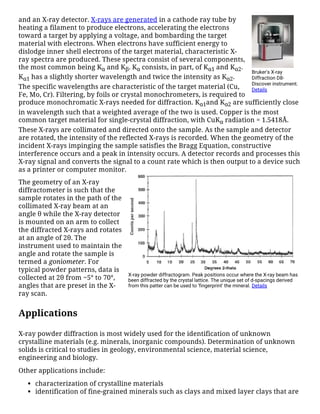
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) is a technique used to identify crystalline materials by analyzing the scattering pattern of monochromatic X-rays through a powdered sample. XRD works by generating X-rays that interact with the sample, producing constructive interference when conditions satisfy Bragg's law. This diffraction pattern is unique to each mineral and can be used for identification. XRD has various applications including phase identification, determination of unit cell dimensions, and characterization of materials. It provides a rapid and accurate method for mineral identification but requires access to reference patterns for comparison.