India's Tade With U.S.A
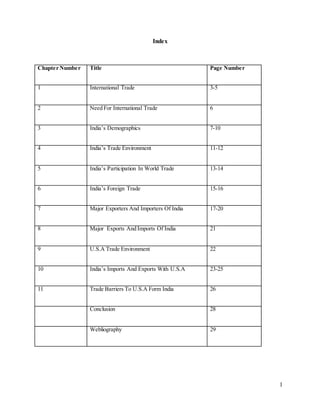
- 1. 1 Index Chapter Number Title Page Number 1 International Trade 3-5 2 Need For International Trade 6 3 India’s Demographics 7-10 4 India’s Trade Environment 11-12 5 India’s Participation In World Trade 13-14 6 India’s Foreign Trade 15-16 7 Major Exporters And Importers Of India 17-20 8 Major Exports And Imports Of India 21 9 U.S.A Trade Environment 22 10 India’s Imports And Exports With U.S.A 23-25 11 Trade Barriers To U.S.A Form India 26 Conclusion 28 Webliography 29
- 2. 2 Index of Tables Table Number Title Page Number Table 3.1: India’s demographics 7 Table 7.1 Top ten exporters to India, by value of trade in US$m 18 Table 7.2 Top ten importers from India, by value of trade in US$m 19 Index of Figures Figure Number Title Page Number Figure 5.1 India’s Imports and Exports 13 Figure 7.1 India’s Export Destinations 18 Figure 7.2 India’s Import Destinations 19 Figure 8.1 Major exports of India 20 Figure 8.2 Major Imports of India 20 Figure 10.1 India’s Exports to U.S.A 23 Figure10.2 India’s Imports from U.S.A 24
- 3. 3 Chapter 1: International trade International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). While international trade has been present throughout much of history its economic, social, and political importance has been on the rise in recent centuries. It is the presupposition of international trade that a sufficient level of geopolitical peace and stability are prevailing in order to allow for the peaceful exchange of trade and commerce to take place between nations. Industrialization, advanced in technology transportation, globalization, multinational corporations, and outsourcing are all having a major impact on the international trade system. Increasing international trade is crucial to the continuance of globalization. Without international trade, nations would be limited to the goods and services produced within their own borders. International trade is, in principle, not different from domestic trade as the motivation and the behavior of parties involved in a trade do not change fundamentally regardless of whether trade is across a border or not. The main difference is that international trade is typically more costly than domestic trade. The reason is that a border typically imposes additional costs such as tariffs, time costs due to border delays and costs associated with country differences such as language, the legal system or culture. Another difference between domestic and international trade is that factors of production such as capital and labor are typically more mobile within a country than across countries. Thus international trade is mostly restricted to trade in goods and services, and only to a lesser extent to trade in capital, labor or other factors of production. Trade in goods and services can serve as a substitute for trade in factors of production. Instead of importing a factor of production, a country can import goods that make intensive use of that factor of production and thus embody it. An example is the import of labor-intensive goods by the United States from China. Instead of importing Chinese labor, the United States imports goods that were produced with Chinese labor. One report in 2010 suggested that international trade was increased when a country hosted a network of immigrants, but the trade effect was weakened when the immigrants became assimilated into their new country.
- 4. International trade is also a branch of economics, which, together with international finance, forms the larger branch called international economics. Trading is a value-added function: it is the economic process by which a product finds its market, in which specific risks are to be borne by the trader. 4 History of International trade Any time you walk into a super market and pick up any stuff like a knife or a toy and chances are that the item has been manufactured in China or assembled in Mexico. Pick up coffee pods and you will see that they have been imported from Africa. When you shop for clothes, it is quite likely that you will see ‘Made In China’ label. We all know that international trade been in vogue for centuries and all civilizations carried on trade with other parts of the world. The need for trading exists due to the variations in availability of resources and comparative advantage. In the present context where technology and innovation in all fields have thrown open borders to globalization, no country can afford to remain isolated and be self-sufficient. International trade has a rich history starting with barter system being replaced by Mercantilism in the 16th and 17th Centuries. The 18th Century saw the shift towards liberalism. It was in this period that Adam Smith, the father of Economics wrote the famous book ‘The Wealth of Nations’ in 1776 where in he defined the importance of specialization in production and brought International trade under the said scope. David Ricardo developed the Comparative advantage principle, which stands true even today. All these economic thoughts and principles have influenced the international trade policies of each country. Though in the last few centuries, countries have entered into several pacts to move towards free trade where the countries do not impose tariffs in terms of import duties and allow trading of goods and services to go on freely. The 19th century beginning saw the move towards professionalism, which petered down by end of the century. Around 1913, the countries in the west say extensive move towards economic liberty where in quantitative restrictions were done away with and customs duties were reduced across countries. All currencies were freely convertible into Gold, which was the international
- 5. 5 monetary currency of exchange. Establishing business anywhere and finding employment was easy and one can say that trade was really free between countries around this period. The First World War changed the entire course of the world trade and countries built walls around themselves with wartime controls. Post world war, as many as five years went into dismantling of the wartime measures and getting back trade to normalcy. But then the economic recession in 1920 changed the balance of world trade again and many countries saw change of fortunes due to fluctuation of their currencies and depreciation creating economic pressures on various Governments to adopt protective mechanisms by adopting to raise customs duties and tariffs. The need to reduce the pressures of economic conditions and ease international trade between countries gave rise to the World Economic Conference in May 1927 organized by League of Nations where in the most important industrial countries participated and led to drawing up of Multilateral Trade Agreement. This was later followed with General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1947. However once again depression struck in 1930s disrupting the economies in all countries leading to rise in import duties to be able to maintain favorable balance of payments and import quotas or quantity restrictions including import prohibitions and licensing. Slowly the countries began to grow familiar to the fact that the old school of thoughts were no longer going to be practical and that they had to keep reviewing their international trade policies on continuous basis and this interns lead to all countries agreeing to be guided by the international organizations and trade agreements in terms of international trade. Today the understanding of international trade and the factors influencing global trade is much better understood. The context of global markets have been guided by the understanding and theories developed by economists based on Natural resources available with various countries which give them the comparative advantage, Economies of Scale of large scale production, technology in terms of e commerce as well as product life cycle changes in tune with advancement of technology as well as the financial market structures.
- 6. 6 Chapter 2: Need for international trade International trade is needed so that all countries can avail themselves of the things that they need (and want), and that are not available in their own country. The most common example is oil, which is needed throughout the world, but it is limited to particular areas, and so is traded internationally. International trade accounts for a huge part of a country's gross domestic product (GDP) and is a vital source of revenue for all countries, particularly those that are developing, though it is the nations that have the strongest international trade, and who have prospered by it, that have become the driving force behind world economy. It is usually accepted that the benefits of international trade, and therefore, the reasons why it is needed are: It enhances domestic competiveness; it increases sales and profits; it takes advantage of international trade technology; it extends the sales potential of existing products; it maintains cost competiveness in the domestic market; it increases the potential for business expansion; it achieves a global market share; it reduces the dependency on markets that already exist; and it stabilizes seasonal market fluctuations. International trade is no new phenomena; the Silk Route is a very famous trading route that was used to transport silk and spices in the 14th and 15th centuries. The 18th century saw Clippers, which were ships designed for speed, being used to transport all manner of things from tea from China, and spices from the Dutch East Indies. Sugar, cotton and other goods were also traded internationally to the delight of both those producing them, and those receiving them, but the most sinister trading happened in a much darker period of history: Slaves also became a commodity to be traded internationally; the very negative repercussions of which can still be seen today.
- 7. 7 Chapter 3 :India’s Demographics Table 3.1: India’s demographics Population 1,236,344,631 (July 2014 est.) Age structure 0-14 years: 28.5% (male 187,016,401/female 165,048,695) 15-24 years: 18.1% (male 118,696,540/female 105,342,764) 25-54 years: 40.6% (male 258,202,535/female 243,293,143) 55-64 years: 7% (male 43,625,668/female 43,175,111) 65 years and over: 5.8% (male 34,133,175/female 37,810,599) (2014 est.) Dependency ratios Total dependency ratio: 51.8 % youth dependency ratio: 43.6 % elderly dependency ratio: 8.1 % potential support ratio: 12.3 (2014 est.) Median age Total: 27 years male: 26.4 years female: 27.7 years (2014 est.) Population growth rate 1.25% (2014 est.) Birth rate 19.89 births/1,000 population (2014 est.) Death rate 7.35 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.) Net migration rate -0.05 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.) Urbanization urban population: 31.3% of total population (2011) rate of urbanization: 2.47% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.) Major cities - population NEW DELHI (capital) 22.654 million; Mumbai 19.744 million; Kolkata 14.402 million; Chennai 8.784 million; Bangalore 8.614 million; Hyderabad 7.837 million (2011) Sex ratio at birth: 1.12 male(s)/female 0-14 years: 1.13 male(s)/female 15-24 years: 1.13 male(s)/female 25-54 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
- 8. 8 55-64 years: 1.08 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.91 male(s)/female total population: 1.08 male(s)/female (2014 est.) Mother's mean age at first birth 19.9 (2005-06 est.) Infant mortality rate Total: 43.19 deaths/1,000 live births male: 41.9 deaths/1,000 live births female: 44.63 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.) Life expectancy at birth Total population: 67.8 years male: 66.68 years female: 69.06 years (2014 est.) Total fertility rate 2.51 children born/woman (2014 est.) Contraceptive 54.8% (2007/08) prevalence rate HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate 0.3% (2012 est.) HIV/AIDS - people LIVING WITH HIV/AIDS 2.085 million (2012 est.) HIV/AIDS - deaths 135,500 (2012 est.) Drinking water source improved: urban: 96.7% of population rural: 90.7% of population total: 92.6% of population unimproved: urban: 3.3% of population rural: 9.3% of population total: 7.4% of population (2012 est.) Sanitation facility access improved: urban: 60.2% of population
- 9. 9 rural: 24.7% of population total: 36% of population unimproved: urban: 39.8% of population rural: 75.3% of population total: 64% of population (2012 est.) Major infectious diseases degree of risk: very high food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever vector borne diseases: dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis, and malaria water contact disease: leptospirosis animal contact disease: rabies note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2013) Nationality noun: Indian(s) adjective: Indian Ethnic groups Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3% (2000) Religions Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.9%, other 1.8%, unspecified 0.1% (2001 census) Languages Hindi 41%, Bengali 8.1%, Telugu 7.2%, Marathi 7%, Tamil 5.9%, Urdu 5%, Gujarati 4.5%, Kannada 3.7%, Malayalam 3.2%, Oriya 3.2%, Punjabi 2.8%, Assamese 1.3%, Maithili 1.2%, other 5.9% note: English enjoys the status of subsidiary official language but is the most important language for national, political, and commercial communication; Hindi is the most widely spoken language and primary tongue of 41% of the people; there are 14 other official languages: Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sindhi, and Sanskrit; Hindustani is a popular variant of Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern
- 10. 10 India but is not an official language (2001 census) Literacy definition: age 15 and over can read and write total population: 62.8% male: 75.2% female: 50.8% (2006 est.) SCHOOL life expectancy (primary to tertiary education) total: 12 years male: 12 years female: 11 years (2011) Child labor - children ages 5-14 total number: 26,965,074 percentage: 12 % (2006 est.) Education expenditures 3.2% of GDP (2011) Maternal mortality rate 200 deaths/100,000 live births (2010) Children under the age of 5 years underweight 43.5% (2006) Health expenditures 3.9% of GDP (2011) PHYSICIANS density 0.65 PHYSICIANS/1,000 population (2009) HOSPITAL BED density 0.9 beds/1,000 population (2005) Obesity - adult prevalence rate 1.9% (2008) Source: www.indexmundi.com
- 11. 11 Chapter 4: India trade environment With the ever increasing globalisation, both the internal and external sectors display substantial linkages and play a vital role in promoting economic development. Macroeconomic stability in the domestic sector provide boost to external sector performance. Similarly achievements in external sector facilitate growth in domestic sector. Hence both are interrelated and effective management of external sector in terms of augmenting inflow of resources while containing exogenous shocks becomes a cardinal principle of economic governance. In totality, foreign trade can have a profound impact on the growth of an economy in terms of production, employment, technology, resource utilisation and so on. Foreign trade plays a very important role in India’s economic development since the commencement of planning. Foreign trade helps to produce those commodities which have a comparative cheaper cost than others. It results in less cost of production in producing a commodity. If all the countries adopt this procedure to produce these goods in. which they have less comparative cost, it will lead to availability of goods at a lower price. Foreign trade also increases the scope of market because of domestic demand and foreign demand for the product. So there is mass production. If the production of goods increases, average cost declines and price of goods declines. It helps the people to get different varieties of goods both in quantities terms and qualitative terms. Foreign trade helps a developing country like India in its economic development. Iron and steel industry, has been established due to stored iron-ore and coal. But for the establishment of this type industry, we have to import technical knowledge from foreign countries. Had there been no foreign trade, then it would not have been only difficult but also too expensive. Without foreign trade, it is not possible to fulfill the demand for petroleum products and it will retard the economic development of our country. There is also scarcity of consumer goods due to natural calamities or due to any other reason. During the time scarcity of consumer goods, we import these goods from foreign countries and keep prices stable which help people to get their commodities. India’s international trade policy following her independence in 1947 focused on being self sufficient, which also implied minimal reliance on international trade as a source of income. An alarming large number of people were living in abject poverty and the central government
- 12. sought to improve the well -being of people by adopting the strategy of ‘import-substituting’ industrialization. To implement this, the government developed a complex, extensive and often costly system of price controls and quantitative restrictions The most significant determinants of economic development in a country are its Foreign Trade. The foreign trade of a country consists of inward and outward movement of goods and services, which result into outflow and inflow of foreign exchange from one country to another country. During present times, International trade is a vital part of development strategy and it can be an effective instrument of economic growth, employment generation and poverty alleviation in an economy. According to Traditional Pattern of development resources are transferred from the agricultural to the manufacturing sector and then into services - sector in an economy. Foreign trade also facilitates the dissemination of technical knowledge, transmission of ideas, and import of know -how/skills, managerial talents and entrepreneurship. In addition, foreign trade encourages movement of foreign capital. In totality, foreign trade can have a profound impact on the growth of an economy in terms of production, employment, technology, resource utilization and so on. Foreign trade plays a very important role in India’s economic development since the commencement of planning. During these period lots of changes were carried out in the composition and direction of foreign trade. The present paper deals with the trends and pattern of India’s foreign trade. The paper also tries to analyze the direction and composition of India’s international trade. 12
- 13. 13 Chapter 5: India’s Participation In World Trade Figure 5.1: India’s Imports and Exports Source: www.theguardian.com There are so many countries in the world. They are in different size and shape. There are large countries with large population and small countries with small population. But there are certain features which are common in them they all are depend upon each other’s for their economic activities. The size of foreign trade and its volume both have increased during pre and post reform period. However, this increase in foreign trade is not satisfactory as India’s share in total foreign trade of the world has rem ained low. India’s share in the total world trade was 1.78 per cent in 1950; it came down to 0.6 percent in 1995. Since 1970, this share has remained
- 14. around 0.6%, which clearly indicates that India has failed to increase its share in the total world trade. India’s share in global exports and imports were also declined since independence. Its share in export was 1.78 percent in 1950 which came down to 0.7 per cent in 2000. Their shares in import were 1.71 per cent in 1950 rising fast since 2004, reached 1.3 per cent in 2009 and 1.5 per cent in 2010. It increased to 1.66 per cent in the 2011, mainly due to the relatively higher Indian export growth of 55 per cent compar ed to the 23.1 per cent export growth of the world. Also, India’s share in global imports increased from 0.8 per cent in 2000 to 2.2 per cent in 2010. Its ranking in the leading exporters improved from 31 in 2000 to 20 in 2010 and in leading importers from 26 to 13 during same period 14
- 15. 15 Chapter 6: India’s Foreign Trade India's foreign trade continuously increased. It has show the position of export and Import of Indian economy. The size or magnitude of India’s foreign trade in rupee terms (export and import) has been rising considerably since 1950-51. For the period of 1950-51 to 1960-61, India’s total value of foreign trade in terms of rupee rose by 45.3 percent. It rose by 69.7 percent during 1960 -61 to 1970-71, by 391.0 percent during 1970-71 to 1980-81. Over the period of six decades India’s export increased by several times. During the first and the second five year plans exports remained almost stagnant around Rs. 600 crores on average. An upward trend was observed during Third Plan as a result of the adoption of various export promotion measures. The export received a further boost after the devaluation of June 1966. The annual average growth rate of export for the period of 1960-70 was a meagre 3.6 percent. The export increased significantly in 1970s. The sixth plan achieved an annual growth rate of 13.0 percent and the Seventh plan 19.8 percent. During the Eight Plan export grew by 26.8 percent. As a result of the introduction of New Economic Policy in 1991, the percentage growth rate of export was 35.3 in 1991-92, 28.6 percent in 1995-96, 27.6 in 2000-01, and 26.1 percent in 2005-06 and again rises to 35.1 percent in 2010-11. As against the modest growth in exports, imports have been increasing at higher rate. Imports play a critical role in Indian economy. In 1950-51 total merchandise imports were valued at Rs.608 crores which increase to Rs. 1122 crores in 1960-61, 1634 in 1970-71, further Rs.12549 crores in 1980-81 and Rs. 43198 crores in 1990-91. in post reform period it has increased from Rs. 47851 crores 1991 -92 to Rs.230872 crores in 2000-01 and further to Rs. 1683467 crores in 2010-11. The volume of trade balance of India has remained always negative (i.e. Due to the volume of imports exceeds the volume of exports) expect for only two years trade balance of India has remained positive i.e. is in the year 1972-73 and 1976-77. The volume of trade balance was Rs -2 crores in 1950-51, and it was increased up to Rs.-169 crores in 1969-70, however there is a continuously increase in the negative volume of trade balance in pre-reform period it was Rs.-7670 crores in1989-90, and in post reform period it has increased up toRs.-27301 crores
- 16. in 2000-01 and in the year 2010-11 further to Rs.-540545 crores. This had adversely affected the balance of payments and foreign exchange position of the country. 16
- 17. 17 Chapter 7: Major Exporter and Importer of India The directional pattern of India’s trade has been changing constantly. There has been significant change in market area of India's trade. Region-wise, while India's exports to Europe and America have declined, its exports to Asia and Africa have increased. Share of major destinations of India’s Exports and sources of Imports during 2012-13 (April– January) are given in table 5 & table 6 respectively. During the period 2012-13 (April–January), the share of Asia comprising of East Asia, ASEAN, West Asia, Other West Asia, North East Asia and South Asia accounted for 50.78 per cent of India’s total exports in US $ terms. The share of Europe and America in India’s exports stood at 18.88 per cent and 18.77 per cent respectively of which EU During the countries (27) comprises 16.99 per cent. During the period, USA (12.89 per cent) has been the most important country of export destination followed by UAE (12.20 per cent), Singapore (4.79 percent), China (4.59 per cent) and Hong Kong (3.95 per cent).Asia accounted for 60.08 per cent of India’s total imports during the period followed by Europe (17.39 per cent) and America (11.64 per cent). Among individual countries the share of China stood highest at (11.21 per cent) followed by UAE (7.67 per cent), Saudi Arabia (6.78 per cent), Switzerland (6.01 per cent) and USA (5.00 per cent).
- 18. 18 Figure 7.1: India’s Export Destinations Source : atlas.media.mit.edu Table 7 .1 :Top ten exporters to India, by value of trade in US$m Country ▾ 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) USA 12208.05 5.19 UAE 19622.81 8.35 Switzerland 10779.45 4.59 Saudi 16094.83 6.85 Arabia Qatar 8144.45 3.47 Kuwait 8134.73 3.46 Iraq 9803.79 4.17 Indonesia 6944.86 2.95 Germany 7154.41 3.04 China 28025.57 11.92 Source: http://www.theguardian.com/
- 19. 19 Figure 7.2: India’s Import Destinations Source : atlas.media.mit.edu Table 7.2: Top ten importers from India, by value of trade in US$m Country 2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) %Share (2012-2013 (Apr- Sep) USA 19704.05 13.87 UAE 18601.71 13.09 Singapore 6652.77 4.68 China 6417.32 4.52 Hong Kong 6137.9 4.32 Saudi Arab 4636.29 3.26 Netherlands 4458.24 3.14 U K 4112.26 2.89 Germany 3491.77 2.46 Brazil 3042.64 2.14 Source: http://www.theguardian.com
- 20. 20 Chapter 8 : Major Exports and Imports of India Major exports of India India's export basket has been changing over the years. While the share of primary products in India's exports fell over the years from 16 per cent in 2000-01, in 2012-13 (April-November) it regained the share of 16 per cent mainly due to the export of agricultural items like rice and guar gum meal. The share of manufacturing exports fell drastically from 78.8 per cent in 2000-01 to 66.1 per cent in 2011-12 and further to 64.5 per cent in 2012-13(April-November) mainly due to the fall in shares of traditional items like textiles and leather and leather manufactures even though the share of engineering goods and chemicals and related products increased. Share of gems and jewellery fell marginally. Share of petroleum, crude & products exports, which also include refined items, increased from 4.3 per cent in 2000-1 to 18.3 per cent in 2011-12 and 18.6 per cent in 2012-13(April-November). The share of top five Principal Commodity Groups in India’s total exports during 2012-13 (April January) are Petroleum (20.2%), Gems & Jewellery (14.4%), Transport Equipment’s (6.1%), Machinery and Instruments (5.1%) and Drugs, Pharmaceuticals & Fine Chemicals (5%). Figure 8.1 Major exports of India Source : atlas.media.mit.edu
- 21. 21 Major Imports of India In case of imports, there are no major compositional changes other than the sudden rise in share of gold and silver imports from 9.3 per cent in 2000-01 to 12.6 per cent in2011-12 with a high import growth rate of 44.5 per cent. The share of pearls, precious, and semiprecious stones decreased from 9.6 per cent in 2000-01 to 6.1 per cent in the 2011-12 following a negative growth of -13.3 per cent and further to 4.1 per cent in 2012-13 (April- November), with a high negative growth rate of - 32.3 per cent. Another important development is related to the share of capital goods imports which increased from 10.5 per cent in 2000 -1 to 13.6 per cent in 2010- 11 and further to 14.1 per cent in 2011-12, declining thereafter to 11.9 per cent in 2012- 13 (April-November) following a negative growth rate of - 6.5 per cent. Imports of the top five commodities during the period 2012 -13 (April-January) registered a share of 61.8 per cent mainly due to significant imports of Petroleum (Crude & Products), Gold, Electronic Go ods, Machinery except electrical and electronic and Pearls, precious and semi-precious stones. The share of top five Principal Commodity in India’s total imports during 2012- 13 (April– January) Figure 8.2: Major Imports of India Source : atlas.media.mit.edu
- 22. 22 Chapter 9: U.S.A trade environment The United States is the world's largest country exporter of goods and services. In 2008, U.S. exports totaled $1.84 trillion and accounted for 13 percent of gross national product. The U.S. imported $2.5 trillion in goods and services in 2008, with that figure reflecting in part high volumes and prices of imported petroleum. The products traded by the United States and the trade related codes of conduct incorporated into trade agreements cover a wide swath of the U.S. economy, touching in one way or another on most Americans. Over one trillion dollars of U.S. goods exports are manufactured products, by far the largest segment of U.S. goods and services exports. Approximately one quarter of these exports are classified as advanced technology products. Agricultural products are also a part of goods trade and totaled $118 billion in 2008. Petroleum, likewise part of goods trade, plays a relatively modest role in U.S. exports ($67 billion), while looming large in U.S. imports ($453 billion). As in goods, the United States is also a competitive exporter of services, with U.S. cross-border export of services valued at $544 billion, greater than U.S. imports ($405 billion) of services. While the United States receives substantial earnings from the export of travel, passenger fares and other transportation services, and royalties and other license fees, the largest U.S. services export category is other private services, accounting for nearly half of U.S. private service exports in 2008. Among the more prominent commitments and trade-related codes of conduct are undertakings in the areas of trade and labor, trade and the environment, trade and intellectual property rights (TRIPS), and trade and investment (TRIMS). Trade and U.S. trade agreements thus affect Americans in our many guises, as consumers, as workers - both unionized and non-unionized, as families, and as manufacturers, farmers, ranchers and services providers of everything from education, to insurance, to industrial engineering, to telecommunications, to computer and information to film and television programming, and to medical services.
- 23. 23 Chapter 10: India’s Imports and Exports with U.S.A India’s Exports to U.S.A Figure 10.1: India’s Exports to U.S.A Source : atlas.media.mit.edu 1) Packaged medicaments 2) Valves 3) Refined petroleum 4) House linens 5) Iron pipe fittings 6) Rubber tires 7) Crustaceans 8) Vegetable saps 9) Jewellery 10) Vehicle parts
- 24. 24 11) Mattresses 12) Prcessed fruits and nuts 13) Bathroom ceramics 14) Trunks and cases 15) Leather footwear 16) Stearic acid 17) Utility meterswood articles 18) Parper notebooks 19) Thermostats 20) Cellulose fiber paper India’s Imports from U.S.A Figure 10.2: India’s Imports from U.S.A Source : atlas.media.mit.edu 1) Gold 2) Coal briquettes 3) Scrap iron
- 25. 25 4) Measuring instruments 5) Vehicle and aircraft parts 6) Recovered pare 7) Other nuts 8) Clothing 9) Sawn wood 10) Hides 11) Paintings 12) Eggs 13) Military weapons 14) Chemical products 15) Edible prepaprations 16) Nuts and fruits
- 26. 26 Chapter 11: Trade barriers to U.S.A from India Despite India's ongoing economic reform efforts,US exporters continue to encounter tariff and non-tariff barriers that impede imports of Americans products to India, an official report has said. In its report 2012 National Trade Estimate Report on Foreign Trade Barriers, the US trade Representatives (USTR) yesterday said the US has actively sought bilateral and multilateral opportunities to open India's market. The structure of India's customs tariff and fees system is complex and characterised by a lack of transparency in determining net effective rates of customs tariff, excise duty and other duties and charges on imports into India," said the India section of the report. US goods trade deficit with India was $ 14.5 billion in 2011, up $ 4.3 billion from 2010, it said. US goods exports in 2011 were $ 21.6 billion, up 12.4 per cent from the previous year. Corresponding US imports from India were $ 36.2 billion, up 22.5 per cent. Noting that India is currently the 17th largest export market for US goods, the report said US exports of private commercial services (excluding military and government) to India were $ 10.3 billion in 2010 (latest data available), and US imports were $ 13.7 billion. Sales of services in India by majority US-owned affiliates were $ 13.1 billion in 2009 (latest data available), while sales of services in the US by majority India-owned firms were $ 7.2 billion. The stock of US foreign direct investment (FDI) in India was $ 27.1 billion in 2010, up from $ 20.9 billion in 2009, it said adding, that US FDI in India is led by the information, professional, scientific, and technical services, and manufacturing sectors. In its report, USTR said India' procurement practices and procedures are often not transparent. Foreign firms also rarely win Indian government contracts due to the preference afforded to Indian state-owned enterprises and the prevalence of such enterprises. USTR said India's tax exemption for profits from export earnings has been completely phased out, but tax holidays continue for certain export-oriented enterprises and exporters in Special Economic Zones.
- 27. "In addition to these programmes, India continues to maintain several other export subsidy programmes, including duty drawback programmes that appear to allow for drawback in excess of duties levied on imported inputs," it said, adding that India also provides pre-shipment and post-shipment financing to exporters at a preferential rate. 27
- 28. 28 Conclusion The pre-reform period did not see much of structural changes in the foreign trade particularly, the export sector. However, there have been some significant changes in Import, specifically high imports of petroleum products and machinery and equipment. In the post-reform period India’s trade has increased significantly because of LPG. India’s trade balance is always negative because of volume of imports are greater than exports, so the government should frame such policy which boost the volume of exports, ultimately it helps to transform negative trade balance into positive trade balance. The volume of imports was always remained high, so it is necessary to curtail the imports of un necessary goods and luxurious goods, which in turn help to maintain positive trade balance. The Government of India must frame such policies which induces the promotions of exports from all the sectors of the economy. To bring the country’s export back on the growth path the Government announced trade policy for 2009-14 in August 2009. It has set the target of export growth at 15 percent for the first two years and at 25 percent per annum in the last three years. It has been targeted to achieve an export figure of $200billion in 2010 -11 as against $168 billion in2008- 09. By 2014, it is expected to double India’s export of goods and services. India’s share in global trade and services is 1.64 percent at present. Aim of the policy is to raise this share to 3.28 percent by 2020.
- 29. 29 Webliography http://atlas.media.mit.edu/ http://www.theguardian.com/ http://www.indexmundi.com/india/demographics_profile.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_trade