More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
General and molecular mechanism of Muscle contraction

General and molecular mechanism of Muscle contraction
Similar to Ppt notes muscle contraction
Similar to Ppt notes muscle contraction (20)
Molecular mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction.2022.pptx

Molecular mechanism of Skeletal muscle contraction.2022.pptx
Ppt notes muscle contraction
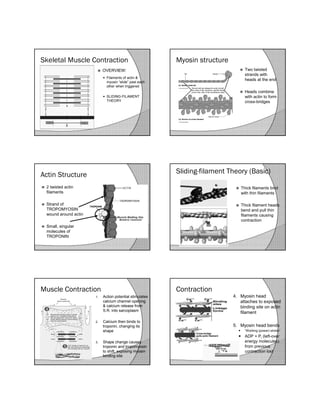
- 1. Skeletal Muscle Contraction OVERVIEW: Filaments of actin & myosin “slide” past each other when triggered SLIDING-FILAMENT THEORY Myosin structure Two twisted strands with heads at the end Heads combine with actin to form cross-bridges Actin Structure 2 twisted actin filaments Strand of TROPOMYOSIN wound around actin Small, singular molecules of TROPONIN Sliding-filament Theory (Basic) Thick filaments bind with thin filaments Thick filament heads bend and pull thin filaments causing contraction Muscle Contraction 1. Action potential stimulates calcium channel opening & calcium release from S.R. into sarcoplasm 2. Calcium then binds to troponin, changing its shape 3. Shape change causes troponin and tropomyosin to shift, exposing myosin binding site Contraction 4. Myosin head attaches to exposed binding site on actin filament 5. Myosin head bends “Working (power) stroke” ADP + Pi (left-over energy molecules) from previous contraction lost
- 2. Contraction 6. New ATP molecule binds to myosin, causing it to change shape and release it from actin Contraction 7. ATPase hydrolyzes (splits) ATP into ADP & Pi giving off energy 8. Returns myosin head to “high-energy” configuration for next cycle Contraction 9. Calcium pumps in S.R. reabsorb ions 10. Troponin returns to normal position 11. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) destroys ACh