More Related Content
Similar to Crystalline solid classification
Similar to Crystalline solid classification (6)
Crystalline solid classification
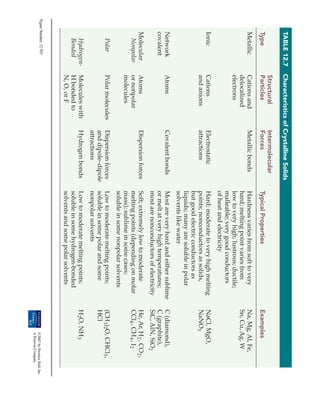
- 1. TABLE 12.7 Characteristics of Crystalline Solids
Structural Intermolecular
Type Particles Forces Typical Properties Examples
Metallic Cations and Metallic bonds Hardness varies from soft to very Na, Mg, Al, Fe,
delocalized hard; melting point varies from Sn, Cu, Ag, W
electrons low to very high; lustrous; ductile;
malleable; very good conductors
of heat and electricity
Ionic Cations Electrostatic Hard; moderate to very high melting NaCl, MgO,
and anions attractions points; nonconductors as solids, NaNO3
but good electric conductors as
liquids; many are soluble in polar
solvents like water
Network Atoms Covalent bonds Most are very hard and either sublime C (diamond),
covalent or melt at very high temperatures; C (graphite),
most are nonconductors of electricity SiC, AlN, SiO2
Molecular Atoms Dispersion forces Soft; extremely low to moderate He, Ar, H 2 , CO2 ,
Nonpolar or nonpolar melting points (depending on molar CCl4 , CH 4 , I 2
molecules mass); sublime in some cases;
soluble in some nonpolar solvents
Polar Polar molecules Dispersion forces Low to moderate melting points; (CH 3)2O, CHCl3 ,
and dipole–dipole soluble in some polar and some HCl
attractions nonpolar solvents
Hydrogen- Molecules with Hydrogen bonds Low to moderate melting points; H 2O, NH 3
Bonded H bonded to soluble in some hydrogen-bonded
N, O, or F solvents and some polar solvents
Figure Number: 12 T07
AABJSWV0
©2007 by Prentice Hall, Inc.
A Pearson Company