ANATOMY OF THE STEM.pptx
- 1. ANATOMY OF THE STEM Dr. Mbinji Omale
- 2. Functions of stems 1. Produces and support appendages of plant (leaves, flowers, fruits). 2. Transport water and solutes between roots and leaves. 3. In some plants are photosynthetic 4. Produce and store material necessary for life (water, starch etc.) 5. In some plants, stem have become adapted for specialized functions.
- 3. Two types of aerial stems Herbaceous stems 1. Soft and green 2. Little growth in diameter 3. Tissues chiefly primary 4. Usually annual 5. Covered by epidermis 6. Buds mostly naked Woody stems 1. Tough and not green 2. Considerable growth in diameter. 3. Tissues chiefly secondary 4. Perennial 5. Covered by cork bark 6. Buds usually covered by scales
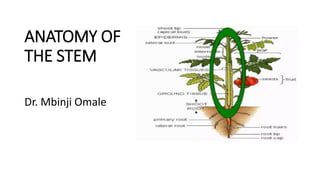
- 5. Internal stem anatomy. Monocots: vascular bundles usually complexity arranged. Dicots: vascular bundles usually arranged in rings.
- 8. Vascular bundles • This system consists of a number of vascular bundles which are distributed in the stele. • The stele is the central cylinder of the stem and the root surrounded by the endodermis. • It consists of vascular bundles, pericycle, pith and medullary rays. Each bundle is made up of xylem and phloem, with a cambium in dicotyledonous stems, or without a cambium in monocotyledonous stems, or only one kind of tissue xylem or phloem, as in roots. • The function of this system is to conduct water and raw food material from the roots to the leaves, and prepared food material from leaves to the storage organs and the growing regions. • The vascular bundle of a dicotyledonous stem, when fully formed, consists of three well-defined tissues: 1. Xylem or wood 2. Phloem or bast, and 3. vascular Cambium.
- 9. Xyllem • XYLEM Xylem is a conducting tissue and is composed of elements of different kinds, (a) tracheids, (b) vessels or tracheae, (c) wood fibres (d) wood parenchyma. • Xylem, as a whole, is meant to conduct water and mineral salts upwards from the root to the leaf to give mechanical strength to the plant body
- 10. Tracheids Tracheids: These are elongated, tube-like cells with hard, thick and lignified walls and large cell cavities. Their ends are tapering, either rounded or chisel-like and less frequently, pointed. They are dead, empty cells and their walls are provided with one or more rows of bordered pits. Tracheids may also be annular, spiral, scalariform or pitted (with simple pits)
- 11. Vessels or tracheae • Vessels are cylindrical, tube-like structures. • They are formed from a row of cells placed end to end, from which the transverse partition walls break down. • A vessel or trachea is, thus, a tube-like series of cells, very much like a series of water pipes forming a pipeline. • Their walls are thickened in various ways, and vessels can be annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulate, or pitted, according to the mode of thickening. • Associated with the vessels are often some tracheids. • Vessels and tracheids form the main elements of the wood or xylem of the vascular bundle. • They serve to conduct water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves. • They are dead, thick-walled and lignified, and as such, they also serve the mechanical function of strengthening the plant body
- 13. (c) Xylem (wood) fibres: • Sclerenchymatous cells associated with wood or xylem are known as wood fibres. • They occur abundantly in woody dicotyledons and add to the mechanical strength of the xylem and of the plant body as a whole. (d) Xylem (wood) parenchyma: • Parenchymatous cells are of frequent occurrence in the xylem, and are known as wood parenchyma. • The cells are alive and generally thin walled. • The wood parenchyma assists, directly or indirectly, in the conduction of water, upwards, through the vessels and the tracheids. • It also serves to store food.
- 14. Phloem • The phloem or bast is another conducting tissue, and is composed of the following elements: (a) sieve tubes, (b) Companion cells, (c) phloem parenchyma and (d) bast fibres (rarely). • Phloem, as a whole, is meant to conduct prepared food materials from the leaf to the storage organs and growing regions
- 15. Sieve tubes • Sieve tubes are slender, tube-like structures, composed of elongated cells which are placed end to end. • Their walls are thin and made of cellulose. • The transverse partition walls are, however, perforated by a number of pores. • The transverse wall then looks very much like a sieve, and is called the sieve plate. • The sieve plate may sometimes be formed in the side (longitudinal) wall. • In some cases, the sieve plate is not transverse (horizontal), but inclined obliquely, and then different areas of it become perforated. A sieve plate of this nature is called a compound plate. • At the close of the growing season, the sieve plate is covered by a deposit of colourless, shining substance in the form of a pad, called the callus or callus pad. • This consists of carbohydrate, called callose. • In winter, the callus completely clogs the pores, but in spring, when the active season begins, it gets dissolved.
- 16. • The sieve tube contains no nucleus, but has a lining layer of cytoplasm, which is continuous through the pores. • Sieve tubes are used for the longitudinal transmission of prepared food materials—proteins and carbohydrates—downward from the leaves to the storage organs, and later upward from the storage organs to the growing regions. • A heavy deposit of food material is found on either side of the sieve plate with a narrow median portion
- 18. Cont.. (b) Companion cells: • Associated with each sieve tube and connected with it by pores is a thin-walled, elongated cell known as the companion cell. • It is living and contains protoplasm and an elongated nucleus. The companion cell is present only in angiosperms (both dicotyledons and monocotyledons). • It assists the sieve tube in the conduction of food. (c) Phloem parenchyma: • There are always some parenchymatous cells forming a part of the phloem in all dicotyledons, gymnosperms and ferns. • The cells are livingand often cylindrical. • They store up food material and help to conduct it. Phloem parenchyma is, however, absent in most monocotyledons. (d) Bast fibres: • Sclerenchymatous cells occurring in the phloem or bast are known as bast fibres. • These are generally absent in the primary but occur frequently in the secondary phloem.
- 19. Cambium • This is a thin strip of primary meristem lying between the xylem and phloem. • It consists of one or a few layers of thin-walled and roughly rectangular cells. Although cambial cells look rectangular in transverse section, they are very elongated, often with oblique ends. • They become flattened tangentially, i.e. at right angles to the radius of the stem
- 20. Types of vascular bundles • According to the arrangement of xylem and phloem, the vascular bundles are of the following types; 1. Radial VB 2. Conjoint VB Collateral bicollateral 1. Concentric VB
- 21. Radial vascular bundles • Radial vascular bundle: When the xylem and phloem form separate bundles which lie on different radii, alternating with each other, as in roots. • The radial vascular bundle is the most primitive type of vascular bundles.
- 22. Conjoint vascular bundles • When the xylem and phloem combine into one bundle, it is called as conjoint vascular bundle. • There are different types of conjoint vascular bundles. • (1) Collateral: When the xylem and phloem lie together on the same radius, the xylem being internal and the phloem external is called collateral. • When cambium is present in collateral as in all dicotyledonous stems, the bundle is said to be open collateral, and when the cambium is absent, it is said to be closed collateral, as in monocotyledonous stems.
- 23. Bicollateral VB • When the both phloem and cambium occur twice in a collateral bundle—once on the outer side of the xylem and again on the inner side of it, is called as bicollateral. • The sequence is outer phloem, outer cambium, xylem, inner cambium and inner phloem. Bicollateral bundles are characteristics of Cucurbitaceae. • They are also often found in Solanaceae, Apocynaceae, Convolvulaceae, Myrtaceae, etc. A bicollateral bundle is always open
- 24. Concentric vascular bundles • When one kind of vascular tissue (xylem or phloem) is surrounded by the other is called as concentric vascular bundle. • Evidently, there are two types, according to whether one is central or the other one is so. • When the phloem lies in the centre and is surrounded by xylem, as in some monocotyledonous, the concentric bundle is said to be amphivasal (leptocentric). • When, on the other hand, the xylem lies in the centre and is surrounded by phloem, the concentric bundle is said to be amphicribral (Hadrocentric). • A concentric bundle is always closed.
- 25. Ground tissues A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. It arises from the ground meristem. It fills in the soft parts of the plants, such as cortex, pith, pericycle, etc. There are three fundamental types of cells that make up a ground tissue, 1. Parenchyma, 2. Sclerenchyma, 3. Collenchyma. • These cells are classified according to the nature, morphology, and composition of the cell walls.
- 26. Parenchyma • The parenchyma consists of a collection of cells which are more or less isodiametric, that is, equally expanded on all sides. • Parenchymatous cells have relatively thin primary walls. • Most of them continue to be alive even upon reaching maturity. They are the most common type of filler cells in ground tissues. In stem, they are found in cortex and pith. In roots they fill the cortical region and leaves they are found in mesophyll region. • Typical parenchymatous cells are oval, spherical or polygonal. • Their walls are thin and made of cellulose. • They are usually living. • Its main function is storage of food material. • When parenchymatous tissue contains chloroplasts, it is called chlorenchyma. Its function is to manufacture food material.
- 27. Collenchyma • Collenchyma is a living tissue derived from the parenchyma but with greater mechanical strength. • Are usually elongated cells. Its walls are thickened with cellulose giving them a plasticity that enables it to be present in herbaceous stems, petioles and midribs of leaves. • The cells are much thickened at the corners against the intercellular spaces. They look circular, oval or polygonal in a transverse section of the stem. • The thickening is due to a deposit of cellulose, hemicellulose and protopectin. • Although thickened, the cells are never lignified. • Simple pits can be found here and there in their walls. • Their thickened walls have a high refractive index and, therefore, this tissue in section is very conspicuous under the microscope. • It is absent from the root and the monocotyledon, except in special cases. • The cells are living and often contain a few chloroplasts. • Being flexible in nature, collenchyma gives tensile strength to the growing organs, and being extensible, it readily adapts itself to rapid elongation of the stem. • Since it contains chloroplasts, it also manufactures sugar and starch. Its function is, therefore, both mechanical and vital.
- 28. Sclerenchyma • Sclerenchyma (scleros means hard) consists of very long, narrow, thick and lignified cells, usually pointed at both ends. • They are fibre-like in appearance and hence, they are also called sclerenchymatous fibres, or simply fibres. • Their walls often become so greatly thickened that the cell cavity is nearly obliterated. • They have simple, often oblique, pits in their walls. The middle lamella is conspicuous in sclerenchyma. • They are dead cells and serve a purely mechanical function, i.e. they give the requisite strength, rigidity, flexibility and elasticity to the plant body and thus enable it to withstand various strains
- 30. Sclereids • Sclereids: Sometimes, special types of sclerenchyma develop in various parts of the plant body to meet local mechanical needs. • They are known as Sclereids or Stone cells. • They may occur in the cortex, pith, phloem, hard seeds, nuts, stony fruits, and in the leaves and stems of many dicotyledons and also gymnosperms. • The cells, though very thick-walled, hard and strongly lignified (sometimes cutinized or suberized), are not long and pointed like sclerenchyma, but are mostly isodiametric, polyhedral, short-cylindrical, slightly elongated, or irregular in shape. • Usually, they have no definite shape. • They are dead cells, and have very narrow cell cavities, which may be almost obliterated, owing to excessive thickness of the cell wall. • They may be somewhat loosely arranged or closely packed. They may also occur singly. • They contribute to the firmness and hardness of the part concerned.
- 31. Thank you