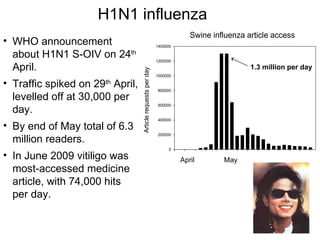
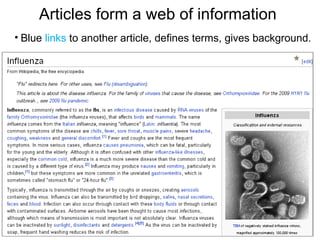
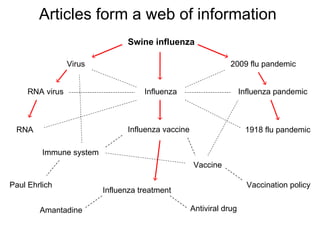
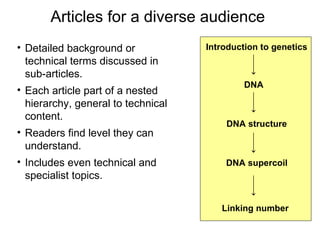
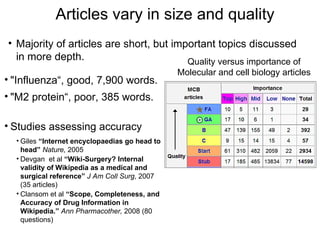
The document discusses the role of Wikipedia as a significant source of scientific information, noting its high visibility and rapid updates on health topics, particularly during events like the H1N1 influenza outbreak. It highlights public scientific literacy issues, with many lacking knowledge on key scientific concepts and topics. While Wikipedia articles serve as useful resources, they vary in depth and quality, indicating a need for expert contributions to improve accuracy and comprehensiveness.