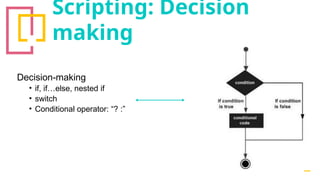
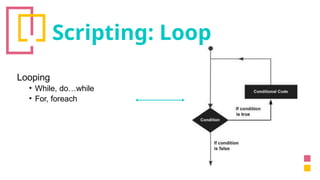
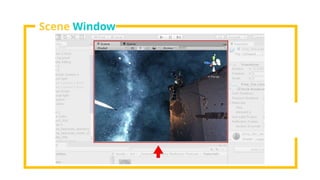
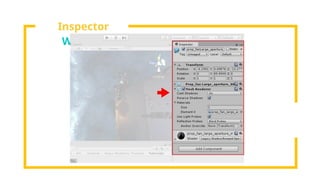
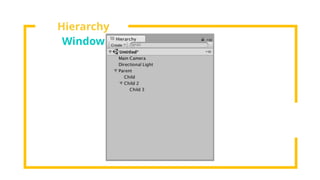
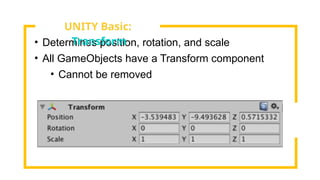
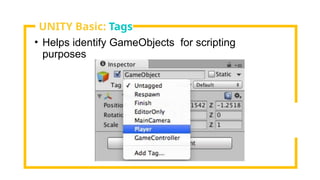
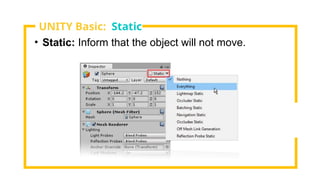
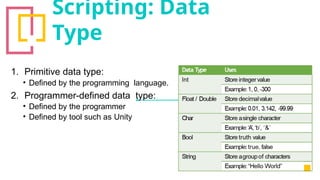
The document provides an overview of Unity, a powerful and versatile game engine used across various industries for developing virtual reality software and games. It details key concepts such as game objects, components, scripting in C#, and the use of different windows in Unity for project management. Additionally, it covers essential programming aspects like data types, variables, classes, and control structures used in game development.
















![Scripting: Array
• A collection or series of the same data type.
• The content of an array are called its elements.
• Array elements always begin with 0;
• Syntax: data-type[] array-name;
• Example: int[] nums;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wig3004notes3sw-240807145452-22621cce/85/WIG3004-virtual-reality-chapter3-software-pptx-26-320.jpg)