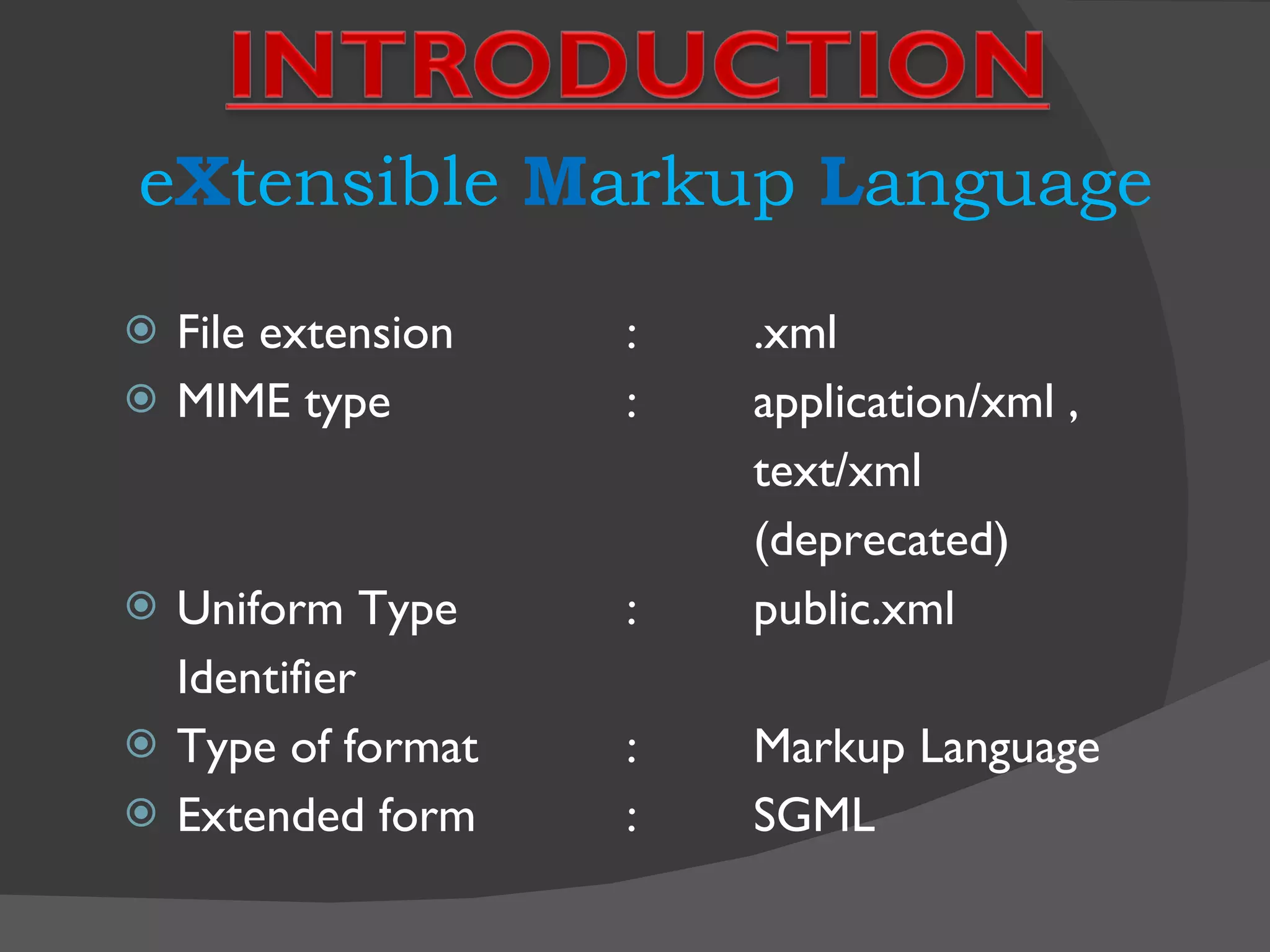
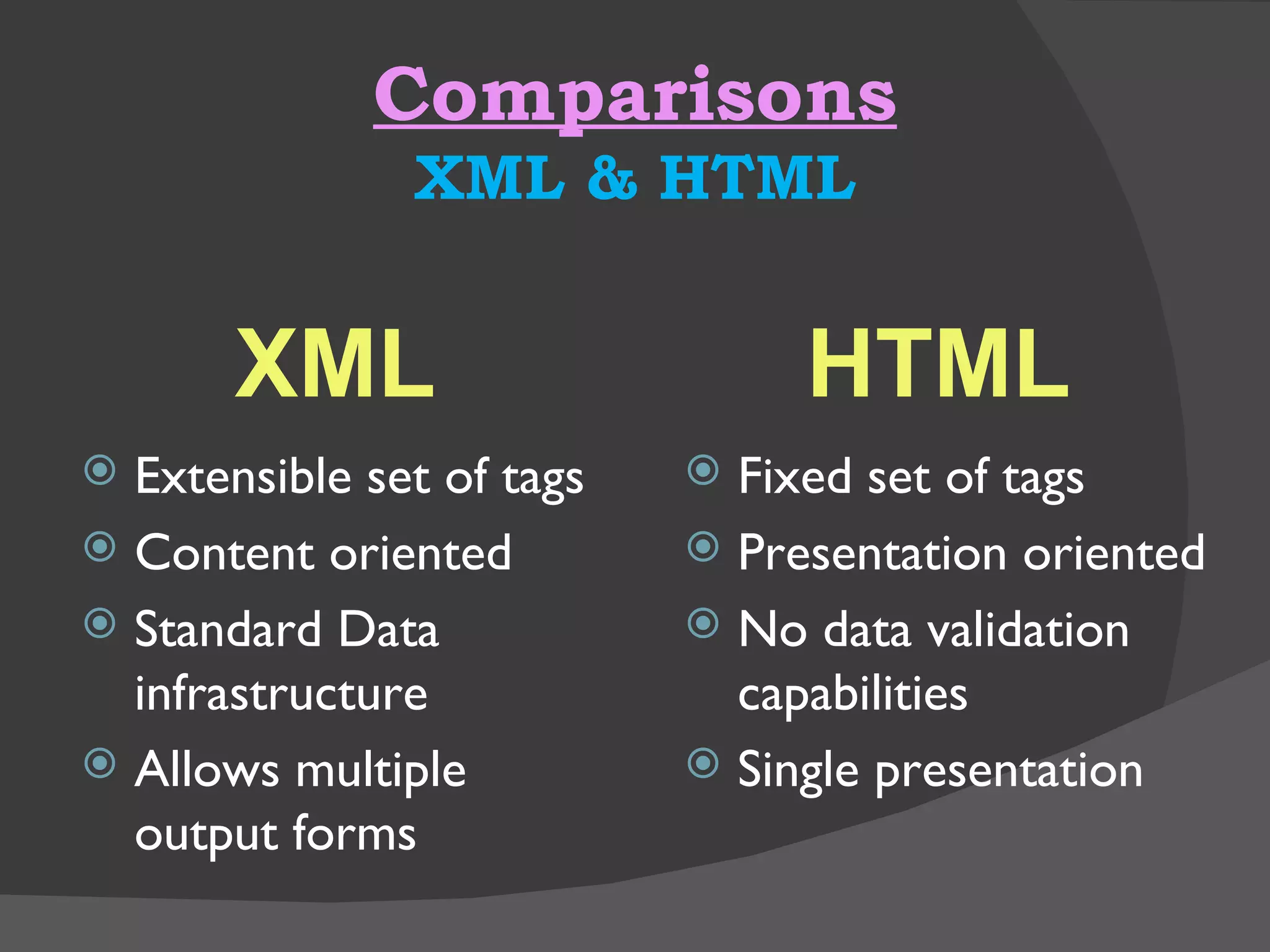
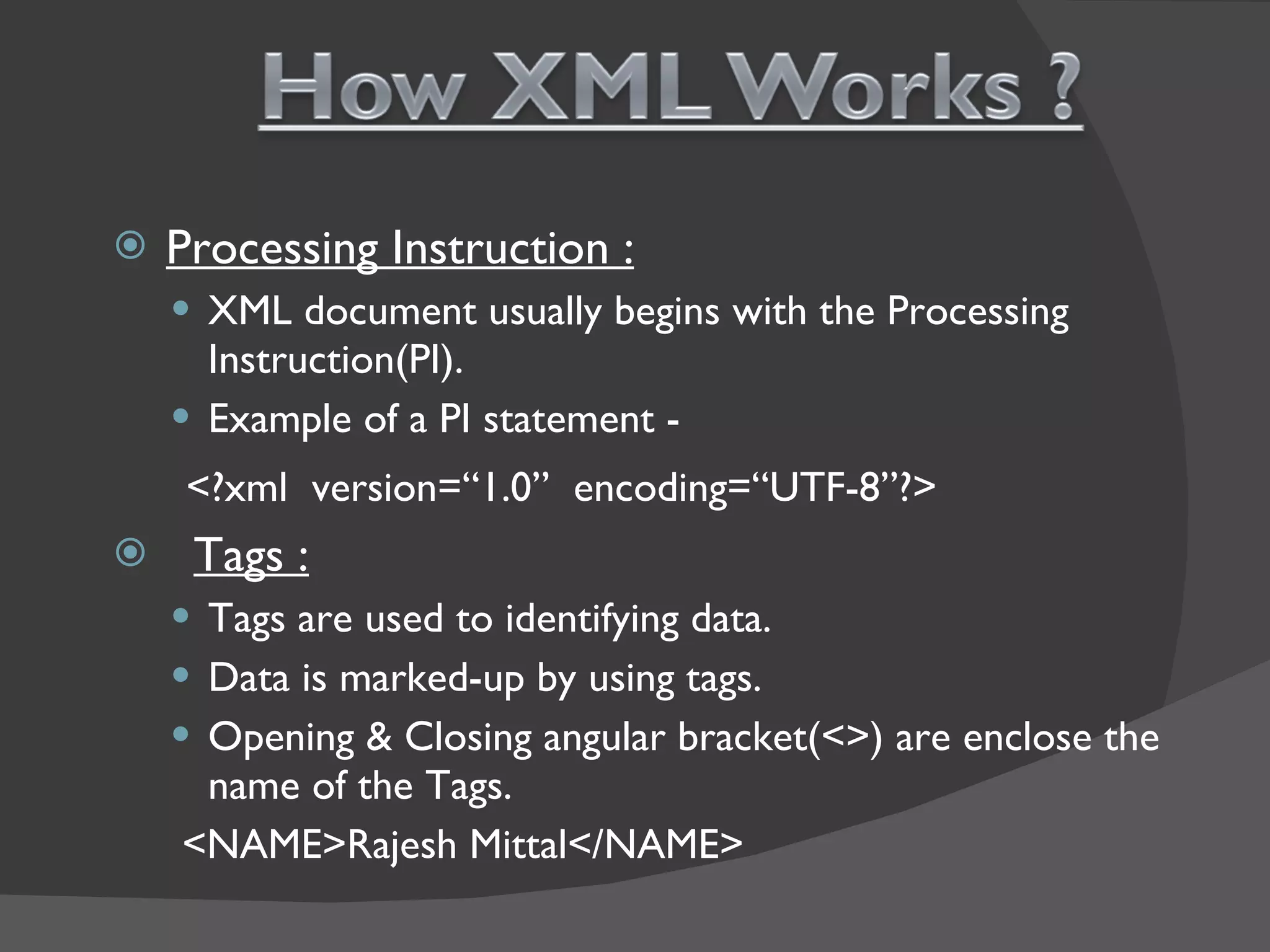
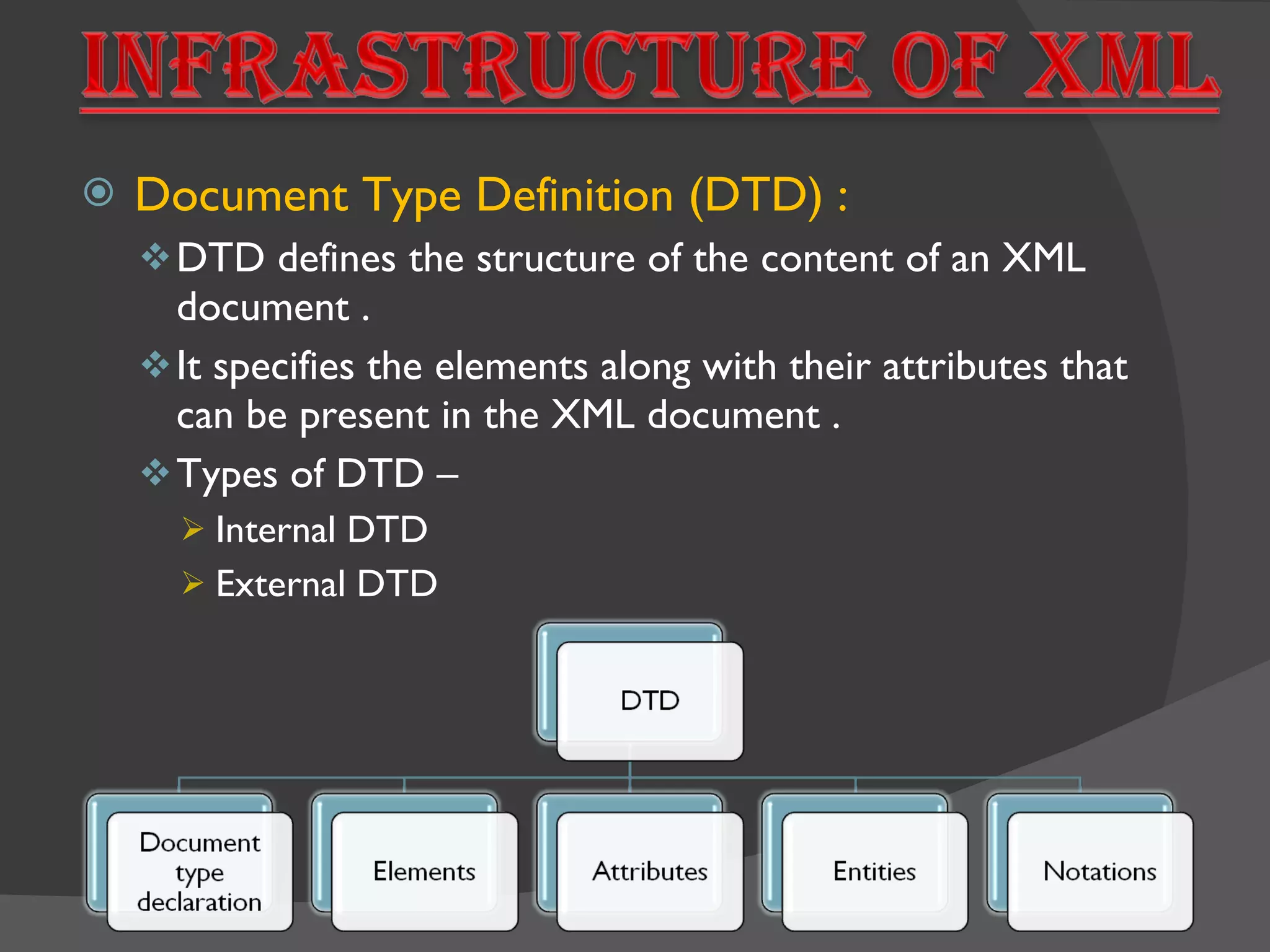
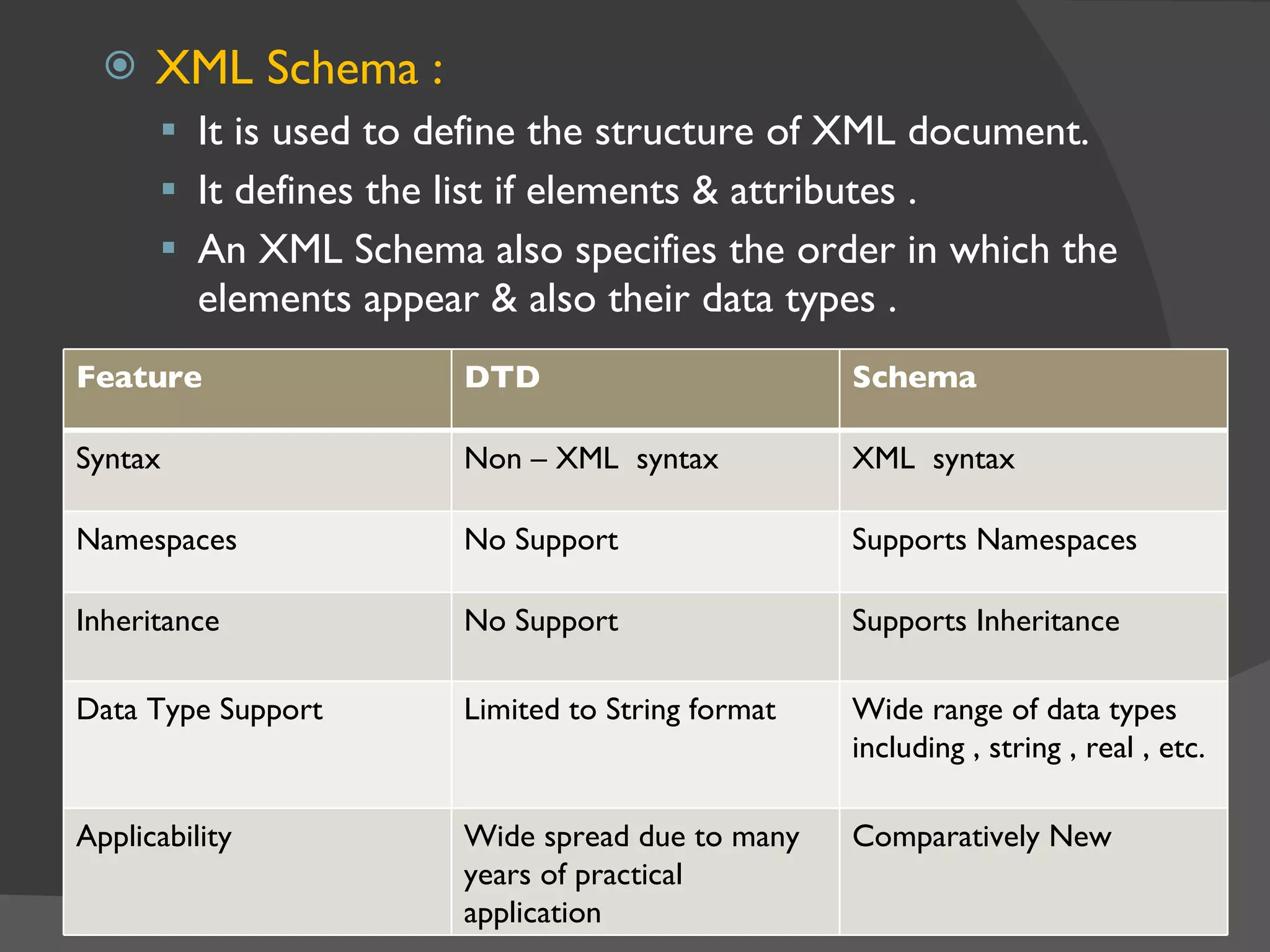
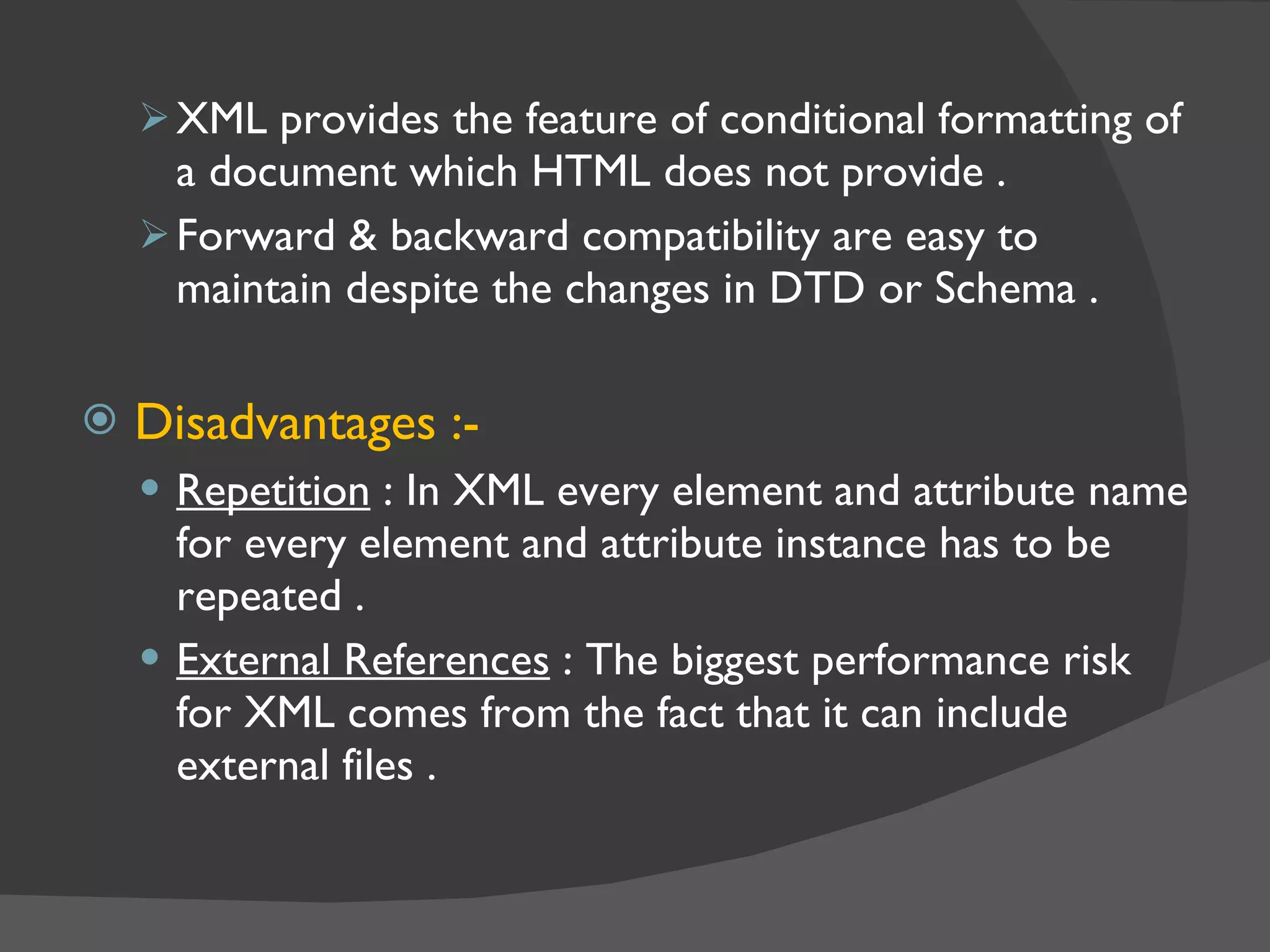
XML is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. It is built on top of SGML and is an open standard developed by W3C. XML allows users to define their own tags to structure documents and is widely used for data exchange across different systems. Some key advantages of XML include being based on international standards, allowing user-defined tags, and having a hierarchical structure suitable for most document types.