Redox
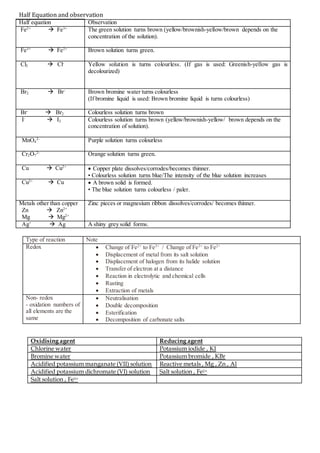
- 1. Half Equation and observation Half equation Observation Fe2+ Fe3+ The green solution turns brown (yellow/brownish-yellow/brown depends on the concentration of the solution). Fe3+ Fe2+ Brown solution turns green. Cl2 Cl- Yellow solution is turns colourless. (If gas is used: Greenish-yellow gas is decolourized) Br2 Br- Brown bromine water turns colourless (If bromine liquid is used: Brown bromine liquid is turns colourless) Br- Br2 Colourless solution turns brown I- I2 Colourless solution turns brown (yellow/brownish-yellow/ brown depends on the concentration of solution). MnO4 2- Purple solution turns colourless Cr2O7 2- Orange solution turns green. Cu Cu2+ Copper plate dissolves/corrodes/becomes thinner. • Colourless solution turns blue/The intensity of the blue solution increases Cu2+ Cu A brown solid is formed. • The blue solution turns colourless / paler. Metals other than copper Zn Zn2+ Mg Mg2+ Zinc pieces or magnesium ribbon dissolves/corrodes/ becomes thinner. Ag+ Ag A shiny grey solid forms. Type of reaction Note Redox Change of Fe2+ to Fe3+ / Change of Fe3+ to Fe2+ Displacement of metal from its salt solution Displacement of halogen from its halide solution Transfer of electron at a distance Reaction in electrolytic and chemical cells Rusting Extraction of metals Non- redox - oxidation numbers of all elements are the same Neutralisation Double decomposition Esterification Decomposition of carbonate salts Oxidising agent Reducing agent Chlorine water Potassium iodide , KI Bromine water Potassium bromide , KBr Acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution Reactive metals , Mg , Zn , Al Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution Salt solution , Fe2+ Salt solution , Fe3+
