Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Featured
Featured (20)
Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings

Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings
How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health

How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health
AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf

AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf
Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)

Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)
How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024

How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024
Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights

Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights
Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024

Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024
5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary

5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary
Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent

Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent
The six step guide to practical project management

The six step guide to practical project management
Beginners Guide to TikTok for Search - Rachel Pearson - We are Tilt __ Bright...

Beginners Guide to TikTok for Search - Rachel Pearson - We are Tilt __ Bright...
Poster Final 2
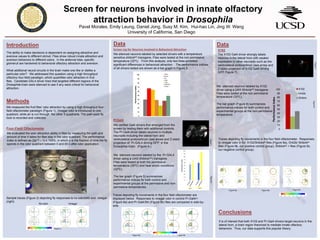
- 1. Screen for neurons involved in innate olfactory attraction behavior in Drosophila Methods Pavel Morales, Emily Leung, Daniel Jong, Susy M. Kim, Hui-hao Lin, Jing W. Wang University of California, San Diego Conclusions X102 The ability to make decisions is dependent on assigning attractive and aversive values to different stimuli. Flies show robust innate attraction and aversion behaviors to different odors. In the antennal lobe, specific glomeruli are hardwired to behavioral olfactory attraction and aversion. What additional neural circuits in the brain make one like or dislike a particular odor? We addressed this question using a high throughput olfactory four-field paradigm, which quantifies odor attraction in fruit flies. Candidate GAL4 driver lines that targeted different regions of the Drosophila brain were silenced to see if any were critical for behavioral attraction. We measured the fruit flies’ odor attraction by using a high throughput four- field olfactometer paradigm (Figure 1). Vinegar odor is introduced to one quadrant, while air is run through the other 3 quadrants. The path each fly took is recorded and collected. Data Sample traces (Figure 2) depicting fly responses to no odor(left) and vinegar (right). We silenced neurons labeled by selected drivers with a temperature sensitive shibirets2 transgene. Flies were tested at the non-permissive temperature (32⁰C). From this analysis, only two lines exhibited significant differences in behavioral attraction . The performance indices of all drivers tested are shown as a bar graph in Figure 3. PrGal4 Traces depicting fly movements in the four field olfactometer. Responses to vinegar odor in for X102/Shibirets flies (Figure 9a), Or42b/ Shibirets flies (Figure 9b, our positive control group), Shibirets/ + flies (Figure 9c, our negative control group). The X102 Gal4 driver strongly labels neurons in the lateral horn with weaker expression in other neuropils such as the ventrolateral protocerbrum (see arrow and Z-stack projection of X102 Gal4 driving GFP, Figure 7). Data We verified Gal4 drivers that emerged from the screen by testing them with additional controls. The Pr-Gal4 driver labels neurons in multiple neuropils including the lateral horn and ventrolateral protocerbrum (see arows and Z-stack projection of Pr-GAL4 driving GFP in the Drosophila brain. (Figure 4.). Vinegar We silenced neurons labeled by the Pr-GAL4 driver using a UAS-Shibire(ts2) transgene. Flies were tested at both the permissive temperature (25⁰C) and heat shock conditions (32⁰C). The bar graph (Figure 5) summarizes performance indices for both control and experimental groups at the permissive and non- permissive temperatures. We silenced neurons labeled by X102 driver using a UAS-Shibirets2 transgene. Flies were tested at the non-permissive temperature (32⁰C). The bar graph (Figure 8) summarizes performance indices for both control and experimental groups at the non-permissive temperature. No-odor Four-Field Olfactometer Figure1. Figure 2. Screen ing for Neurons involved in Behavioral Attraction Traces depicting fly movements in the four field olfactometer are displayed below. Responses to vinegar odor in control Pr-Gal4/+ (Figure 6a) and Pr-Gal4/Shi (Figure 6b) flies are compared in side-by- side. Figure5. Figure 6a. Figure 6b. Figure8. Figure 9a. Figure 9b. Figure 9c. Figure4. It is of interest that both X102 and Pr-Gal4 drivers target neurons in the lateral horn, a brain region theorized to mediate innate olfactory behaviors. Thus, our data supports this popular theory. Introduction Figure7. We evaluated the odor attraction ability in flies by measuring the path and amount of time it takes for flies stay in the odor quadrant. The performance index is defined as (2p1/2 – 1) x 100%, in which p is the fraction of time the fly spends in the odor quadrant between 0 and 60 s after odor application. 3.02.52.01.51.00.50.0 3.02.52.01.51.00.50.0 3.02.52.01.51.00.50.0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 PerformanceIndex X102 Or42b Shibire
Editor's Notes
- Four-Field Olfactometer (Figure 1.) consists of four chambers in the center where the flies are loaded through a small hole in the middle of the chamber. On each corner of the paradigm lie the odor bottles from which one is arbitrarily chosen to have the vinegar odor. We traced the path for X102/Shibirets flies (Figure 9a), our experimental fly where X102 neurons were silenced. We see that X102/Shibirets flies mostly stayed in quadrant I, which is the vinegar quadrant. Trace for Or42b/ Shibirets(Figure 9b) is our negative control group. Or42b an odorant receptor silenced by Shiberets. Flies in this cross can’t trace the smell, thus showing no attraction to the odor. Trace for Shiberets/ W118 (Figure 9c) is our positive control group. Flies in this cross were observed to see Shiberets behaved with wild type flies, when no select neurons were silenced.