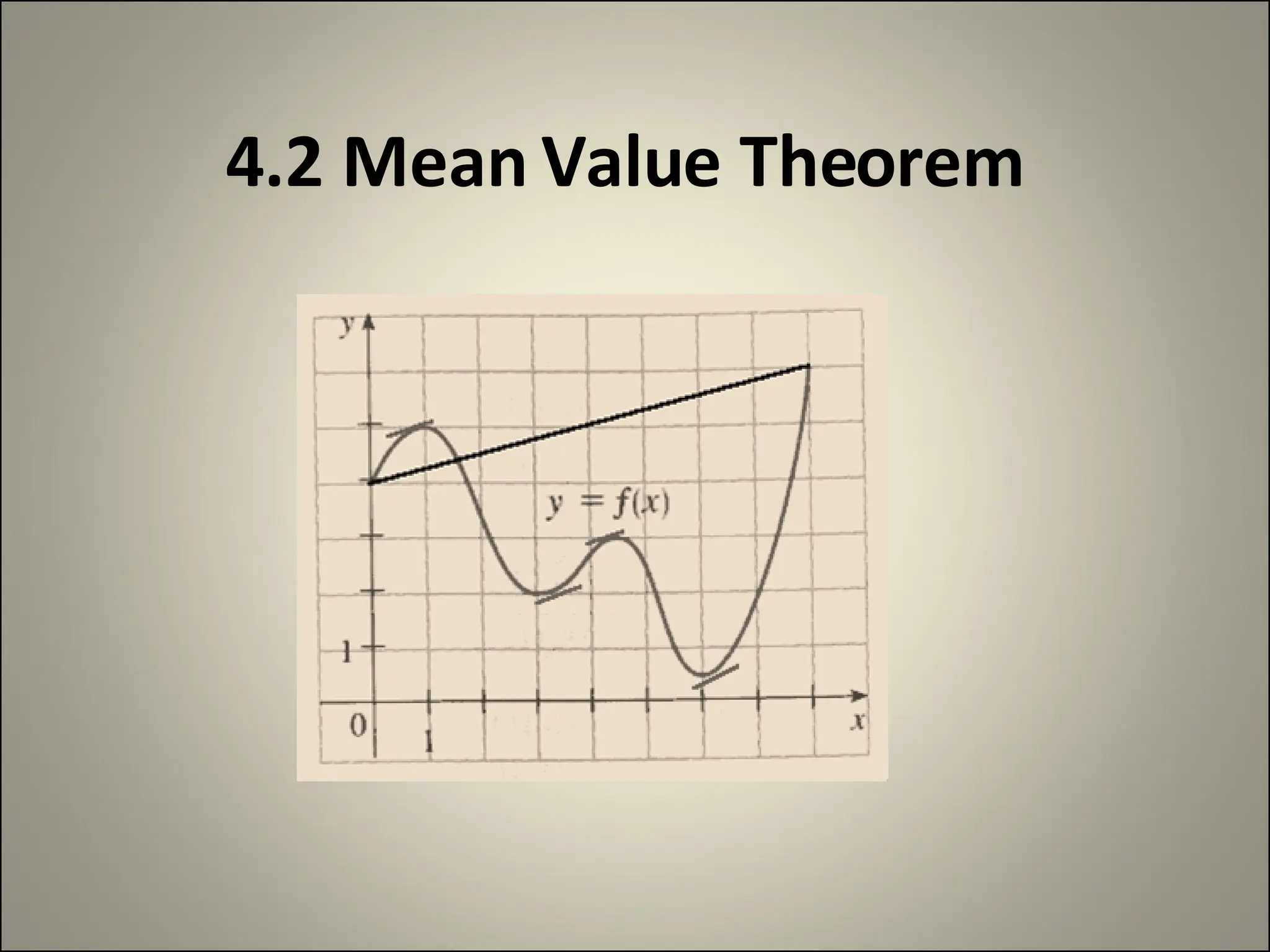
Mean Value Theorem 1. 2. Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives If y = f(x) is continuous at every point of the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable at every point of its interior (a,b) then there is at least one point c in (a,b) at which 3. Using Mean Value Theorem Show that f(x) = 2x 2 satisfies the mean value theorem on the interval [0,2]. Then find the solution to the equation on the interval. Find f’(x) f’(x) = 4x 4 = 4x X= 1 4. Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = l x – 1 l on [0, 4] f(a) = -1 f(b) = 3 1 = l x -1 l The function does not satisfy the mean value theorem because there is a cusp so the function is not continuous on [0,4] 5. Mean Value Theorem f(x) = -2x 3 + 6x – 2 , [-2 , 2] f(-2) = -2(-2) 3 + 6(-2) - 2 = 2 f(2) = -2(2) 3 + 6(2) - 2 = - 6 f(x) = -6 - 2 = -2 2 - (-2) f '(x) = -6x 2 + 6 -2 = -6x 2 + 6 X = 2 -2 √3, √3 Mean value is satisfied because the function is continuous on [-2, 2] 6. Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = x 3 + 3x – 1, [0,1] f(b) = 3 f(a) = -1 f’(x) = 3x 2 + 3 4 = 3x 2 +3 X = 7. 8.
![Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives If y = f(x) is continuous at every point of the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable at every point of its interior (a,b) then there is at least one point c in (a,b) at which](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-2-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem Show that f(x) = 2x 2 satisfies the mean value theorem on the interval [0,2]. Then find the solution to the equation on the interval. Find f’(x) f’(x) = 4x 4 = 4x X= 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-3-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = l x – 1 l on [0, 4] f(a) = -1 f(b) = 3 1 = l x -1 l The function does not satisfy the mean value theorem because there is a cusp so the function is not continuous on [0,4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-4-2048.jpg)
![Mean Value Theorem f(x) = -2x 3 + 6x – 2 , [-2 , 2] f(-2) = -2(-2) 3 + 6(-2) - 2 = 2 f(2) = -2(2) 3 + 6(2) - 2 = - 6 f(x) = -6 - 2 = -2 2 - (-2) f '(x) = -6x 2 + 6 -2 = -6x 2 + 6 X = 2 -2 √3, √3 Mean value is satisfied because the function is continuous on [-2, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-5-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = x 3 + 3x – 1, [0,1] f(b) = 3 f(a) = -1 f’(x) = 3x 2 + 3 4 = 3x 2 +3 X =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-6-2048.jpg)



![Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives If y = f(x) is continuous at every point of the closed interval [a,b] and differentiable at every point of its interior (a,b) then there is at least one point c in (a,b) at which](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-2-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem Show that f(x) = 2x 2 satisfies the mean value theorem on the interval [0,2]. Then find the solution to the equation on the interval. Find f’(x) f’(x) = 4x 4 = 4x X= 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-3-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = l x – 1 l on [0, 4] f(a) = -1 f(b) = 3 1 = l x -1 l The function does not satisfy the mean value theorem because there is a cusp so the function is not continuous on [0,4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-4-2048.jpg)
![Mean Value Theorem f(x) = -2x 3 + 6x – 2 , [-2 , 2] f(-2) = -2(-2) 3 + 6(-2) - 2 = 2 f(2) = -2(2) 3 + 6(2) - 2 = - 6 f(x) = -6 - 2 = -2 2 - (-2) f '(x) = -6x 2 + 6 -2 = -6x 2 + 6 X = 2 -2 √3, √3 Mean value is satisfied because the function is continuous on [-2, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-5-2048.jpg)
![Using Mean Value Theorem f(x) = x 3 + 3x – 1, [0,1] f(b) = 3 f(a) = -1 f’(x) = 3x 2 + 3 4 = 3x 2 +3 X =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mean-value-theorem-1198034652877849-5/75/Mean-Value-Theorem-6-2048.jpg)

