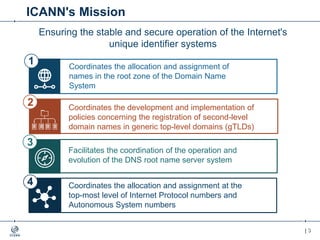
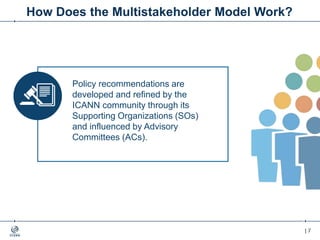
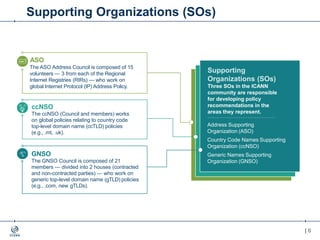
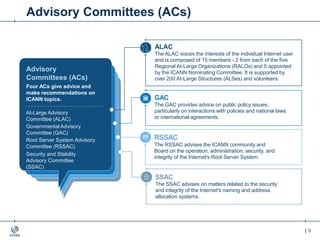
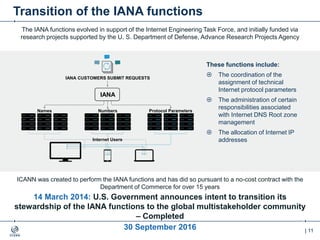
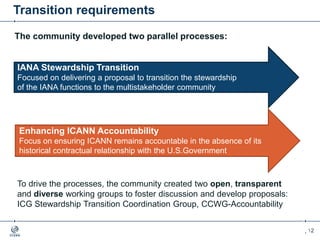
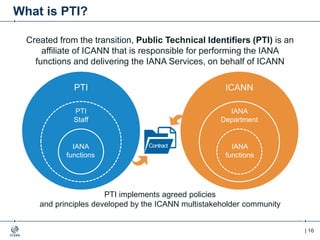
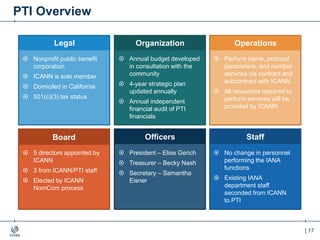
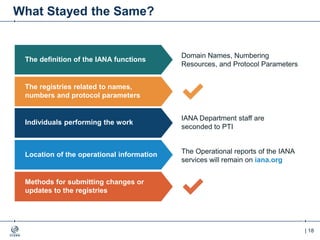
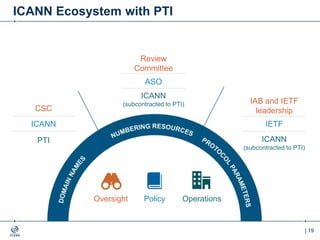
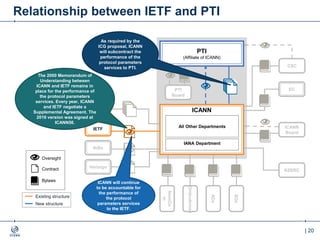
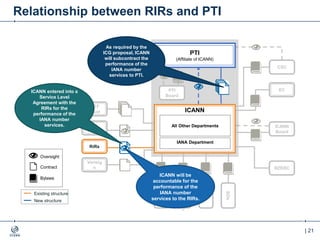
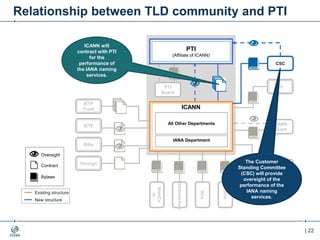
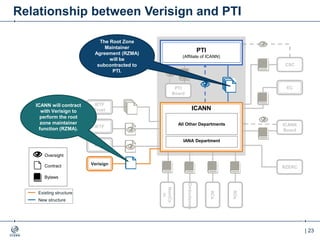
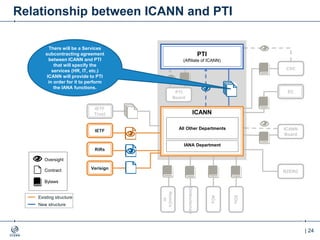
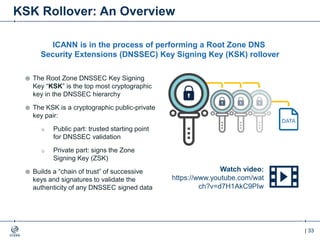
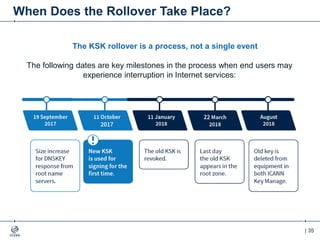
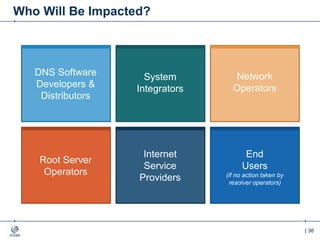
The document outlines the IANA stewardship transition and ICANN's role in enhancing accountability through a multistakeholder approach. It details the coordination of domain name system functions, the establishment of Public Technical Identifiers (PTI) to perform IANA functions post-transition, and the planned rollout of a key signing key (KSK) for DNSSEC on October 11, 2017. The KSK rollover aims to periodically change cryptographic keys for maintaining security in the DNS infrastructure while ensuring minimal disruption to internet services.