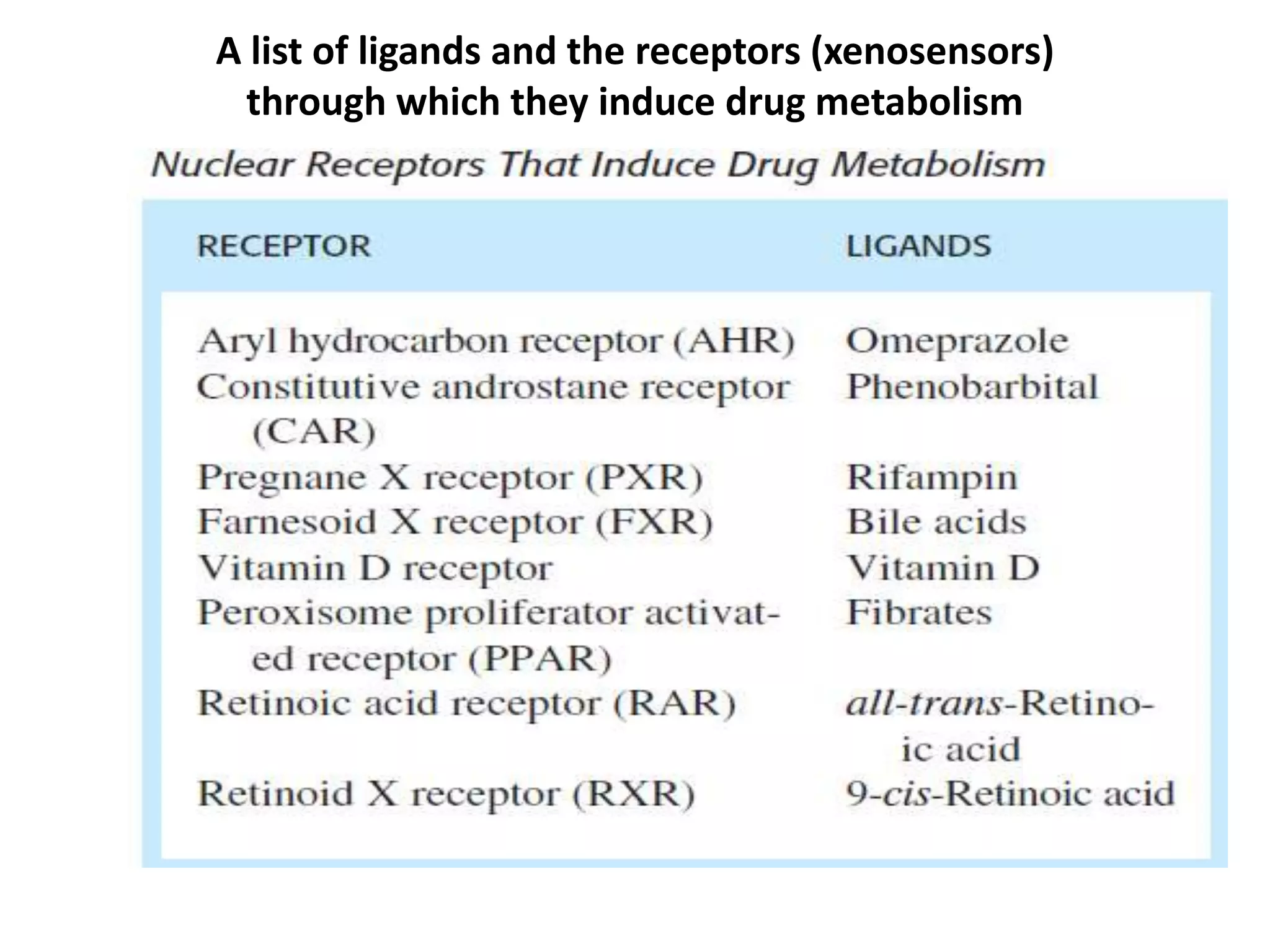
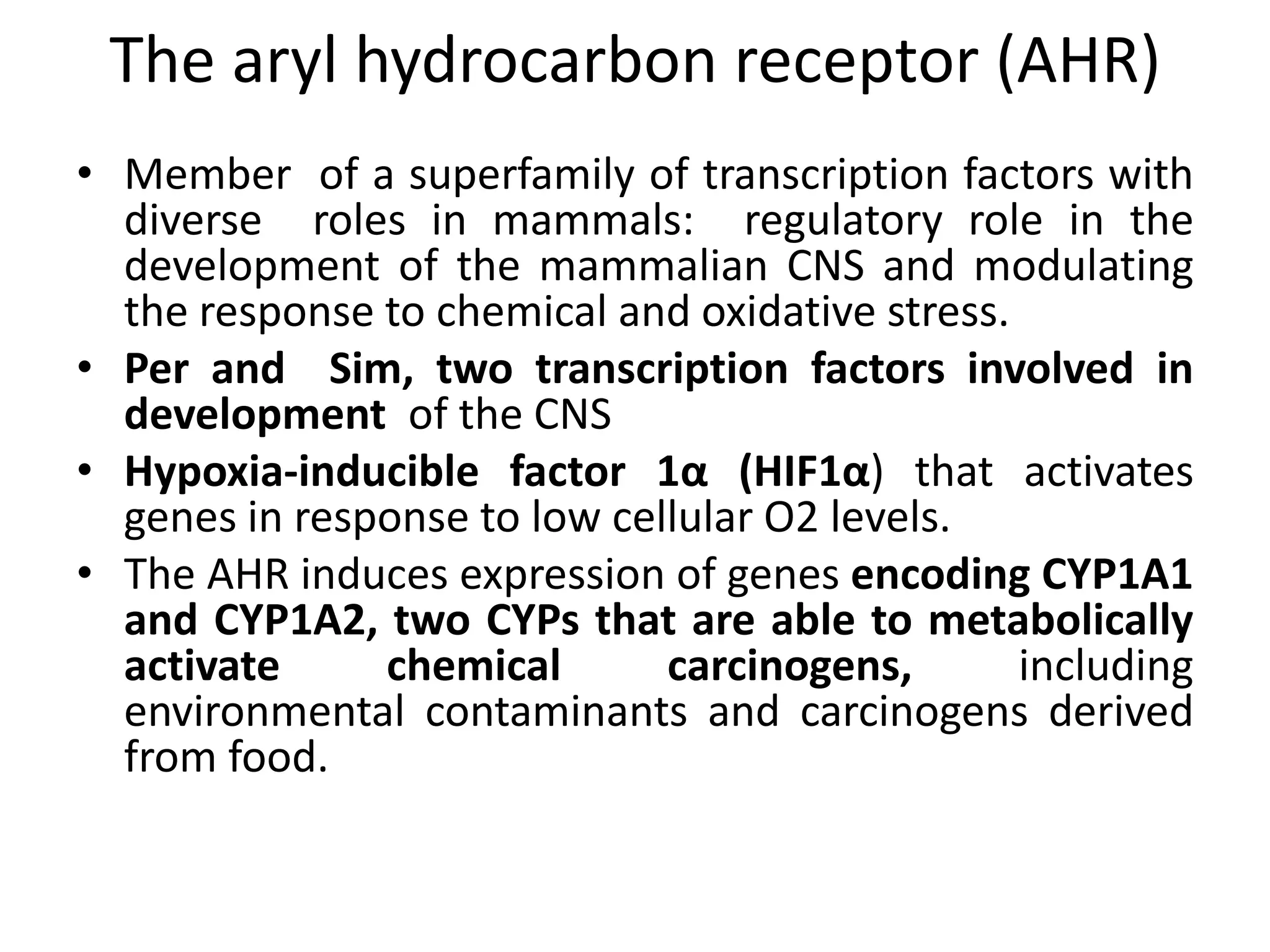
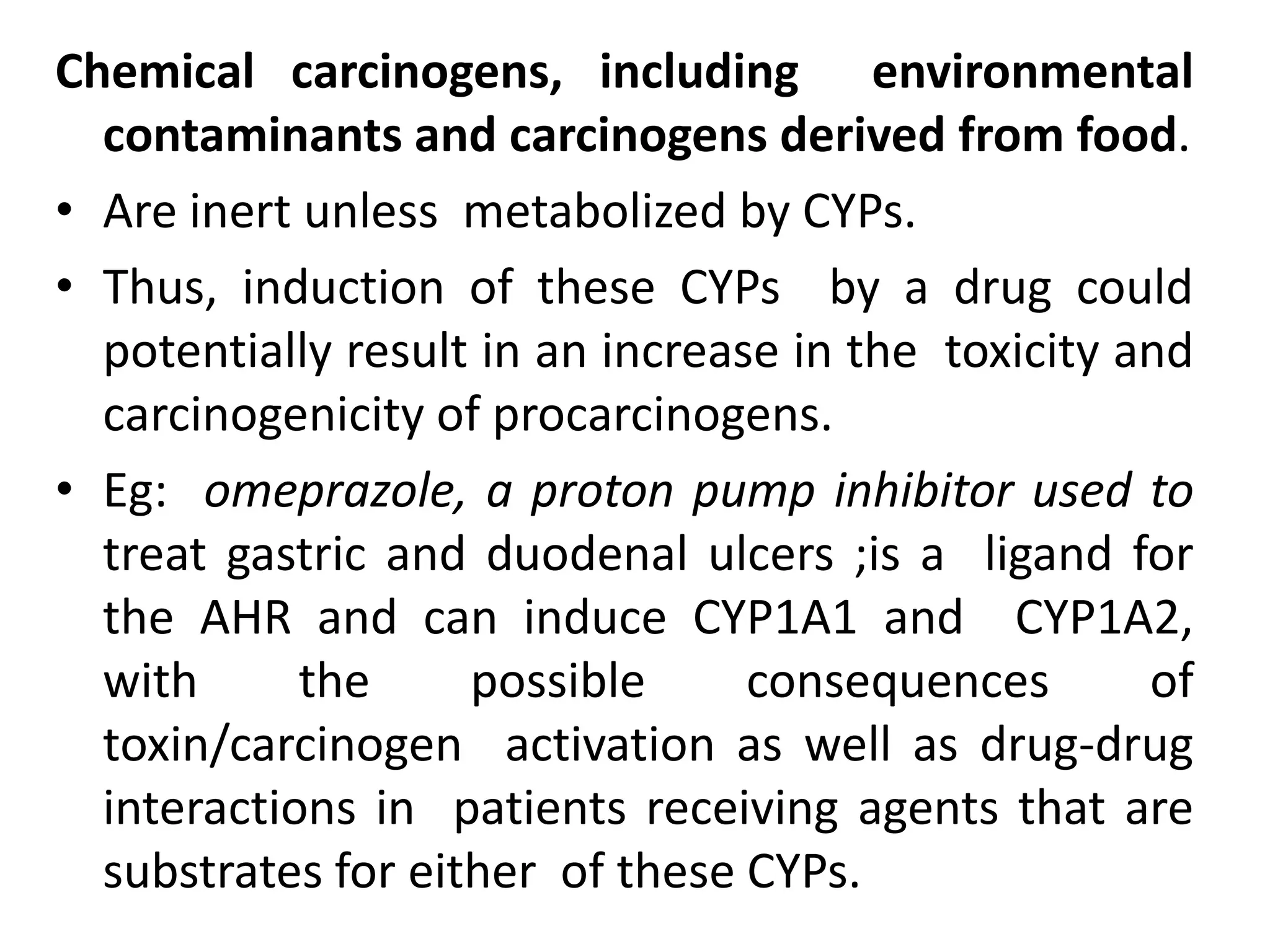
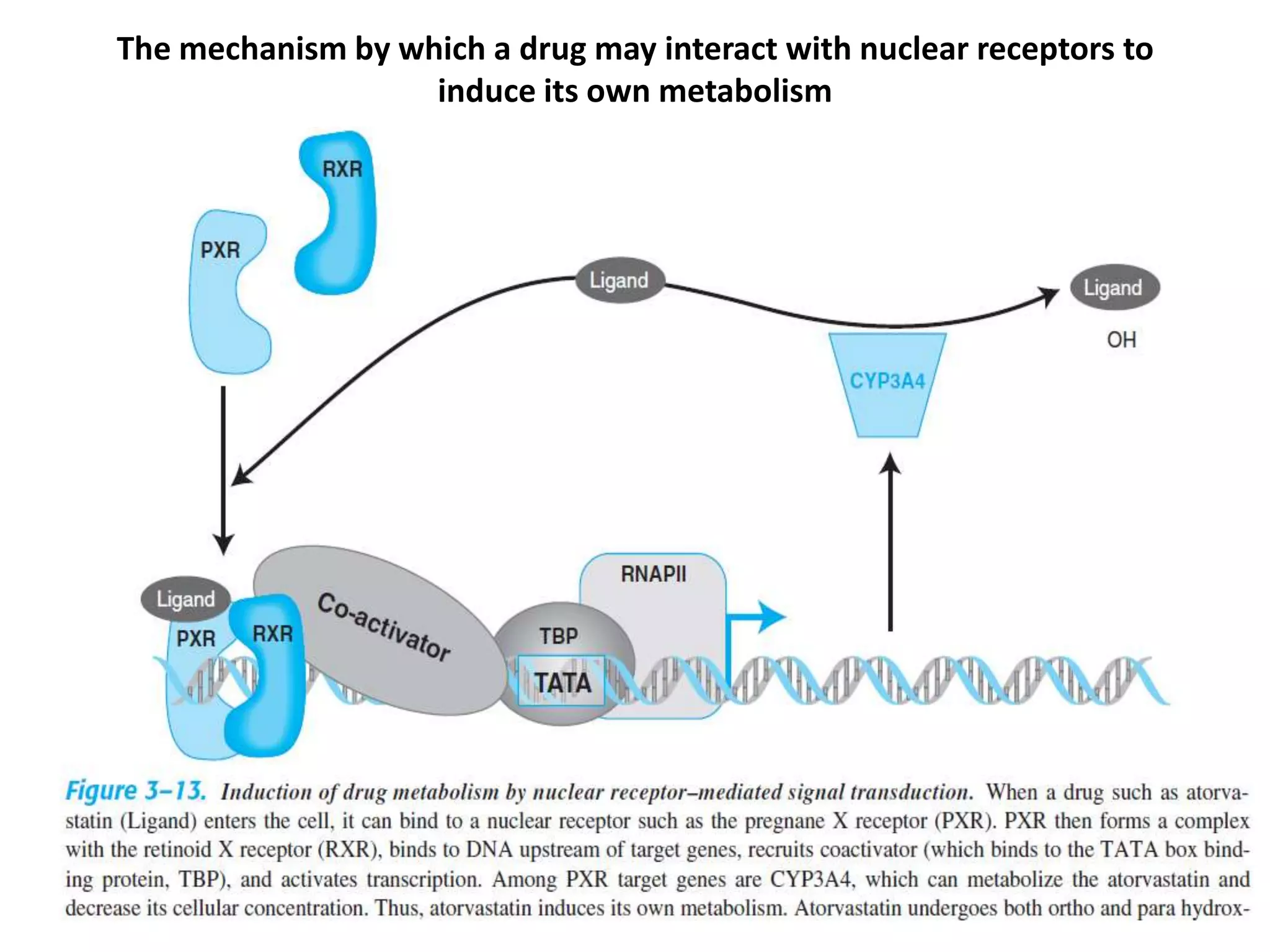
Xenosensors are ligand-activated receptors that induce the expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes like cytochrome P450s in response to exposure to foreign compounds. The main xenosensors are the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Activation of these receptors by drugs and other ligands can lead to auto-induction of the drug's own metabolism and drug-drug interactions by inducing drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters. Species differences exist in the specific ligands that activate these xenosensors.



![CAR :
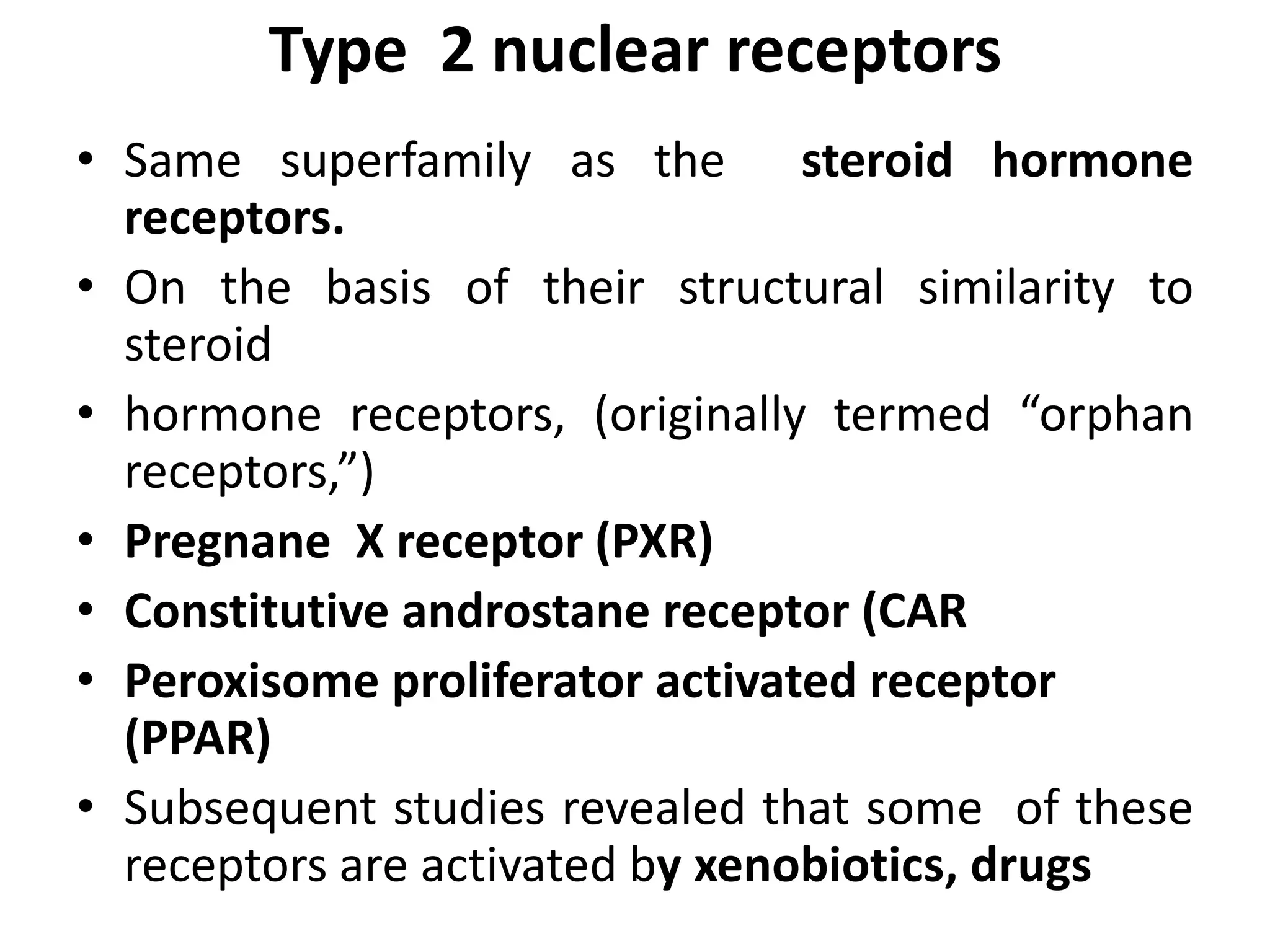
• CAR and PXR are closely related, activated by the same ligands
and bind to the sameDNA-response elements
• Ability to activate genes in the absence of ligand.
• Steroid- androstanol; clotrimazole,meclizine are inverse
agonists that inhibit gene activation by CAR
• Pesticide1,4-bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene, steroid 5β-pregnane-
3,20-dione, -activate gene exp.when bound to CAR.
• Genes induced : encoding several CYPs (CYP2B6, CYP2C9, and
CYP3A4), Phase 2 enzymes (GSTs, UGTs, and SULTs), and drug
and endobiotic transporters.
• CYP3A4 is induced by both PXR and CAR
• Potential role in inducing the degradation of drugs-
acetaminophen, also function in the control of bilirubin
degradation, the process by which the liver decomposes
heme.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xenosensors-130403020029-phpapp02/75/Xenosensors-11-2048.jpg)