sistemas democráticos y no democráticos
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
3 likes•17,890 views
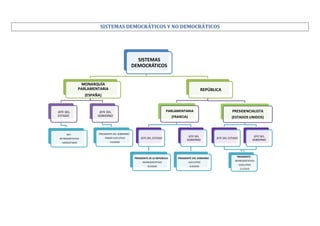
Mapa conceptual en el que se estudian los diferentes sistemas políticos, distinguiendo entre los democráticos y los no democráticos.
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
More from DavidProfeSoc
More from DavidProfeSoc (20)
Saint valentine's Day. The origin of this festivity.

Saint valentine's Day. The origin of this festivity.
Formation and expansion of the peninsular kingdoms

Formation and expansion of the peninsular kingdoms
Arte del Barroco de Italia para 2º ESO Ciencias Sociales

Arte del Barroco de Italia para 2º ESO Ciencias Sociales
sistemas democráticos y no democráticos
- 1. SISTEMAS DEMOCRÁTICOS Y NO DEMOCRÁTICOS SISTEMAS DEMOCRÁTICOS MONARQUÍA PARLAMENTARIA REPÚBLICA (ESPAÑA) JEFE DEL ESTADO PARLAMENTARIA REY: - PODER EJECUTIVO - HEREDITARIO (ESTADOS UNIDOS) PRESIDENTE DEL GOBIERNO: -RETRESENTATIVO PRESIDENCIALISTA (FRANCIA) JEFE DEL GOBIERNO - ELEGIDO JEFE DEL ESTADO JEFE DEL GOBIERNO PRESIDENTE DE LA REPÚBLICA: PRESIDENTE DEL GOBIERNO: - REPRESENTATIVO - EJECUTIVO - ELEGIDO - ELEGIDO JEFE DEL ESTADO JEFE DEL GOBIERNO PRESIDENTE: PRESIDENTE: - REPRESENTATIVO REPRESENTATIV O - EJECUTIVO EJECUTIVO - ELEGIDO -
- 2. SISTEMAS NO DEMOCRÁTICOS DICTADURA PERSONAL (LIBIA DE GADAFI, ESPAÑA FRANQUISTA) TODOS LOS PODERES LOS TIENE UNA SOLA PERSONA LLEGA AL PODER COMO CONSECUENCIA DE UN GOLPE DE ESTADO RÉGIMEN TOTALITARIO MONARQUÍA ABSOLUTA (CHINA, CUBA) (OMÁN, NEPAL HASTA 1990) LOS CIUDADANOS TIENEN MUY LIMITADOS LOS DERECHOS TODOS LOS PODERES ESTÁN EN MANOS DE UN SOLO PARTIDO TODOS LOS PODERES LOS TIENE EL REY LLEGA AL PODER DE FORMA HEREDITARIA LOS CIUDADANOS SON MEROS VASALLOS LLEGA AL PODER MEDIANTE UN GOLPE DE ESTADO (CUBA) O MEDIANTE ELECCIONES (ALEMANIA NAZI) LOS CIUDADANOS TIENEN MUY RECORTADOS LOS DERECHOS