Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
How changes in nurses workload assignments can improve quality of care and increase workplace safety. Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffing

Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffingRoberto Rivera-Olmo, BSN, RN
Why registered nurse staffing benefits nurses, patients and the health care system
Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...

Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...Roberto Rivera-Olmo, BSN, RN
More Related Content
What's hot
How changes in nurses workload assignments can improve quality of care and increase workplace safety. Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffing

Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffingRoberto Rivera-Olmo, BSN, RN
Why registered nurse staffing benefits nurses, patients and the health care system
Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...

Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...Roberto Rivera-Olmo, BSN, RN
What's hot (20)
Independentpracticeissuesinnursing 111115105545-phpapp01

Independentpracticeissuesinnursing 111115105545-phpapp01
Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffing

Quality of care improvement by changes to workload assignment for safe staffing
Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...

Registered Nurse Staffing Legislation: Why registered nurse staffing benefits...
Increase quality care with staff involvement with workload assignment

Increase quality care with staff involvement with workload assignment
Hospital Pathways programme - Intentional Rounding

Hospital Pathways programme - Intentional Rounding
Safe staffing = safe care the role of nurse-patient ratios

Safe staffing = safe care the role of nurse-patient ratios
Annette Bartley: Making it happen - Intentional Rounding

Annette Bartley: Making it happen - Intentional Rounding
Acs0109 Fast Track Inpatient And Ambulatory Surgery

Acs0109 Fast Track Inpatient And Ambulatory Surgery
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (17)
Adding E-Commerce to your website by Barbara Luhring

Adding E-Commerce to your website by Barbara Luhring
Dal progetto "nuovo ingegnere" la proposta di coworking all’Ordine Ingegneri ...

Dal progetto "nuovo ingegnere" la proposta di coworking all’Ordine Ingegneri ...
Open gov, opendata, smartcity: la rivoluzione digitale nelle mani dei cittadini

Open gov, opendata, smartcity: la rivoluzione digitale nelle mani dei cittadini
La integración de niños sordomudos al nivel educativo

La integración de niños sordomudos al nivel educativo
Towards an overarching classification model of CSCW and groupware: a socio-te...

Towards an overarching classification model of CSCW and groupware: a socio-te...
Similar to india_improving_care_in_hisar_gh_dec2014
Similar to india_improving_care_in_hisar_gh_dec2014 (20)
Copyright © 2020 wolters kluwer health, inc. all rights reserv

Copyright © 2020 wolters kluwer health, inc. all rights reserv
Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserv

Copyright © 2020 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserv
An Education Change Project To Improve Pharmacy And Nursing Collaboration

An Education Change Project To Improve Pharmacy And Nursing Collaboration
113DNP Prospectus Comment by Cynthia Fletcher Th.docx

113DNP Prospectus Comment by Cynthia Fletcher Th.docx
The Saskatchewan Surgical Initiative: Lessons Learned

The Saskatchewan Surgical Initiative: Lessons Learned
CLINICAL BRIEFA Quality Improvement Initiative Improving .docx

CLINICAL BRIEFA Quality Improvement Initiative Improving .docx
CLINICAL BRIEFA Quality Improvement Initiative Improving .docx

CLINICAL BRIEFA Quality Improvement Initiative Improving .docx
Health Care Reform (The Affordable Care Act) .docx

Health Care Reform (The Affordable Care Act) .docx
Hardwiring Bedside Shift Report Quantitative Research Article.pdf

Hardwiring Bedside Shift Report Quantitative Research Article.pdf
india_improving_care_in_hisar_gh_dec2014
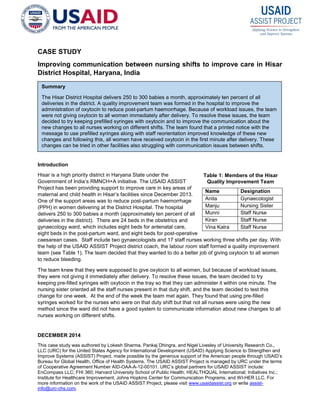
- 1. DECEMBER 2014 This case study was authored by Lokesh Sharma, Pankaj Dhingra, and Nigel Livesley of University Research Co., LLC (URC) for the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Applying Science to Strengthen and Improve Systems (ASSIST) Project, made possible by the generous support of the American people through USAID’s Bureau for Global Health, Office of Health Systems. The USAID ASSIST Project is managed by URC under the terms of Cooperative Agreement Number AID-OAA-A-12-00101. URC’s global partners for USAID ASSIST include: EnCompass LLC; FHI 360; Harvard University School of Public Health; HEALTHQUAL International; Initiatives Inc.; Institute for Healthcare Improvement; Johns Hopkins Center for Communication Programs; and WI-HER LLC. For more information on the work of the USAID ASSIST Project, please visit www.usaidassist.org or write assist- info@urc-chs.com. CASE STUDY Improving communication between nursing shifts to improve care in Hisar District Hospital, Haryana, India Introduction Hisar is a high priority district in Haryana State under the Government of India’s RMNCH+A initiative. The USAID ASSIST Project has been providing support to improve care in key areas of maternal and child health in Hisar’s facilities since December 2013. One of the support areas was to reduce post-partum haemorrhage (PPH) in women delivering at the District Hospital. The hospital delivers 250 to 300 babies a month (approximately ten percent of all deliveries in the district). There are 24 beds in the obstetrics and gynaecology ward, which includes eight beds for antenatal care, eight beds in the post-partum ward, and eight beds for post-operative caesarean cases. Staff include two gynaecologists and 17 staff nurses working three shifts per day. With the help of the USAID ASSIST Project district coach, the labour room staff formed a quality improvement team (see Table 1). The team decided that they wanted to do a better job of giving oxytocin to all women to reduce bleeding. The team knew that they were supposed to give oxytocin to all women, but because of workload issues, they were not giving it immediately after delivery. To resolve these issues, the team decided to try keeping pre-filled syringes with oxytocin in the tray so that they can administer it within one minute. The nursing sister oriented all the staff nurses present in that duty shift, and the team decided to test this change for one week. At the end of the week the team met again. They found that using pre-filled syringes worked for the nurses who were on that duty shift but that not all nurses were using the new method since the ward did not have a good system to communicate information about new changes to all nurses working on different shifts. Name Designation Anita Gynaecologist Manju Nursing Sister Munni Staff Nurse Kiran Staff Nurse Vina Kalra Staff Nurse Summary The Hisar District Hospital delivers 250 to 300 babies a month, approximately ten percent of all deliveries in the district. A quality improvement team was formed in the hospital to improve the administration of oxytocin to reduce post-partum haemorrhage. Because of workload issues, the team were not giving oxytocin to all women immediately after delivery. To resolve these issues, the team decided to try keeping prefilled syringes with oxytocin and to improve the communication about the new changes to all nurses working on different shifts. The team found that a printed notice with the message to use prefilled syringes along with staff reorientation improved knowledge of these new changes and following this, all women have received oxytocin in the first minute after delivery. These changes can be tried in other facilities also struggling with communication issues between shifts. Table 1: Members of the Hisar Quality Improvement Team
- 2. USAID Applying Science to Strengthen and Improve Systems (ASSIST) Project University Research Co., LLC • 7200 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 600 • Bethesda, MD 20814 • USA Alps Building, 1st Floor • 56 Janpath • New Delhi 110001 • India This case study was made possible by the support of the American people through USAID. The contents of this case study are the sole responsibility of URC and do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or United States Government. Introducing changes to communication between staff nurses The team discussed new ways of communicating messages so that all the staff nurses would be aware of the new practice. Staff nurses who attended the team meeting decided they would first handover the message verbally to evening and night duty staff nurses. To ensure that the message was properly conveyed to the incoming shift, the nursing sister agreed to repeat the message to each shift. Three days later, the team met again. They found the system of communicating between shifts worked but nurses who were coming back from time off and needed more information about the new processes to reduce PPH. The team decided to print information about giving oxytocin in the first minute after delivery and to paste it on the maternity wing’s notice board where the duty roster is kept and on the labour room wall near the delivery table as a reminder. Results After one week, the team again sat down to discuss the progress. They found the last change idea of printing and pasting the notice with message for use of prefilled syringe improved the communication within the team and that 80 percent of women were now getting oxytocin in the first minute. The remaining women were being cared for by nurses who had just completed leave. The team reoriented these nurses and following this, 100 percent of women have received oxytocin in the first minute after delivery (see Figure 1). Conclusion Communicating across multiple shifts can be challenging in large facilities. In this facility, poor communication was a barrier to providing best-practice care to prevent PPH. They managed to improve communication using four main changes. This enabled them to improve oxytocin administration no matter when a patient delivered and ensure standard care. These changes can be tried in other facilities also struggling with communication issues between shifts. Figure 1: Percentage of bed head tickets having record of oxytocin injection given within one minute in Hisar District Hospital, February-May 2014 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Feb-8 Feb-22 Mar-8 Mar-22 Apr-5 Apr-19 May-3 Hundreds February-Week 1: Staff is orientated and shift-to-shift communication is introduced. February-Week 2: Signs for oxytocin administration posted in common areas. February-Week 3: Staff reorientation Print information about oxytocin administration on notice board. Photo courtesy of Hisar staff.
