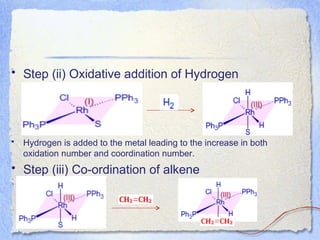
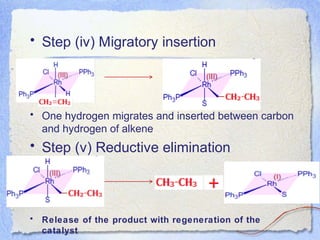
Wilkinson's catalyst, chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), is an organometallic catalyst that is very effective for the homogeneous hydrogenation of unsaturated compounds at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Its mechanism involves five steps - ligand dissociation, oxidative addition of hydrogen, alkene coordination, migratory insertion, and reductive elimination - known as Tolman's catalytic cycle. This cycle allows the catalyst intermediates to shuttle between 18 and 16 electron configurations, making the electron shifts energetically favored.



![Wilkinson's catalyst
• Chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I),
[RhCl(PPh3)3]
•
• Discovered accidentally by Fred Jardine,(PhD scholor) working for Geoffrey
Wilkinson was trying to make [RhCl3(PPh3)3], from the reaction of hydrated
rhodium trichloride and excess triphenylphosphine in boiling ethanol.
[RhCl3(H2O)3] + 4 PPh3 [RhCl(PPh3)3] + Ph3PO + 2 HCl + 2
H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wilkinson-190214145345/85/Wilkinson-s-catalyst-4-320.jpg)