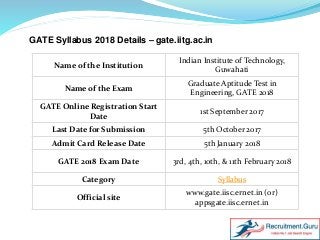
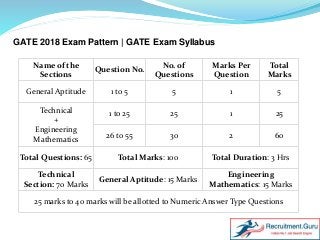
Download GATE Syllabus 2018. Get Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering Syllabus and Exam Pattern here. Check Latest GATE Syllabus. Here, we have uploaded the Subject wise Syllabus for GATE 2018 Exam. Also, visit https://www.recruitment.guru/syllabus/gate-syllabus/ for more detailed information.