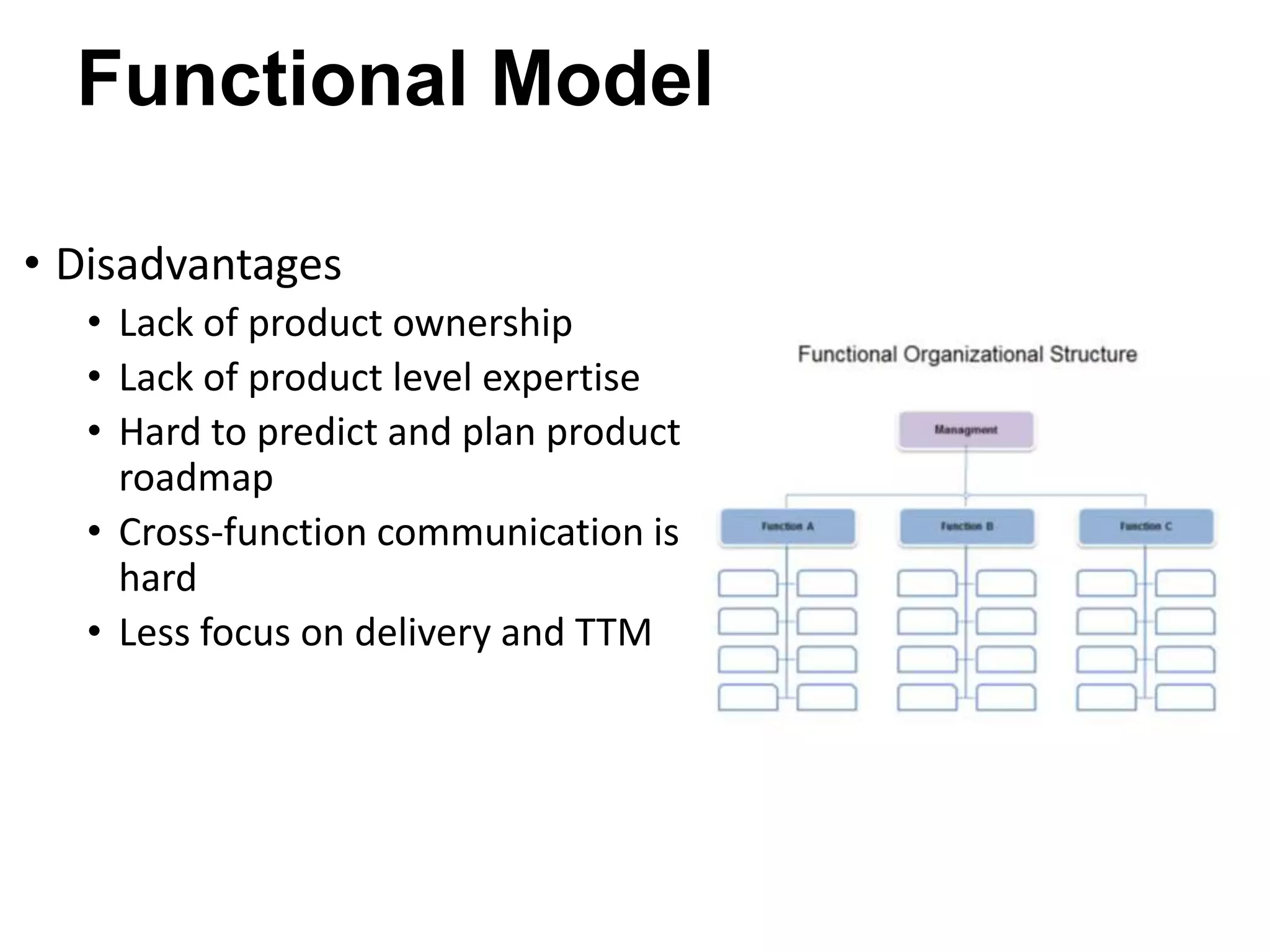
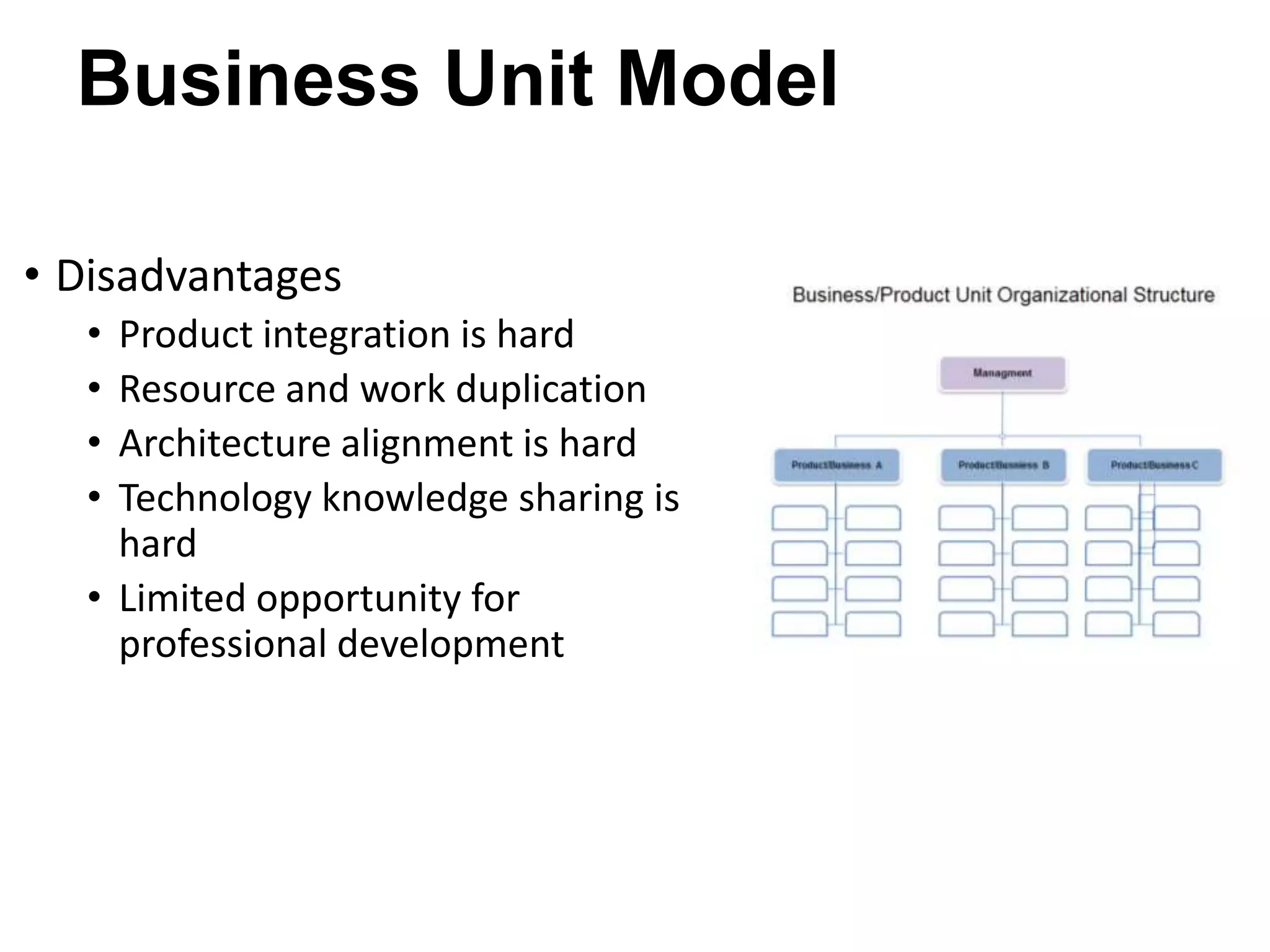
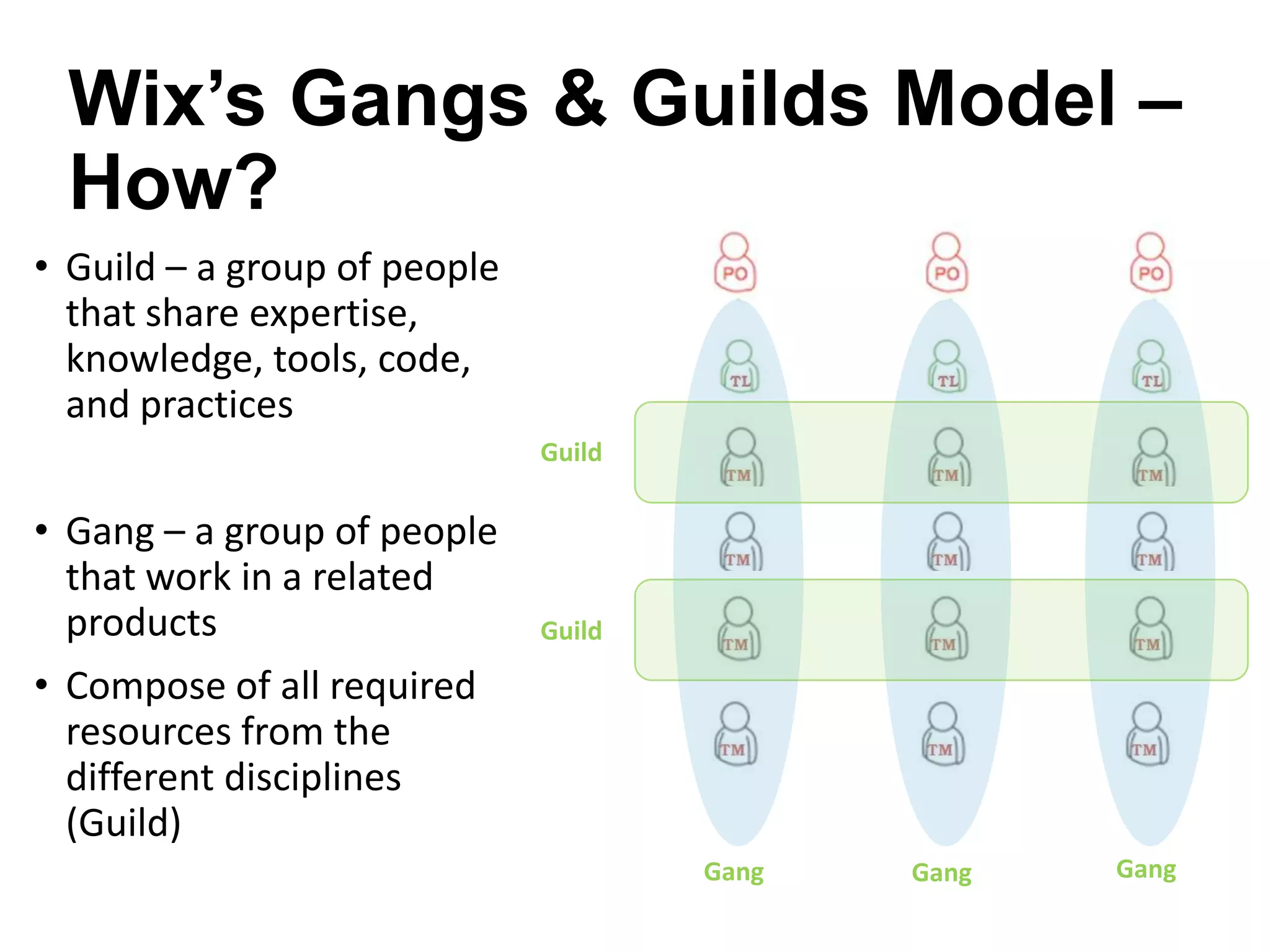
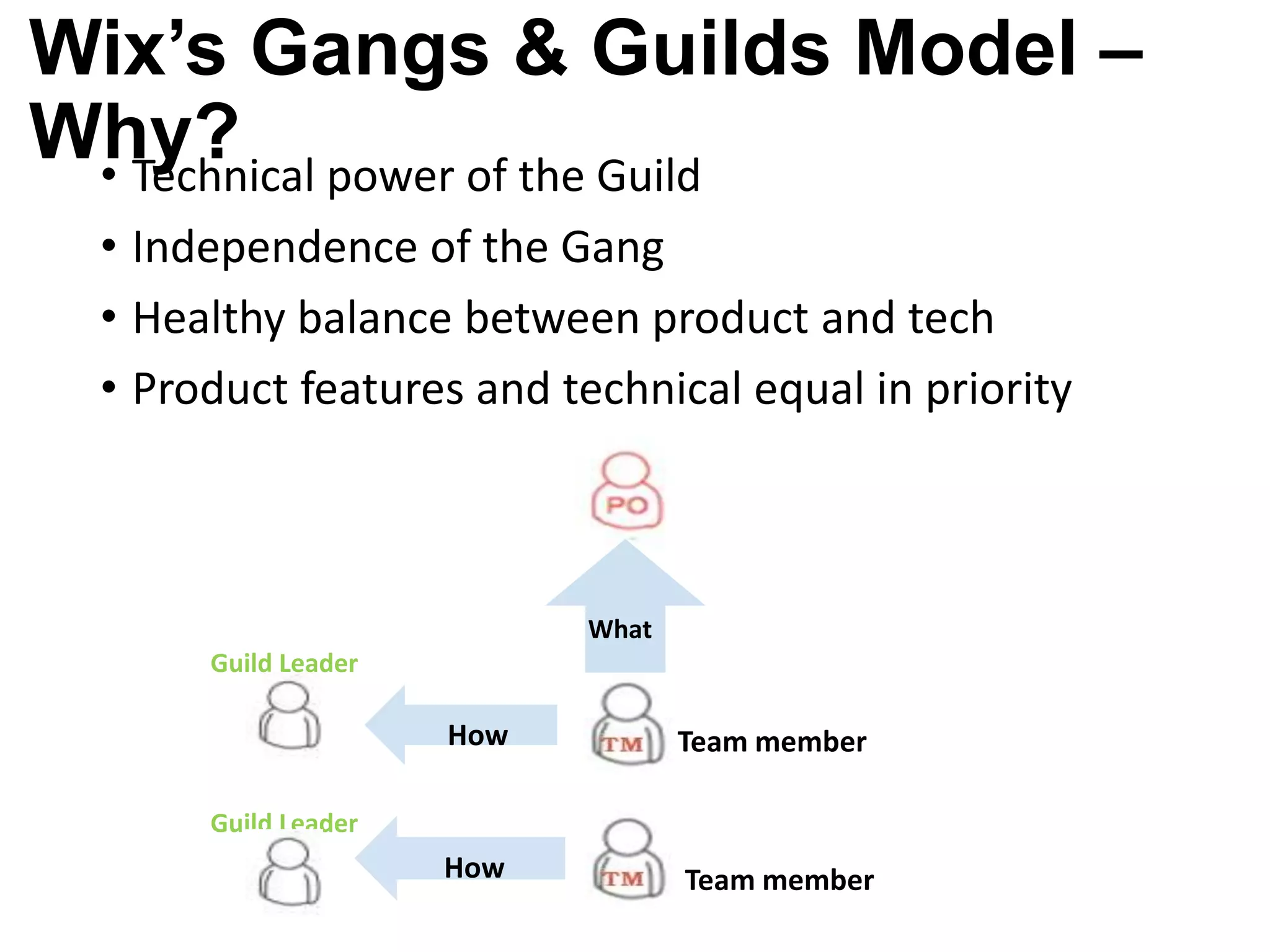
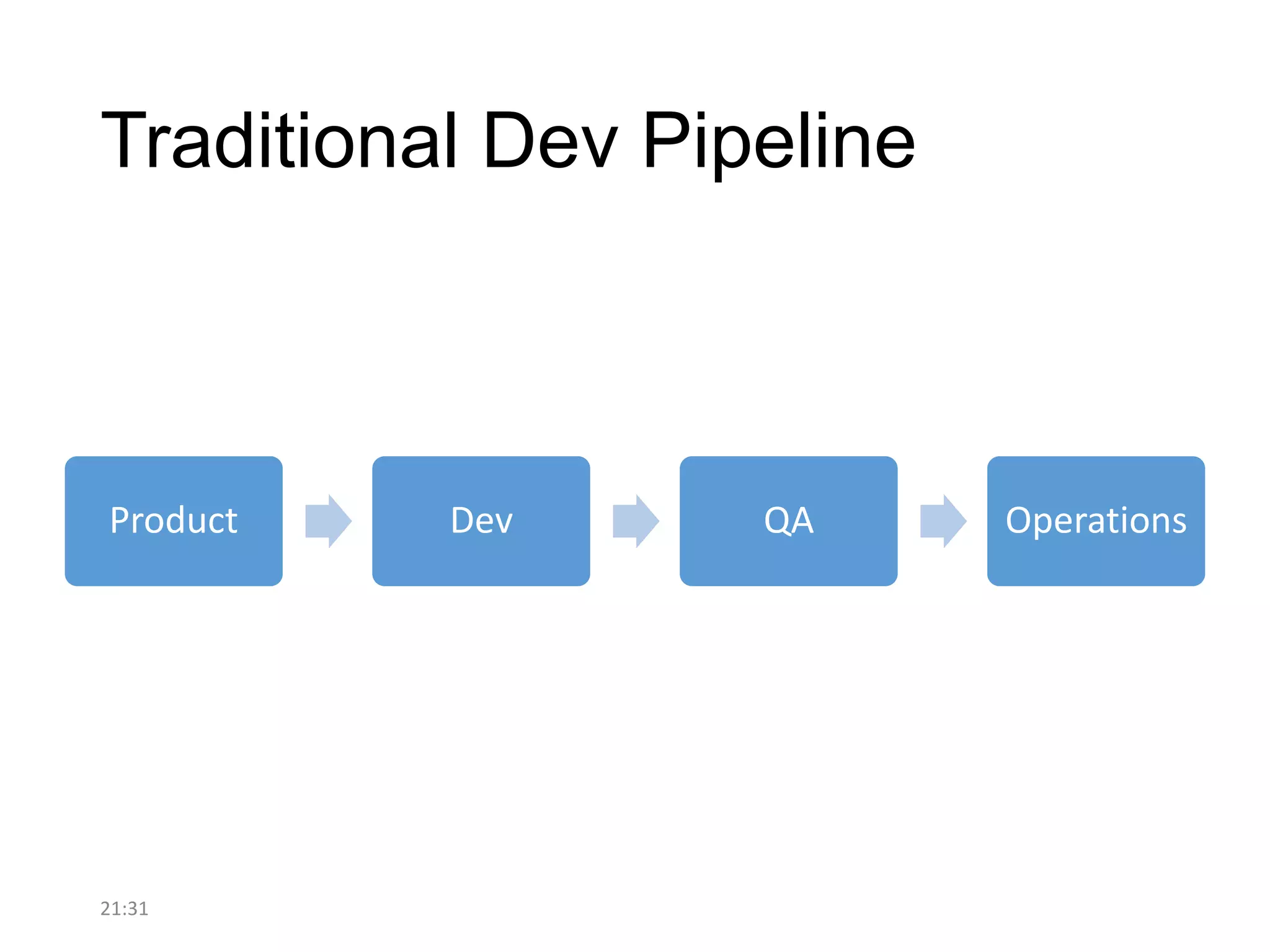
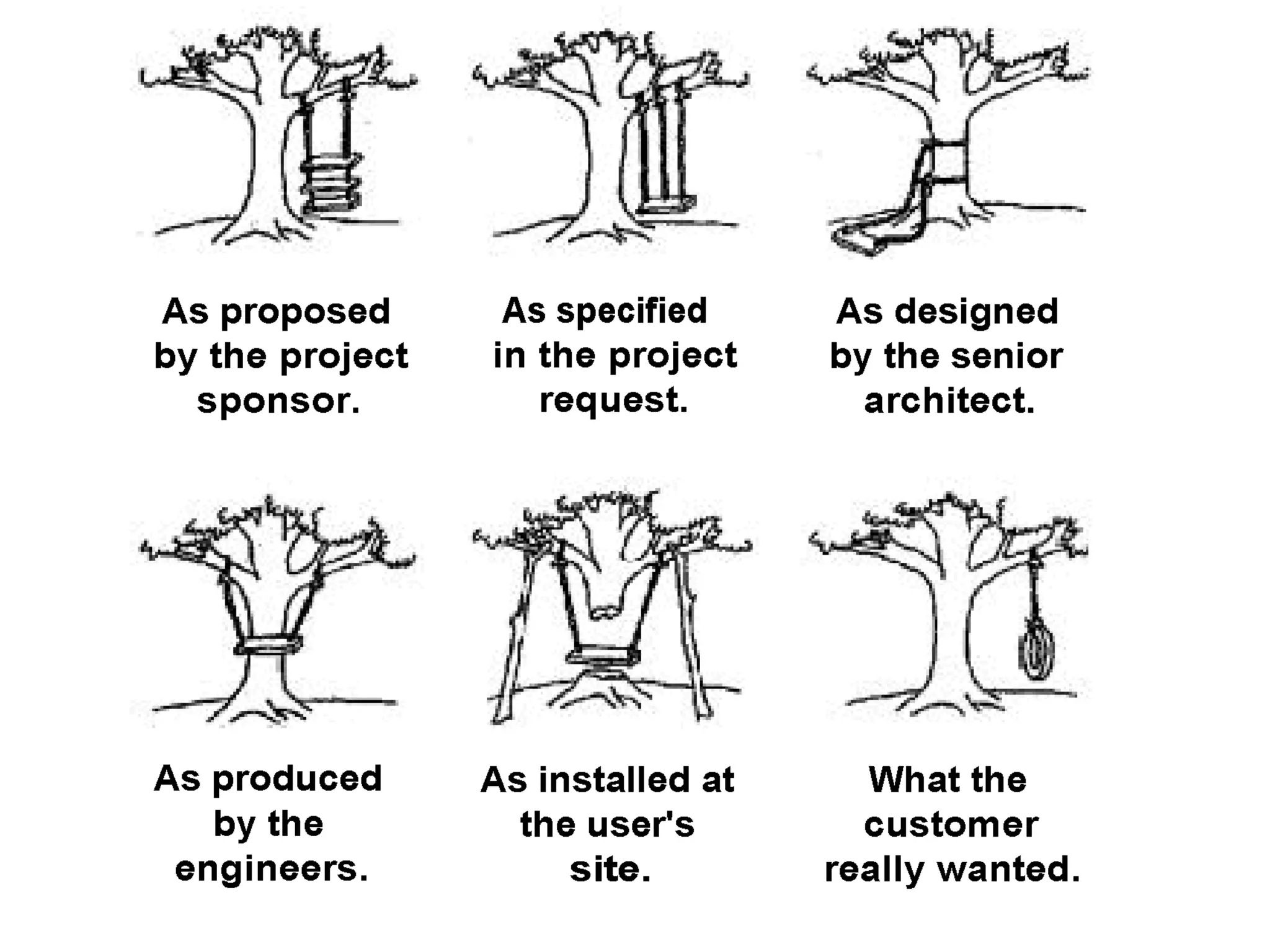
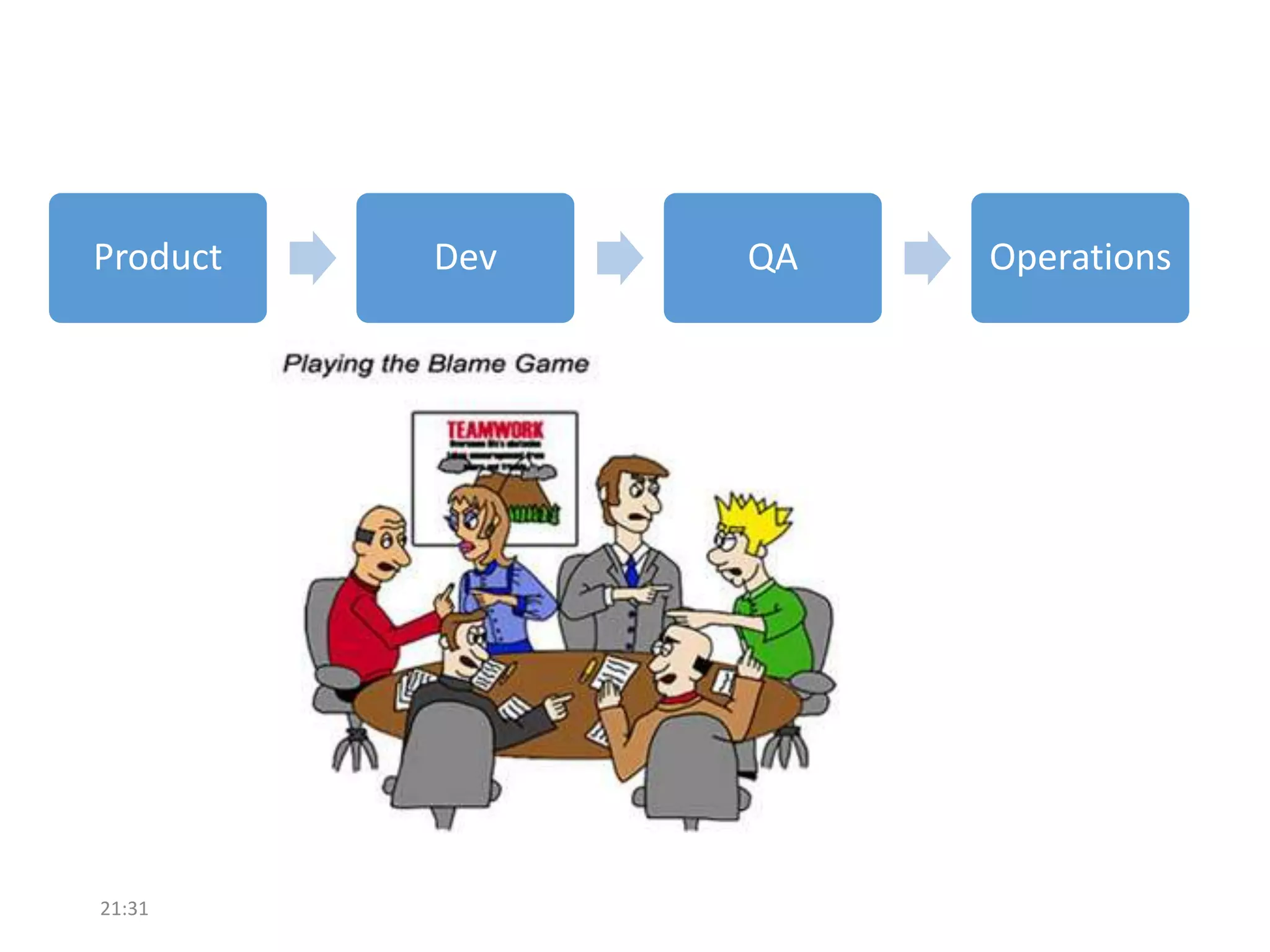
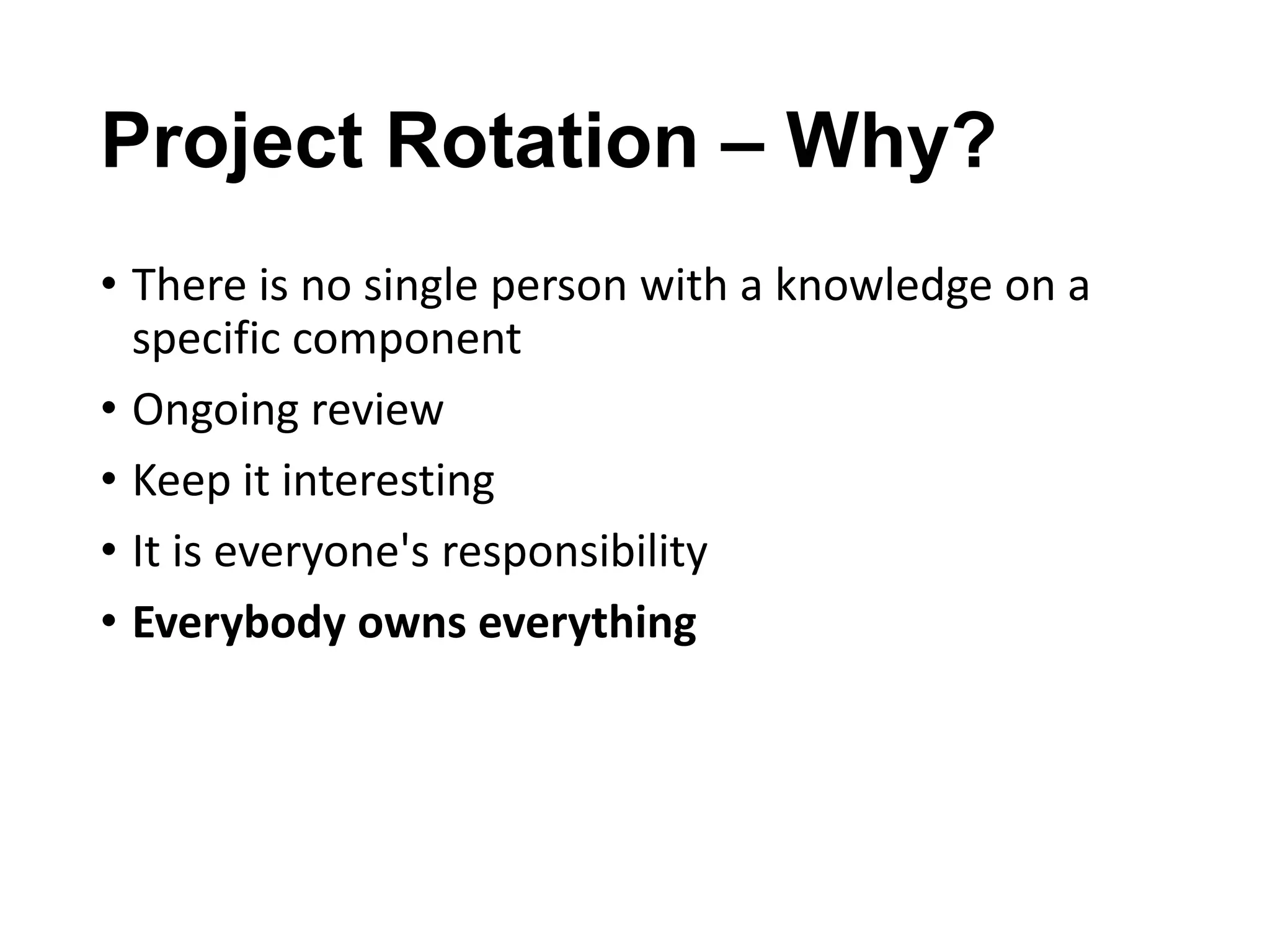
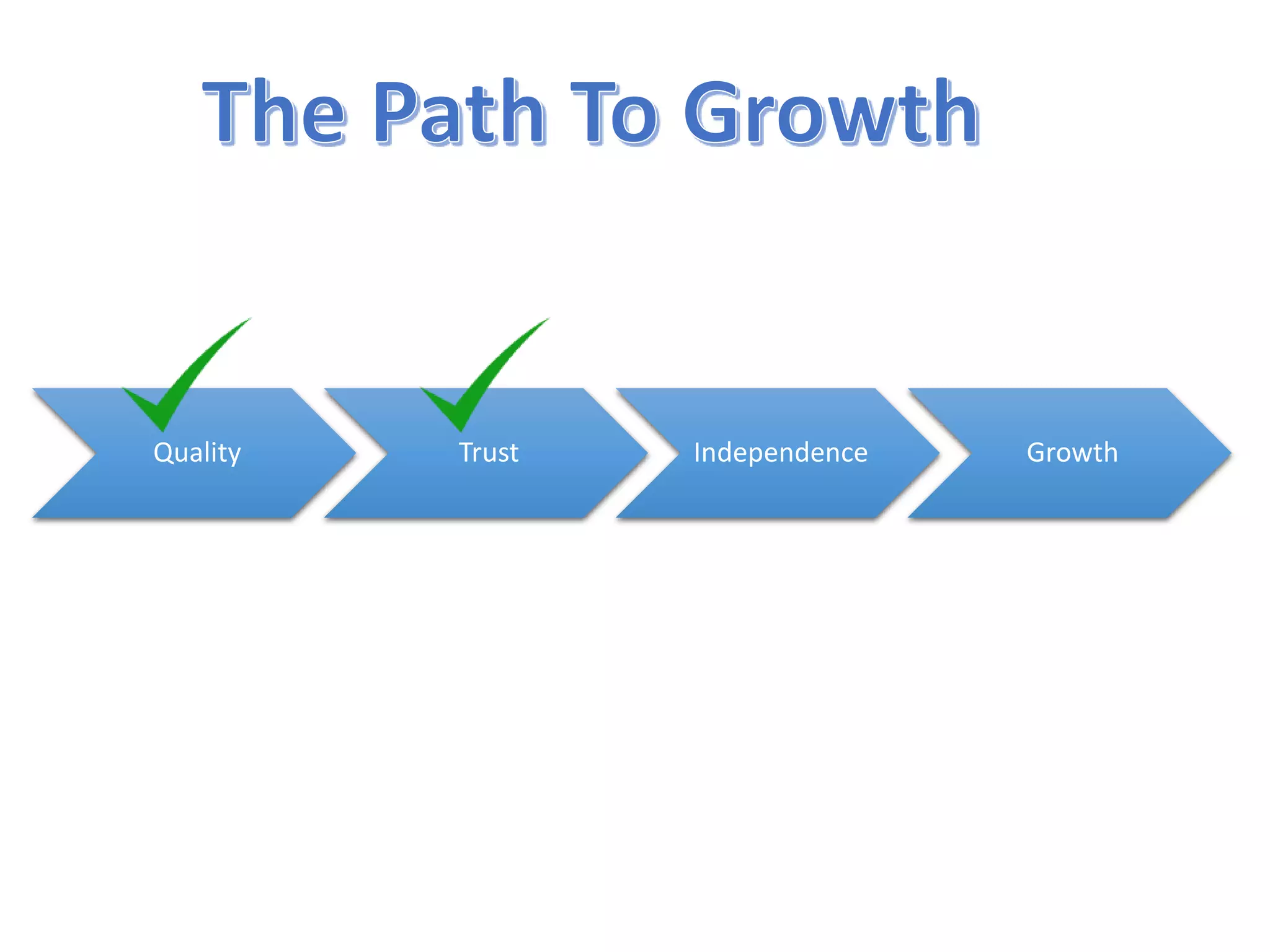
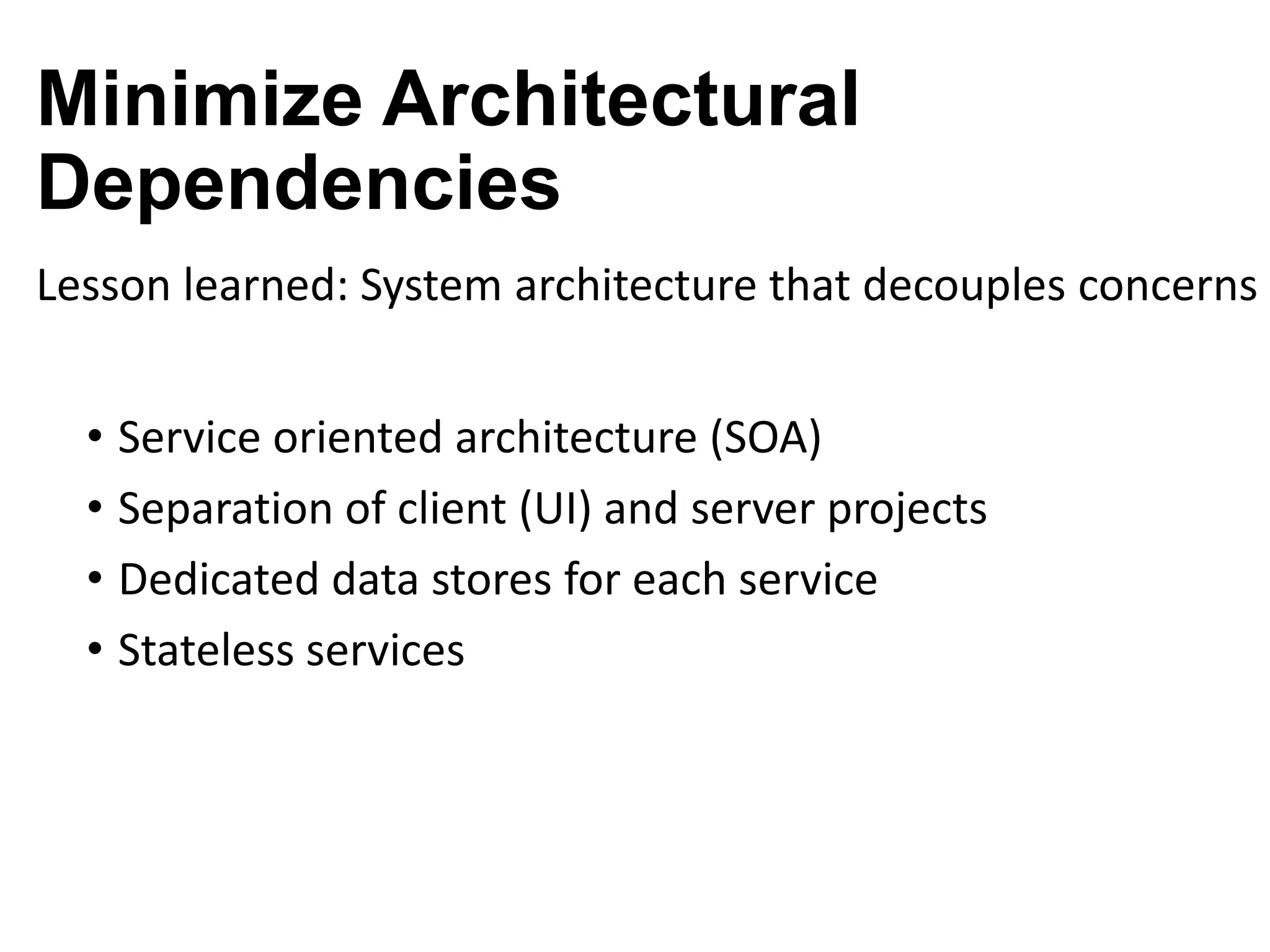
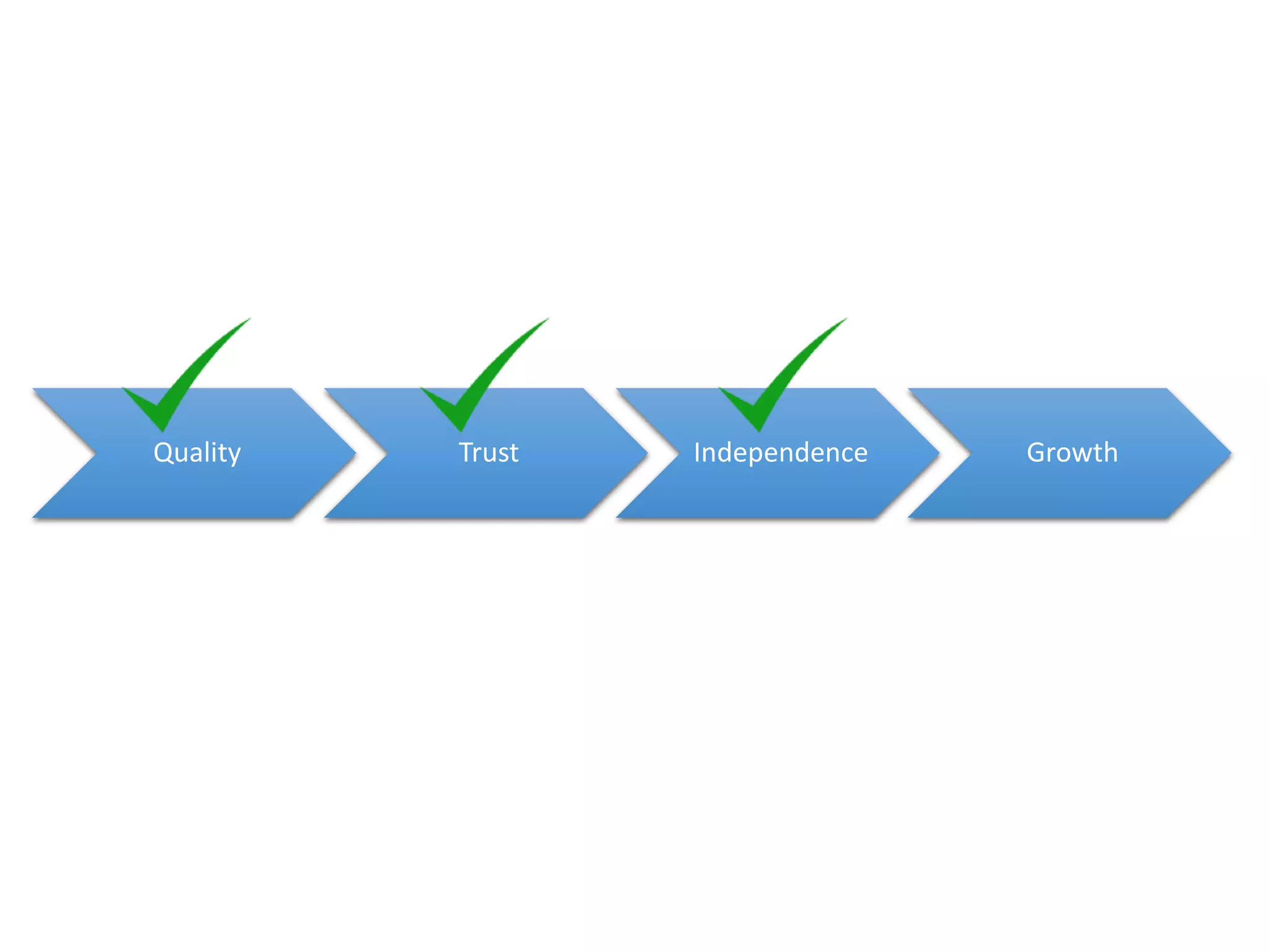
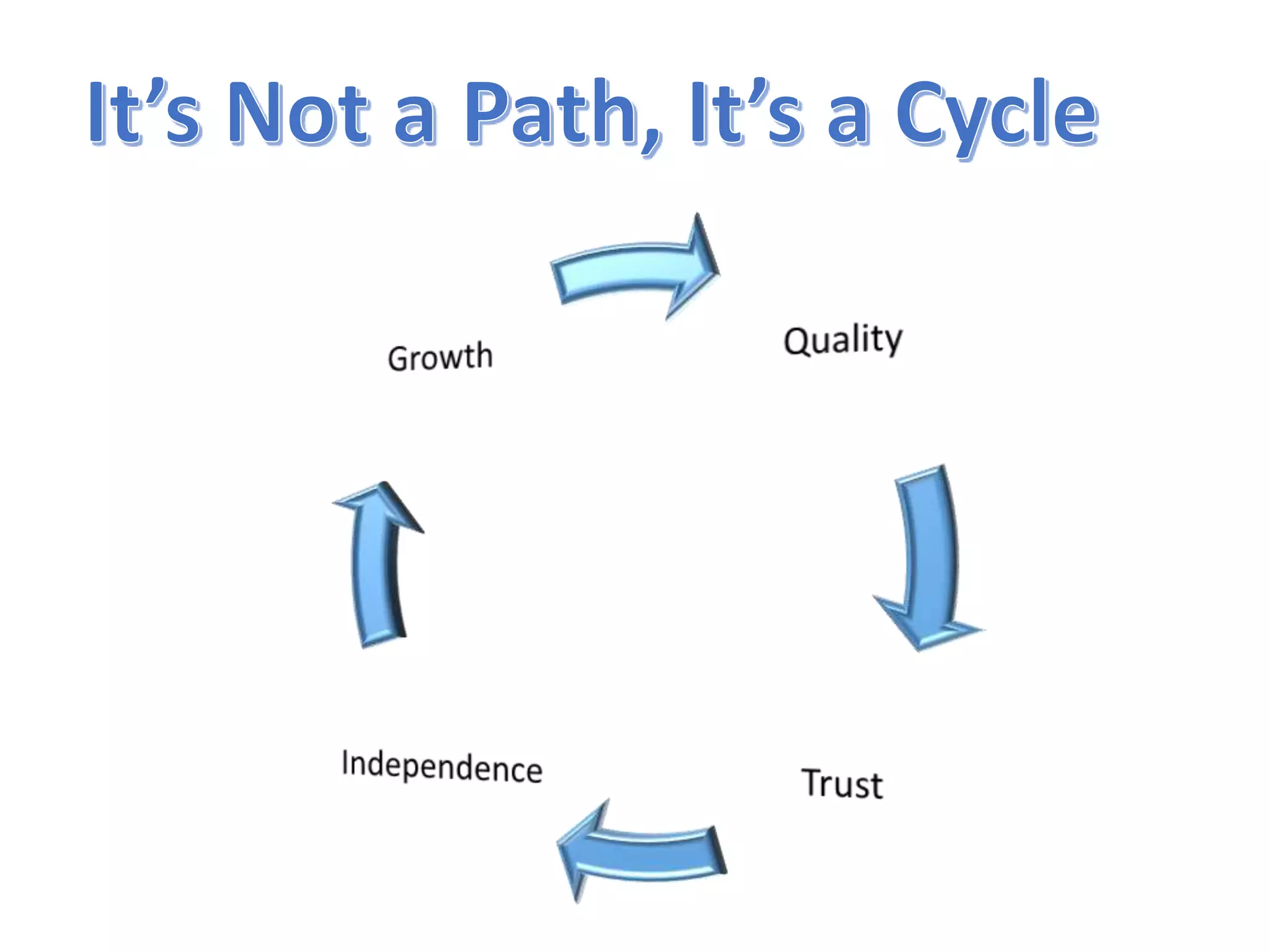
The document discusses the strategies employed by Wix to scale their R&D organization while ensuring quality, highlighting the use of a 'guilds and gangs' model to foster collaboration and knowledge sharing among teams. It outlines various structures for scalability, the importance of a dev-centric culture, and initiatives like 'Quality Thursday' and 'Tech Talks' to enhance team dynamics and continuous learning. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of hiring quality talent and maintaining a system architecture that minimizes dependencies.