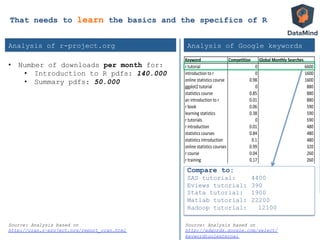
The document presents an interactive e-learning platform named Datamind, designed for teaching data analysis using R, addressing the need for scalable learning tools due to a rapidly growing user base. It highlights features such as automated feedback through submission correctness tests, gamification, and the ability to create courses using R packages and web interfaces. Additionally, it emphasizes the platform's focus on practical coding skills and ease of access by running R in the cloud, thus eliminating installation issues for users.

















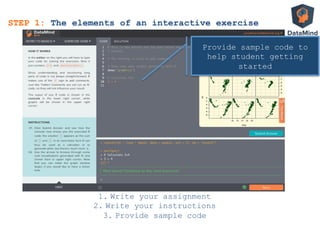













![• Everything in the student’s workspace
• DM.user.code
all code written by student
• DM.console.output
everything printed to user console
INPUT
Automated exercise correction with SCT
Assignment to the student:
Print a matrix with 3 rows
containing the numbers 1 up to 9
If Student does this correctly
then:
DM.console.ouput contains
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[2,] 4 5 6
[3,] 7 8 9
STEP 3: Explaining Interactivity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataminddublinsept112013-130912091542-phpapp01/85/DataMind-interactive-learning-Dublin-R-User-Group-September-2013-41-320.jpg)
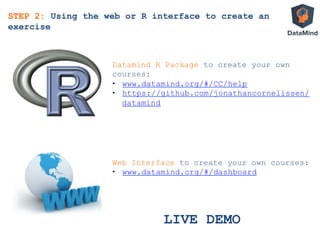
![• Everything in the student’s workspace
• DM.user.code
all code written by student
• DM.console.output
everything printed to user console
INPUT
Automated exercise correction with SCT
Assignment to the student:
Print a matrix with 3 rows
containing the numbers 1 up to 9
If Student does this correctly
then:
DM.console.ouput contains
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[2,] 4 5 6
[3,] 7 8 9
STEP 3: Explaining Interactivity
Submission Correctness Test written by course
creator (potentially using datamind package)
DM.result <- output_contains("matrix(1:9,
byrow=TRUE, nrow=3)”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataminddublinsept112013-130912091542-phpapp01/85/DataMind-interactive-learning-Dublin-R-User-Group-September-2013-42-320.jpg)
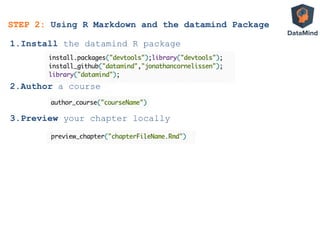
![• Everything in the student’s workspace
• DM.user.code
all code written by student
• DM.console.output
everything printed to user console
INPUT
Automated exercise correction with SCT
Assignment to the student:
Print a matrix with 3 rows
containing the numbers 1 up to 9
If Student does this correctly
then:
DM.console.ouput contains
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[2,] 4 5 6
[3,] 7 8 9
STEP 3: Explaining Interactivity
Submission Correctness Test written by course
creator (potentially using DM package)
DM.result <- output_contains("matrix(1:9,
byrow=TRUE, nrow=3)”)
• Assigned to variable DM.result
• List with two elements
1. TRUE / FALSE
2. Message to provide to student with
feedback
DM.result is shown to student
OUTPUT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataminddublinsept112013-130912091542-phpapp01/85/DataMind-interactive-learning-Dublin-R-User-Group-September-2013-43-320.jpg)