More Related Content
More from Citlali Islas (20)
Razonamiento ecuaciones citlali
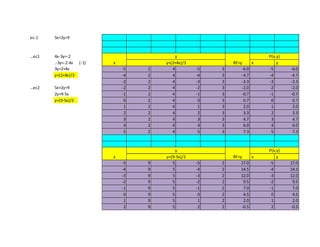
- 1. ec-1 5x+2y=9
…ec1 4x-3y=-2
x
y
RF=y
P(x,y)
.-3y=-2-4x (-1) y=(2+4x)/3 x y
3y=2+4x -5 2 4 -5 3 -6.0 -5 -6.0
y=(2+4x)/3 -4 2 4 -4 3 -4.7 -4 -4.7
-3 2 4 -3 3 -3.3 -3 -3.3
…ec2 5x+2y=9 -2 2 4 -2 3 -2.0 -2 -2.0
2y=9-5x -1 2 4 -1 3 -0.7 -1 -0.7
y=(9-5x)/2 0 2 4 0 3 0.7 0 0.7
1 2 4 1 3 2.0 1 2.0
2 2 4 2 3 3.3 2 3.3
3 2 4 3 3 4.7 3 4.7
4 2 4 4 3 6.0 4 6.0
5 2 4 5 3 7.3 5 7.3
x
y
RF=y
P(x,y)
y=(9-5x)/2 x y
-5 9 5 -5 2 17.0 -5 17.0
-4 9 5 -4 2 14.5 -4 14.5
-3 9 5 -3 2 12.0 -3 12.0
-2 9 5 -2 2 9.5 -2 9.5
-1 9 5 -1 2 7.0 -1 7.0
0 9 5 0 2 4.5 0 4.5
1 9 5 1 2 2.0 1 2.0
2 9 5 2 2 -0.5 2 -0.5
- 2. 3 9 5 3 2 -3.0 3 -3.0
4 9 5 4 2 -5.5 4 -5.5
5 9 5 5 2 -8.0 5 -8.0
1, 2.01, 2.0
-10.0
-5.0
0.0
5.0
10.0
15.0
20.0
-6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6
y=(2+4x)/3
y=(9-5x)/2
- 3. EC-2 4x-5y=-9
e-1 2x+3y=1
y
x
RF=y
P(X,Y)
x=1-3y/2 x=1-3y/2 X Y
-5 1 3 -5 2 -7.0 -5 -7
-4 1 3 -4 2 6.5 -4 6.5
-3 1 3 -3 2 5.0 -3 5
e2 4x-5y=-9 -2 1 3 -2 2 3.5 -2 3.5
x=-9+5y/4 -1 1 3 -1 2 2.0 -1 2
0 1 3 0 2 0.5 0 0.5
1 1 3 1 2 -1.0 1 -1
2 1 3 2 2 -2.5 2 -2.5
3 1 3 3 2 -4.0 3 -4
4 1 3 4 2 -5.5 4 -5.5
5 1 3 5 2 -7.0 5 -7
Y
X
RF=y
P(X,Y)
x=-9+5y/4 X Y
-5 9 5 -5 4 -8.5 -5 -8.5
-4 9 5 -4 4 -7.3 -4 -7.3
-3 9 5 -3 4 -6.0 -3 -6.0
-2 9 5 -2 4 -4.8 -2 -4.8
-1 9 5 -1 4 -3.5 -1 -3.5
0 9 5 0 4 -2.3 0 -2.3
1 9 5 1 4 -1.0 1 -1.0
2 9 5 2 4 1.5 2 1.5
- 4. 3 9 5 3 4 1.5 3 1.5
4 9 5 4 4 2.8 4 2.8
5 9 5 5 4 4.0 5 4.0