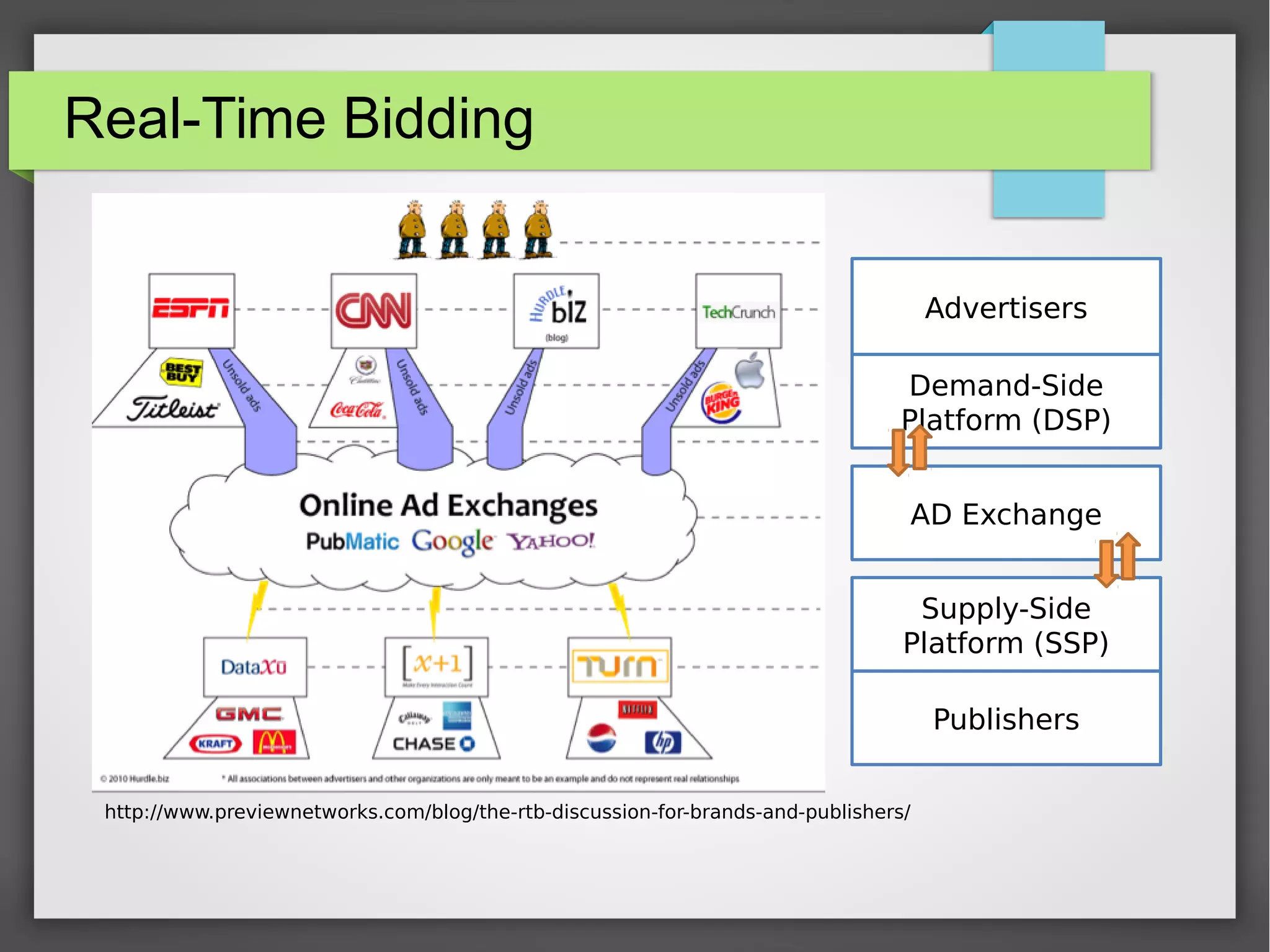
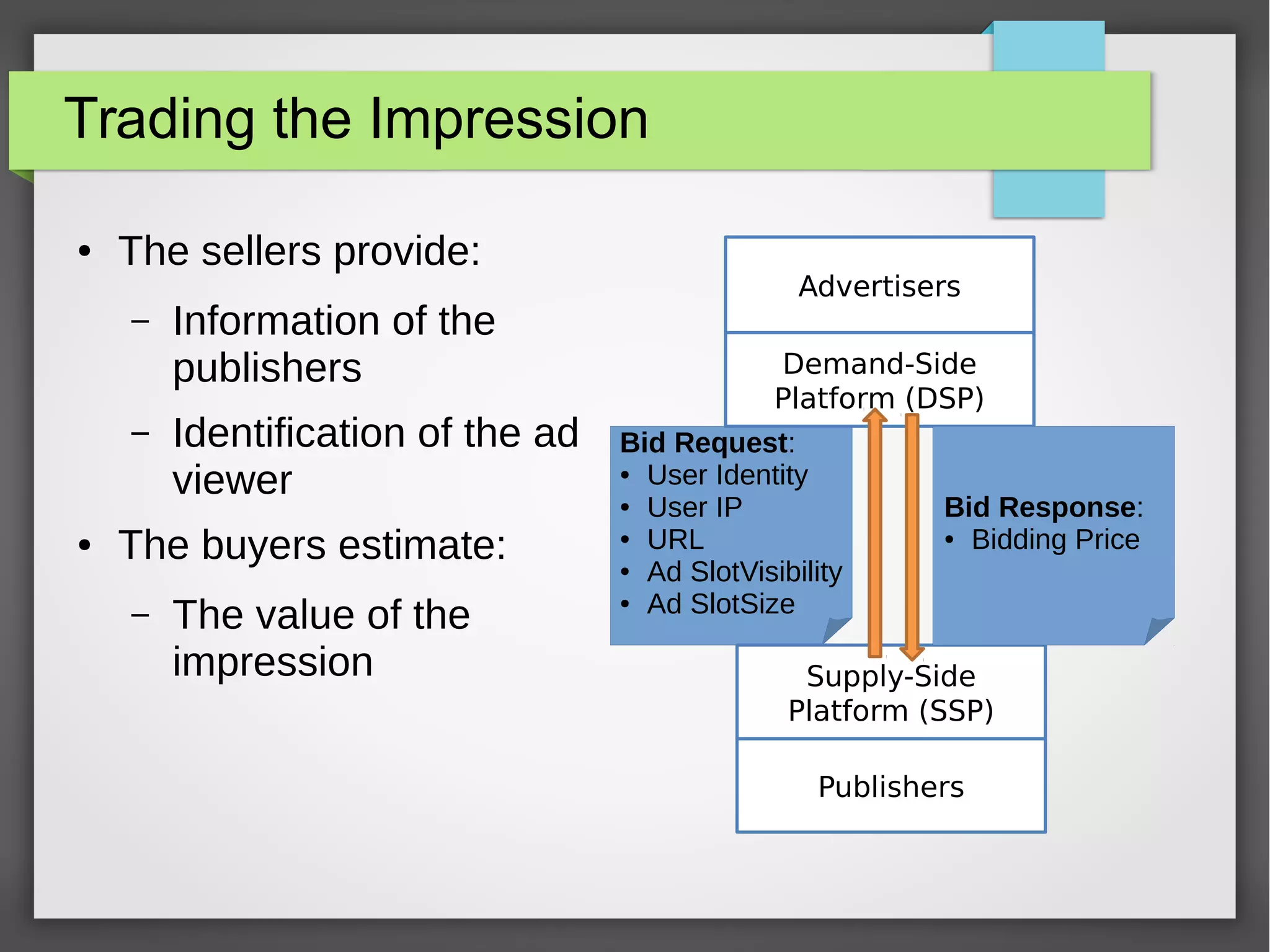
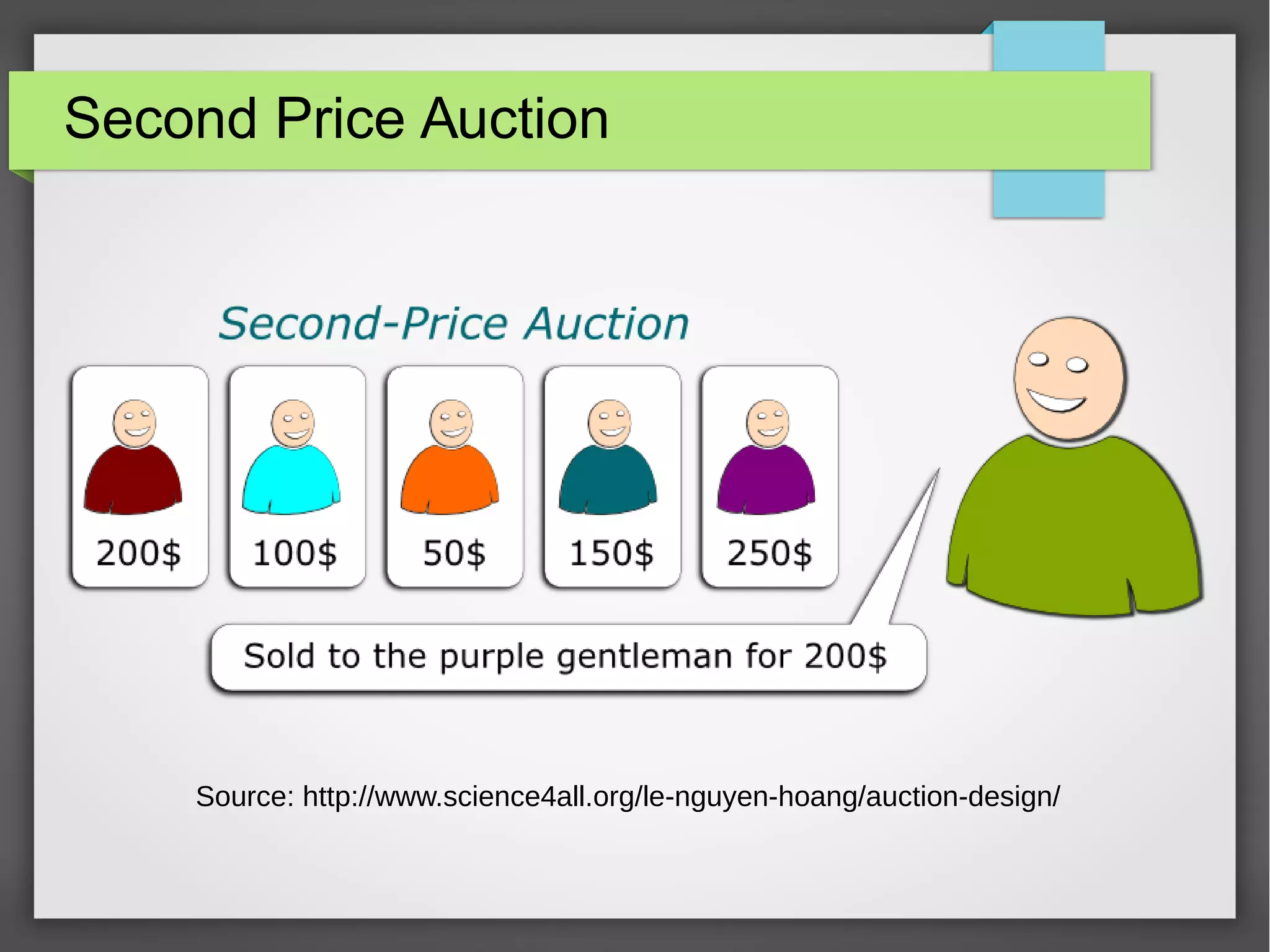
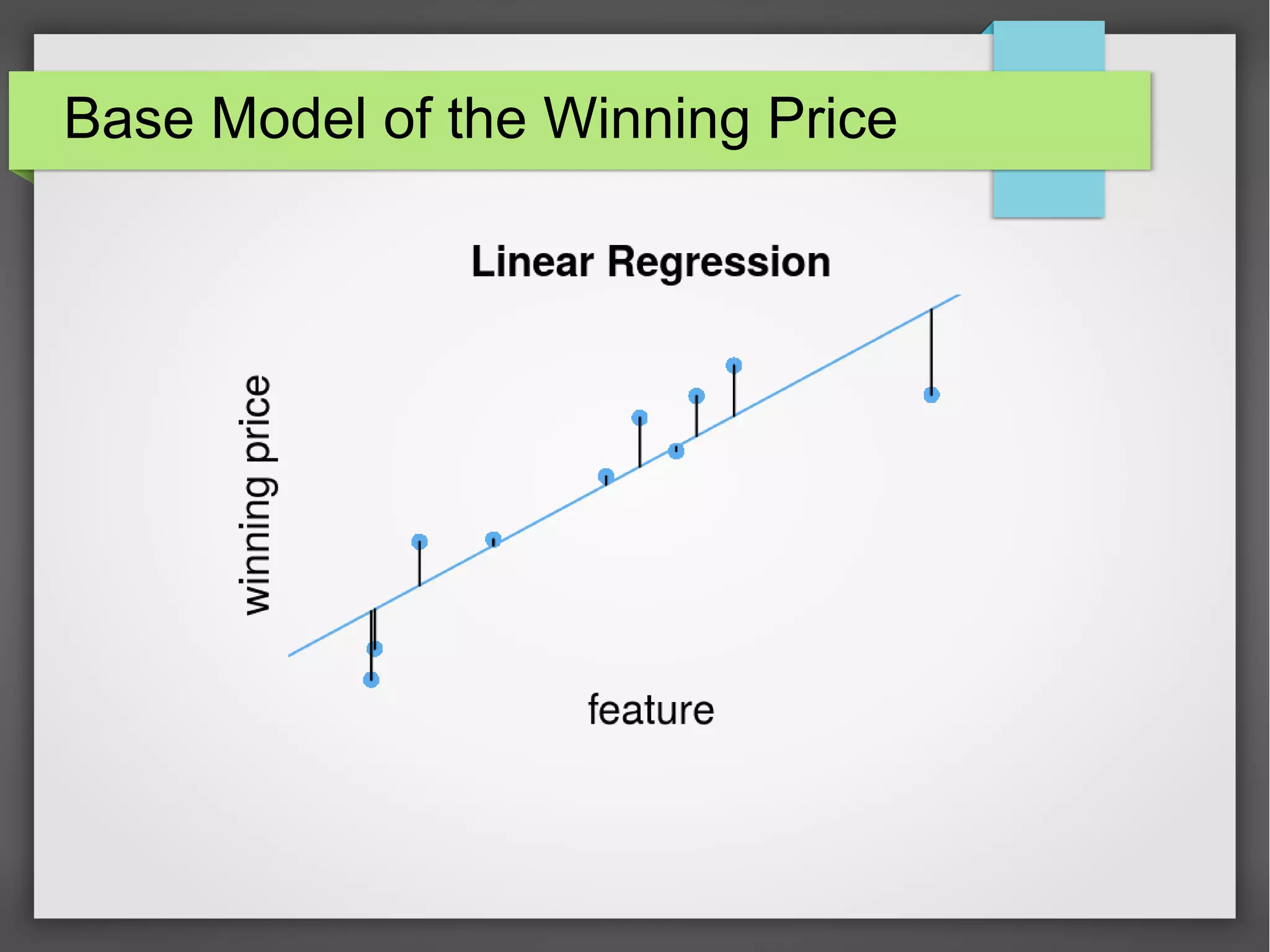
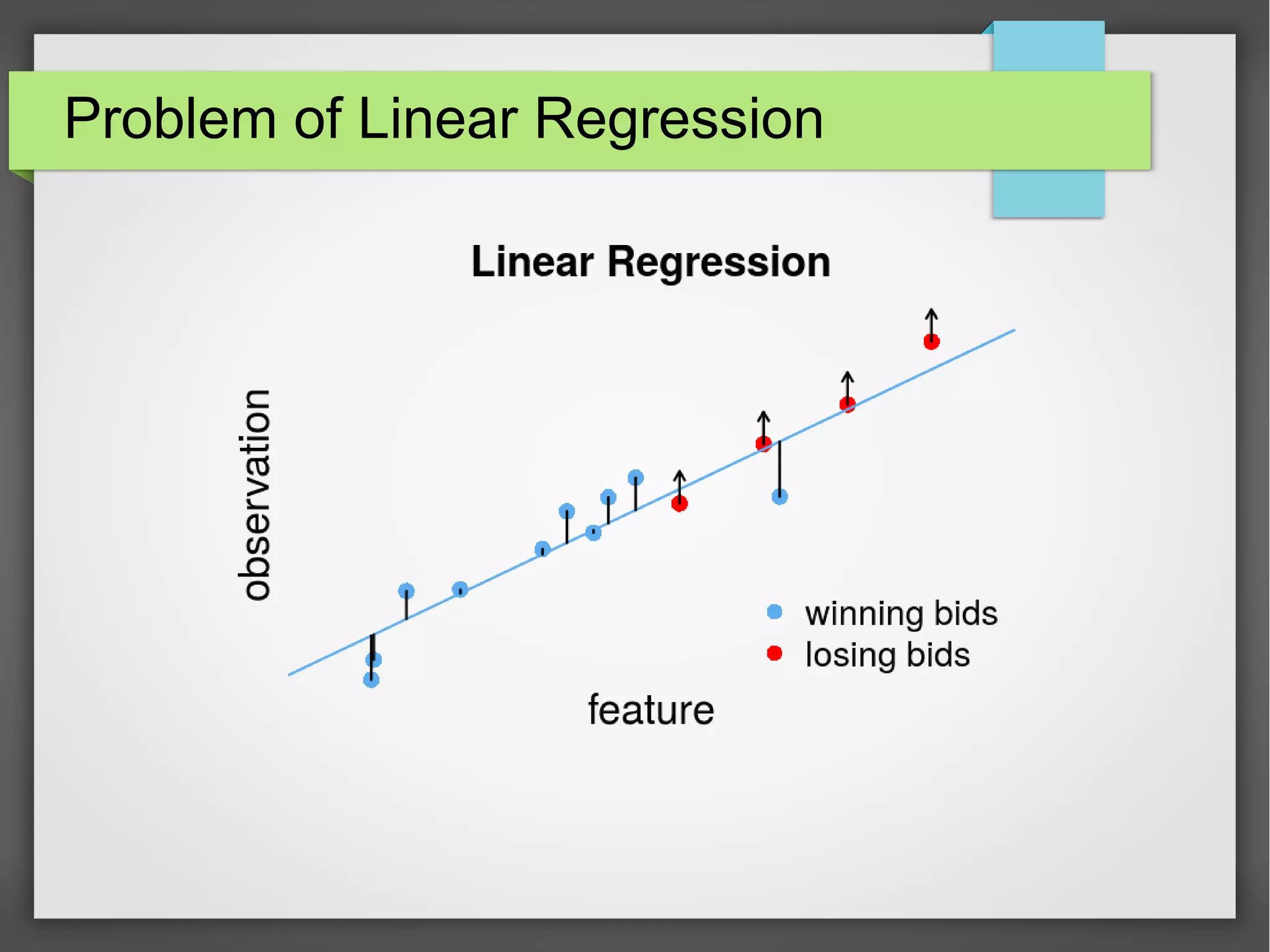
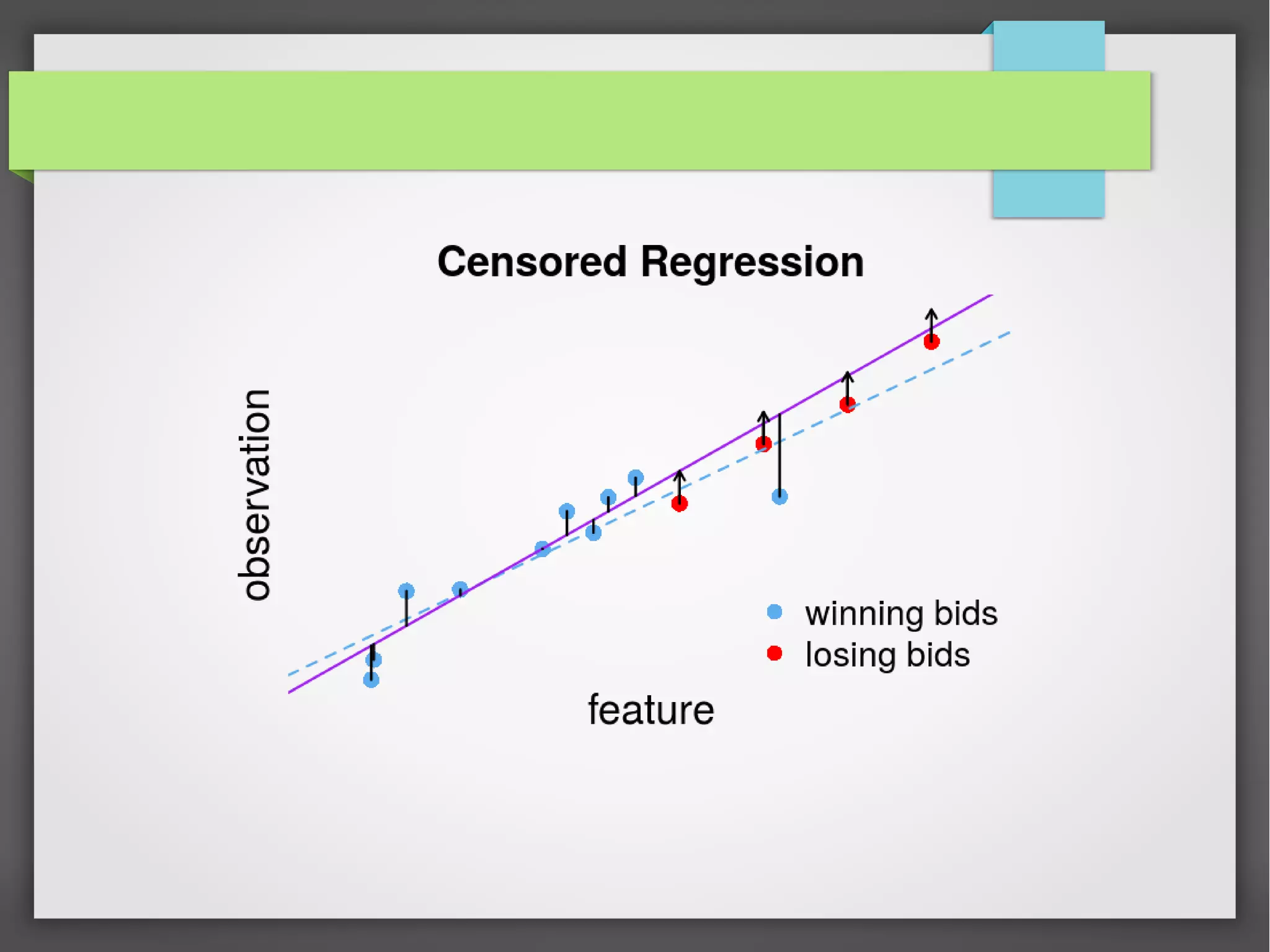
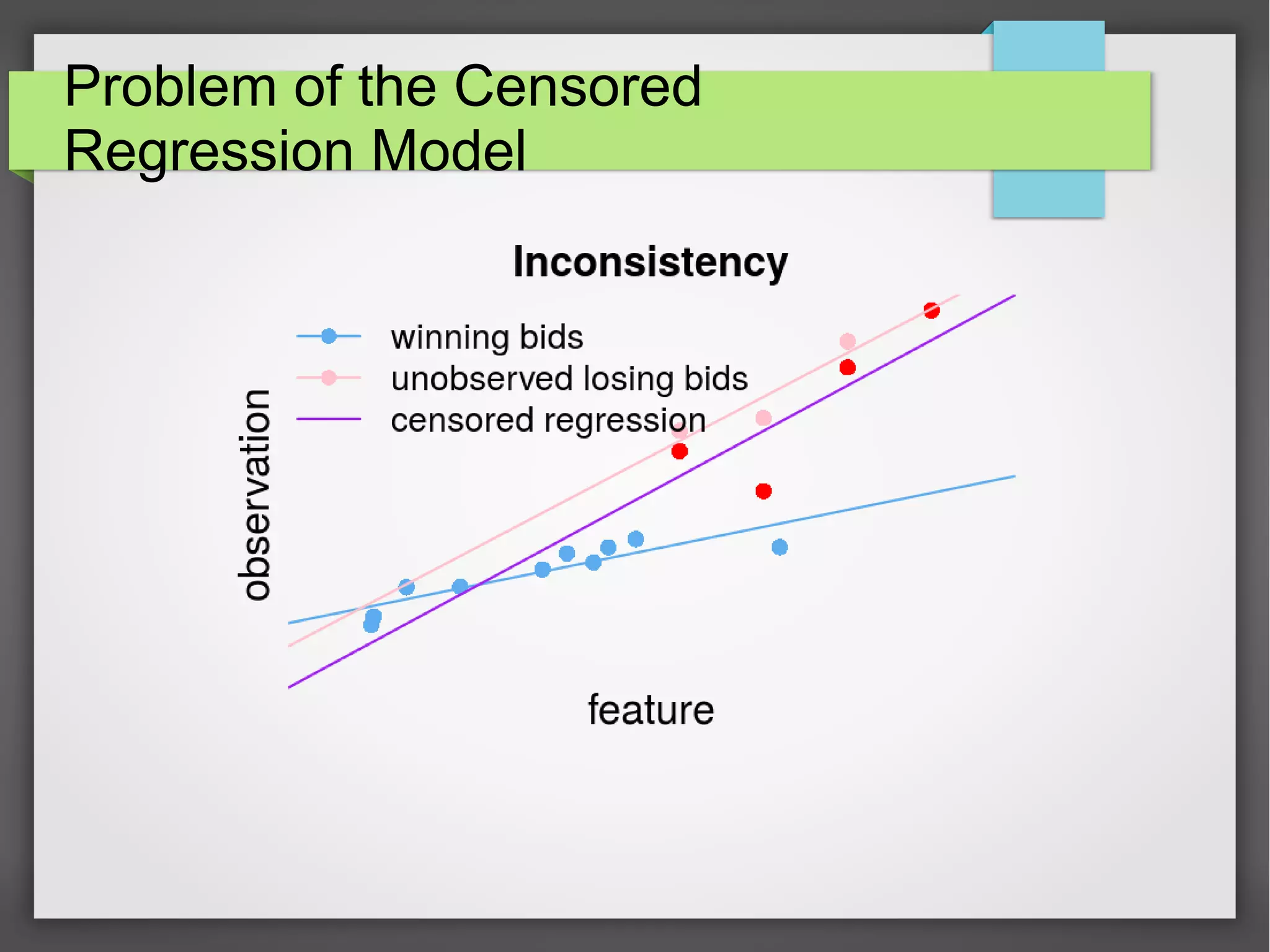
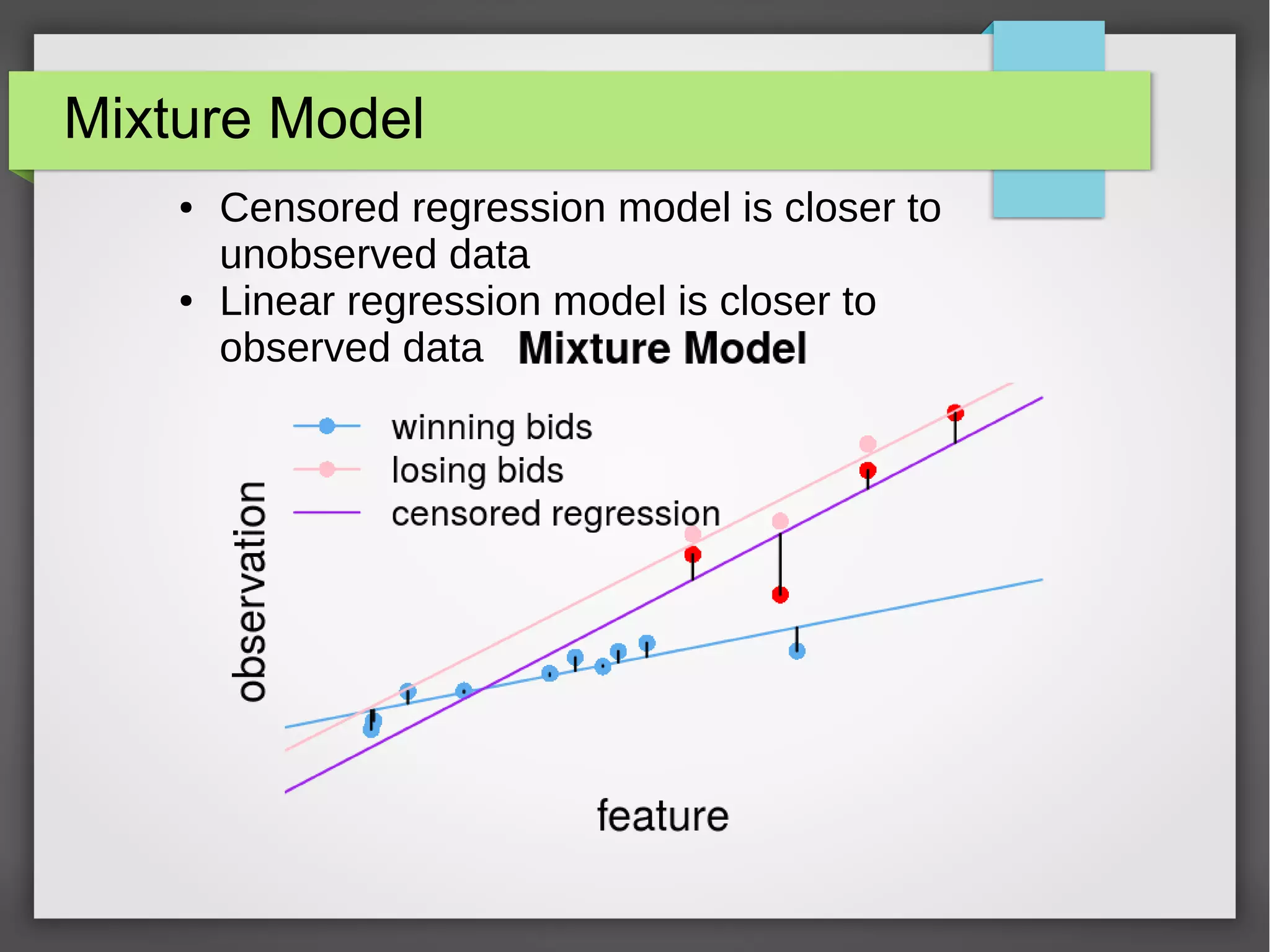
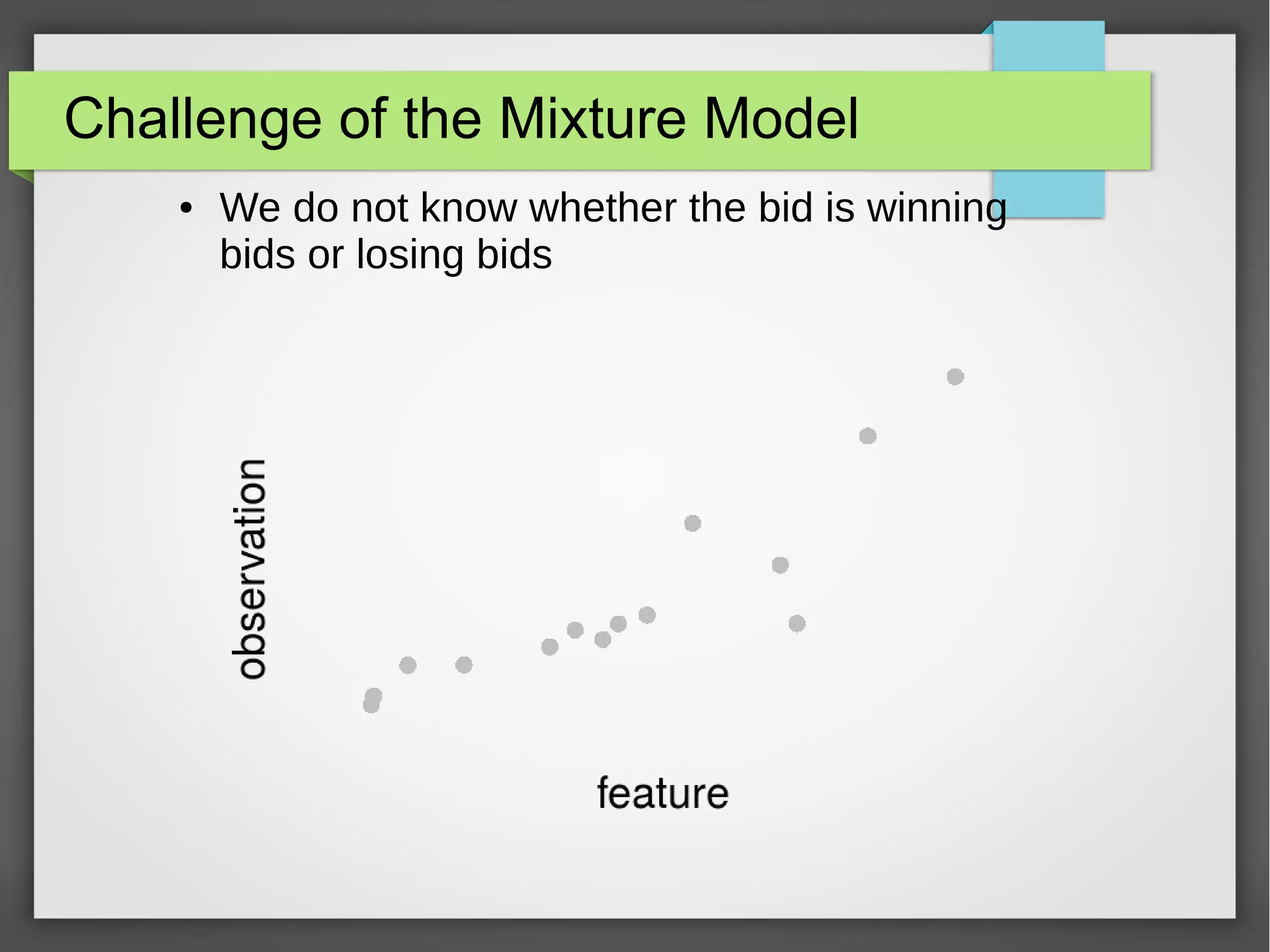
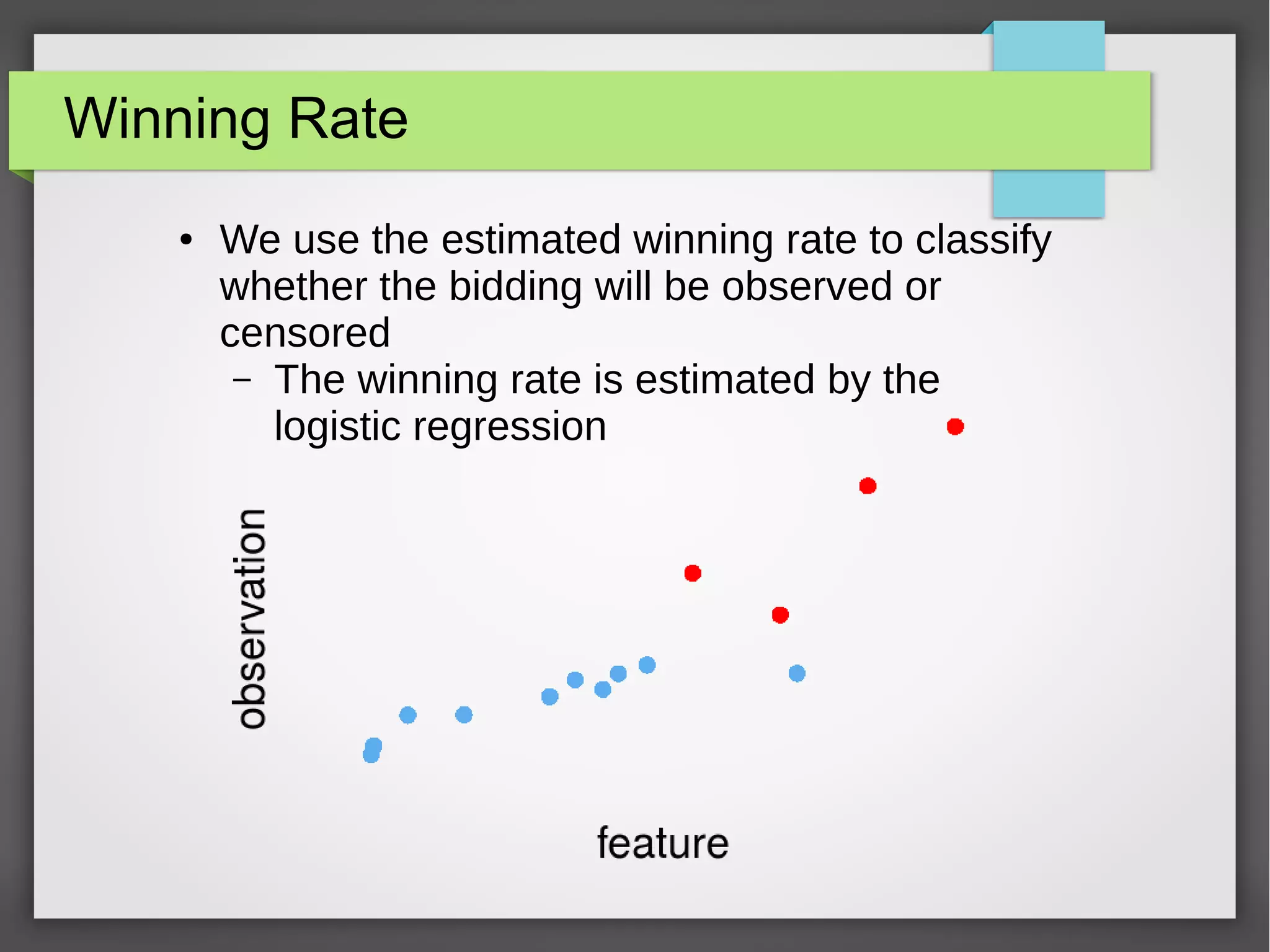
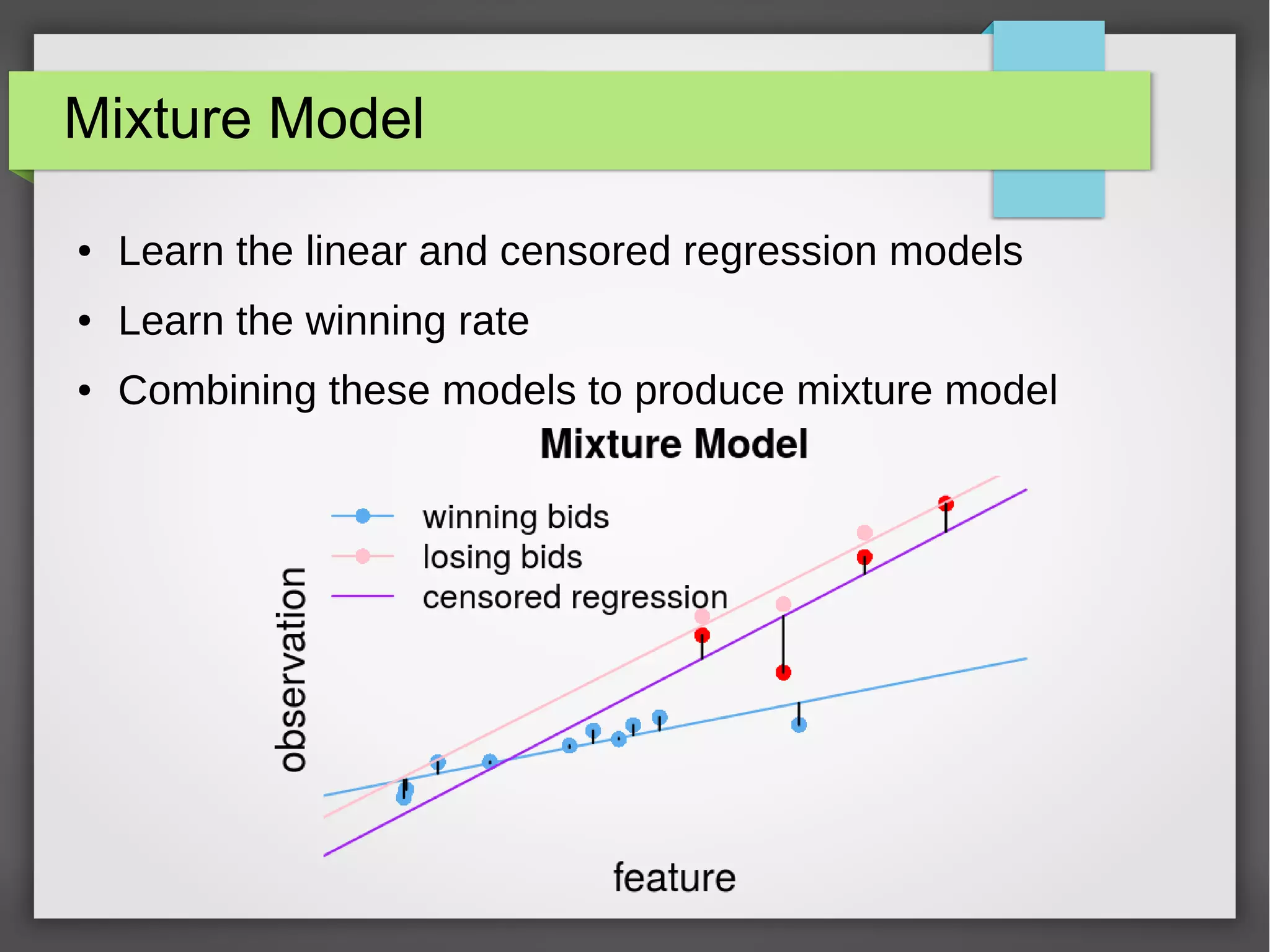
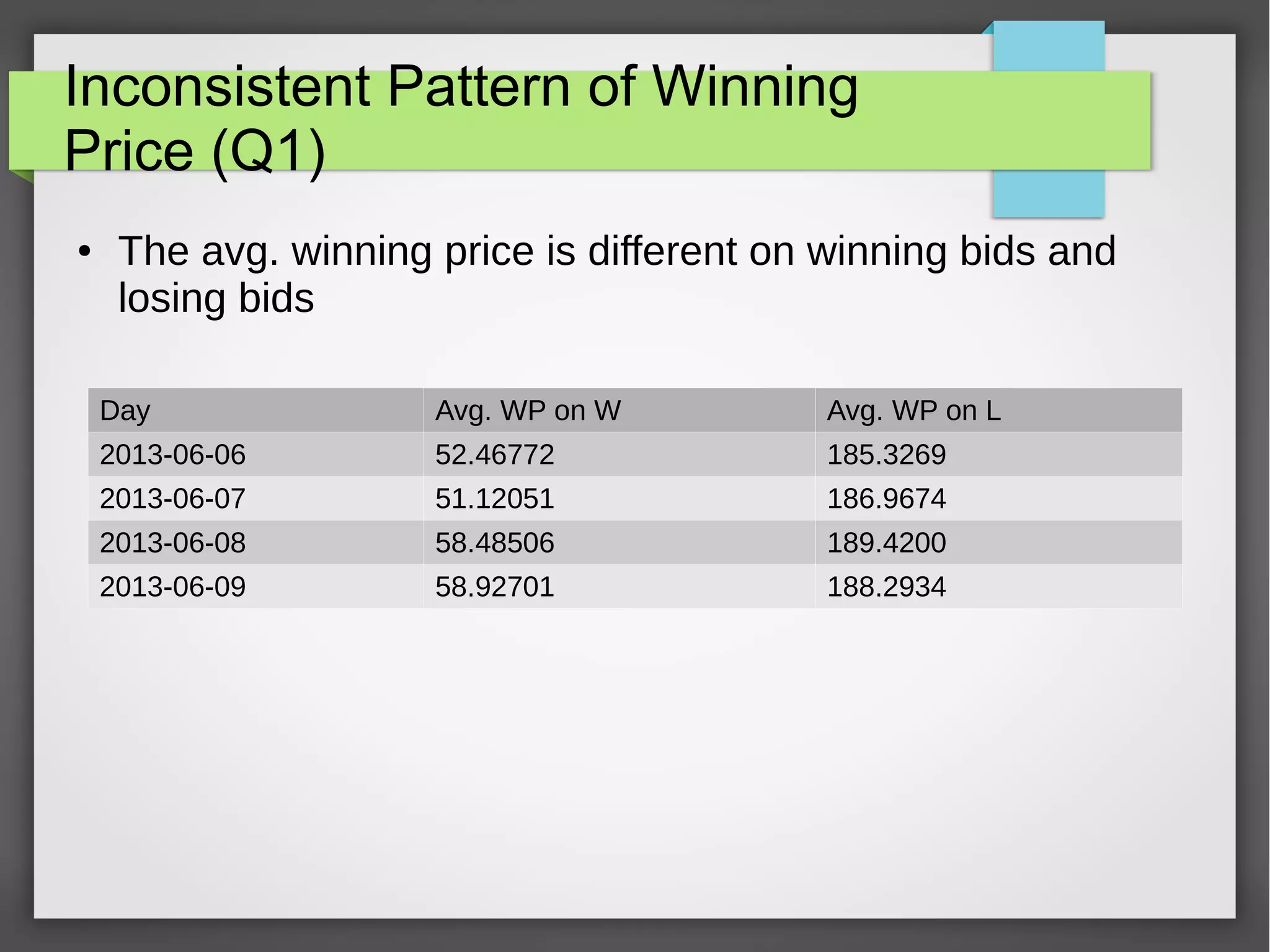
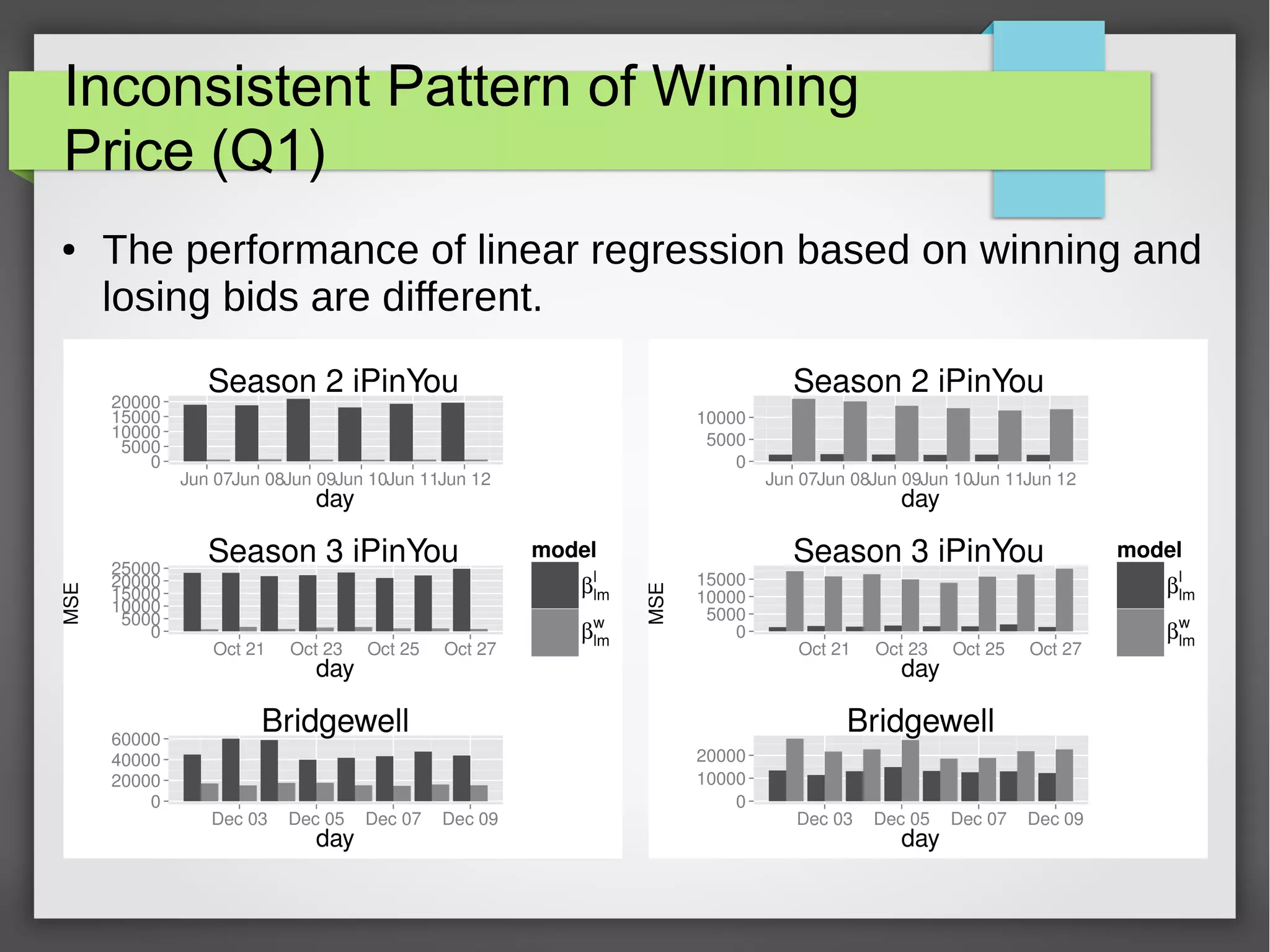
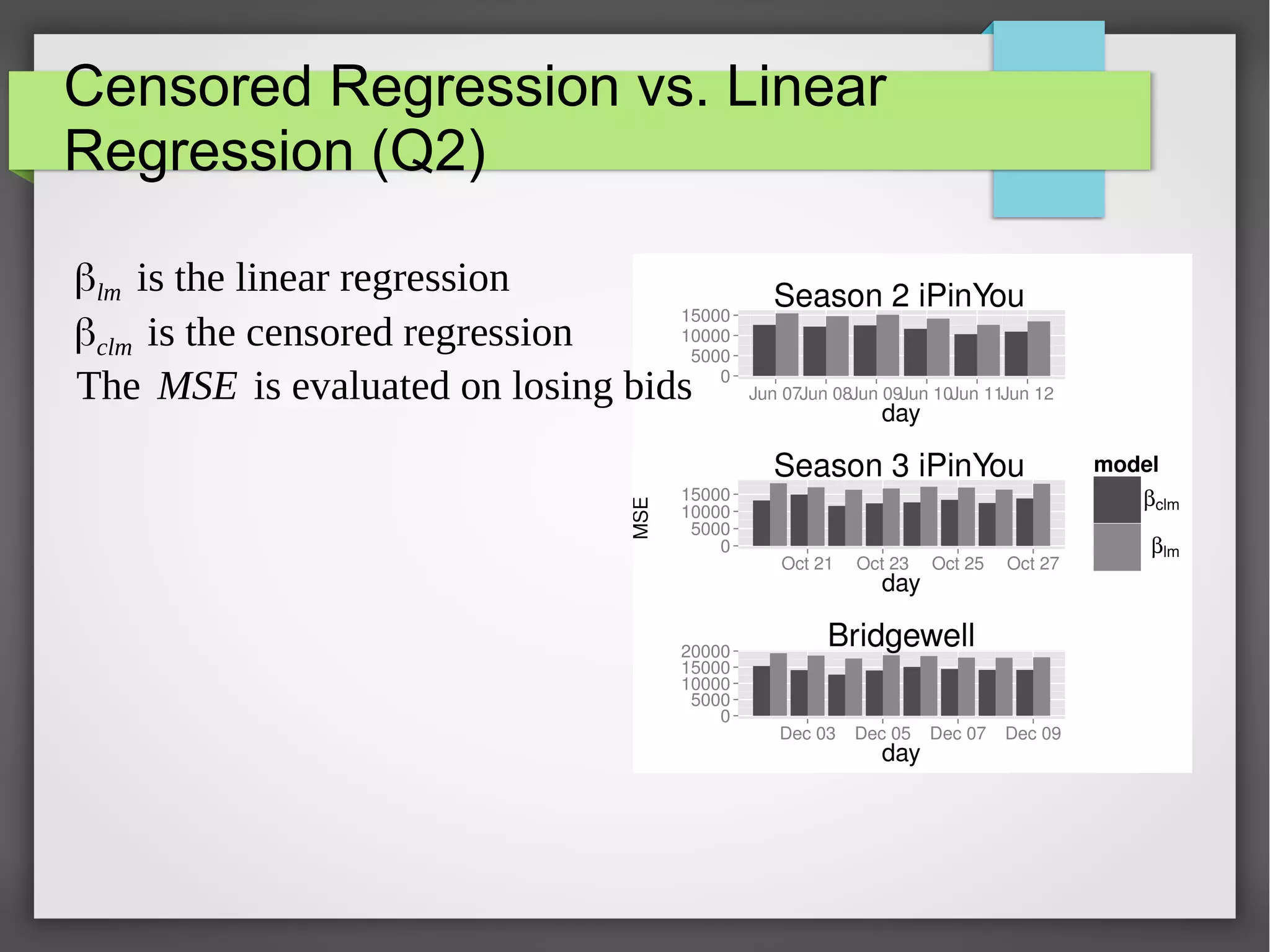
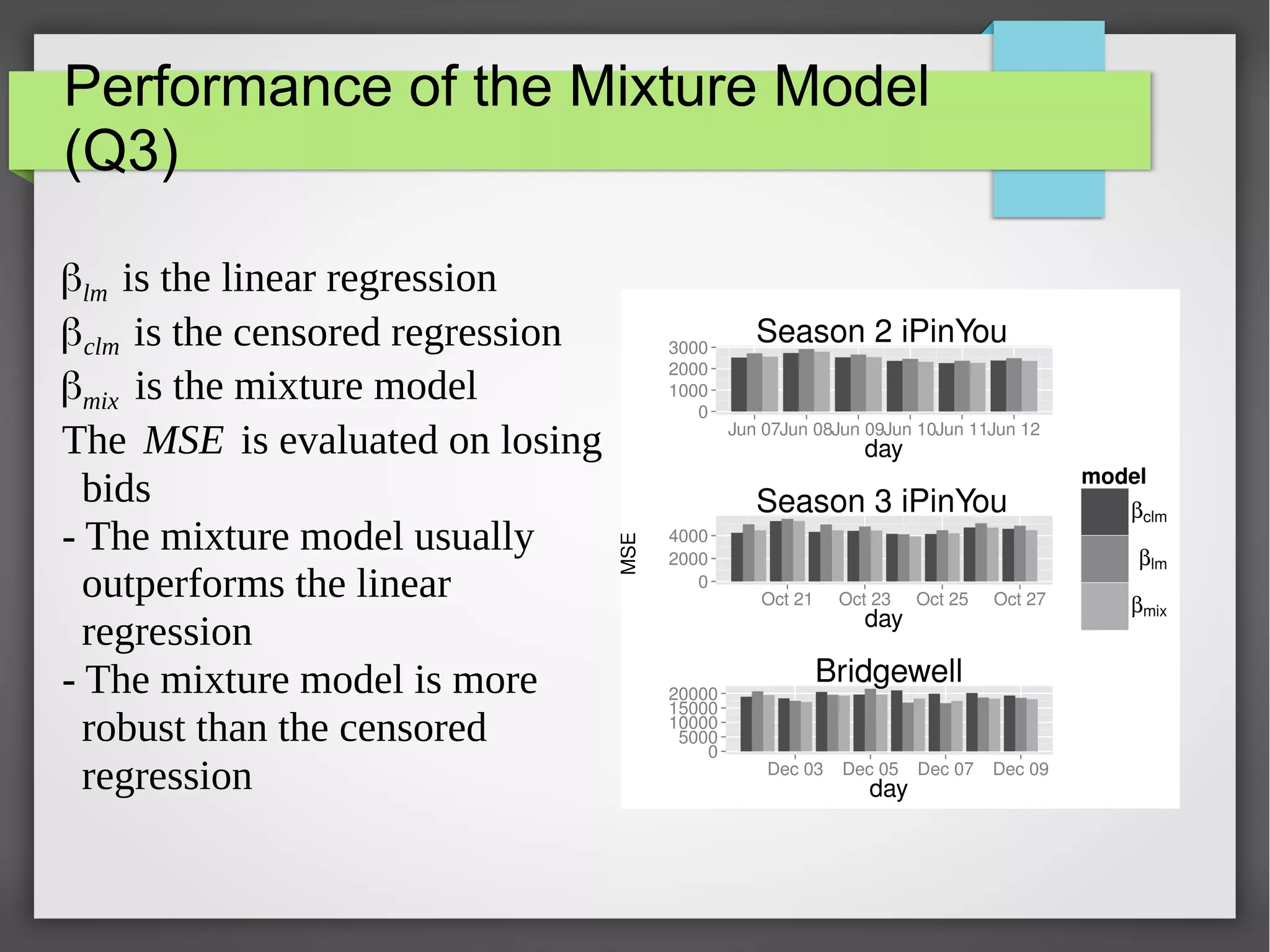
This document discusses the prediction of winning prices in real-time bidding (RTB) using censored data. It highlights the challenges of predicting winning prices due to unobservable outcomes in second price auctions and presents a combined modeling approach that utilizes censored regression and mixture models, showing improved prediction performance. The study utilizes datasets and experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed models compared to traditional linear regression techniques.