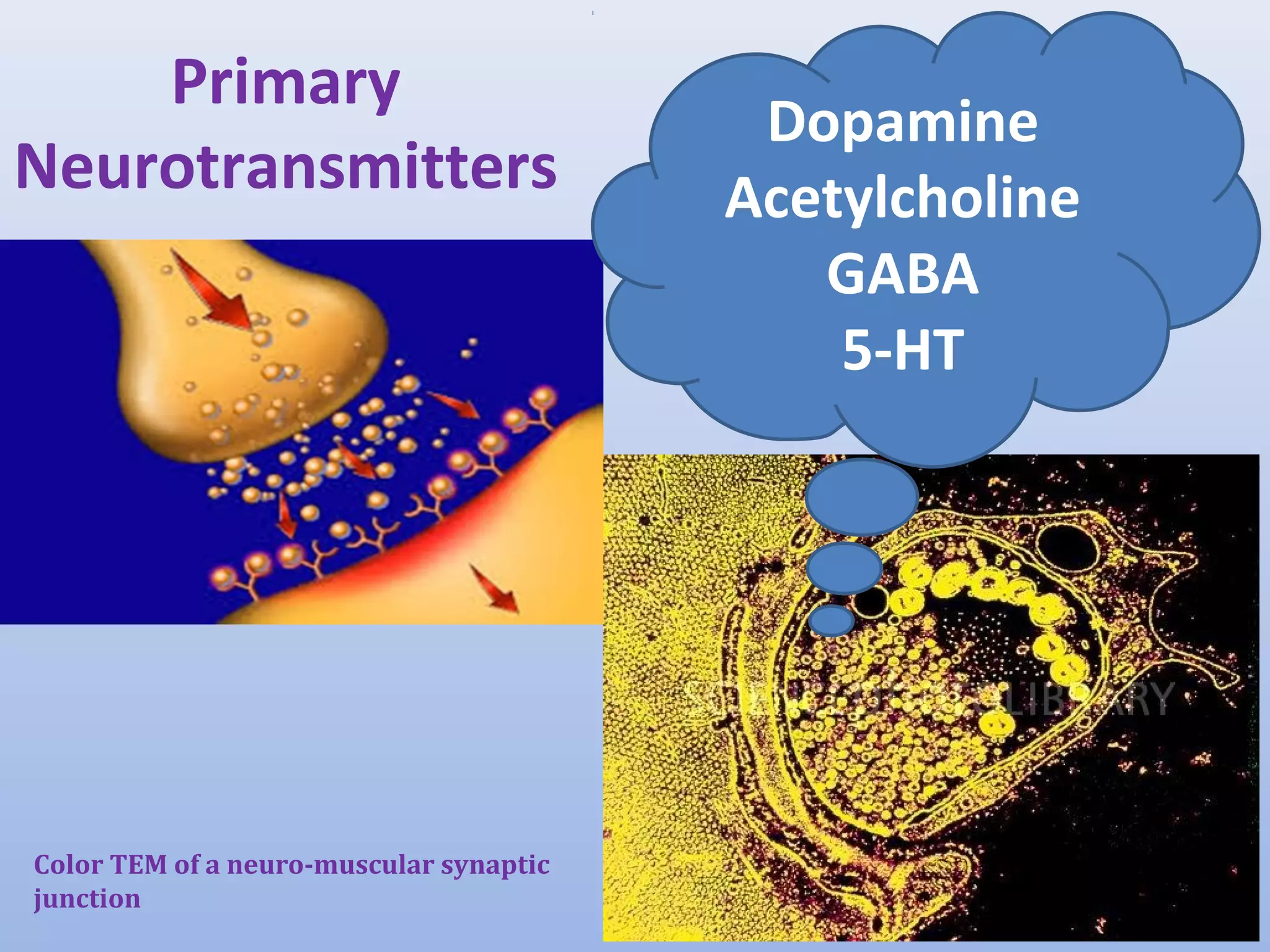
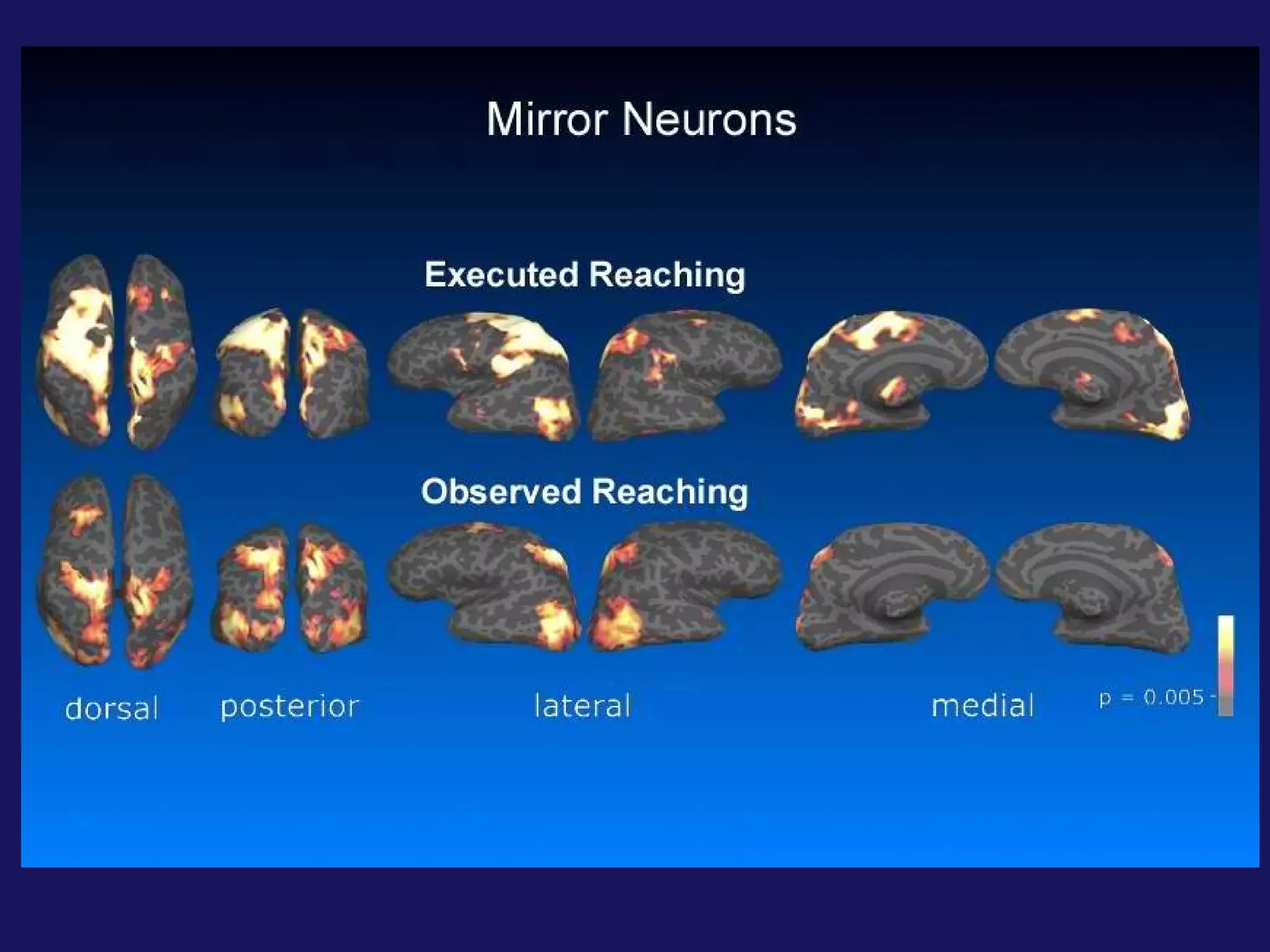
This document discusses discrimination and how patterns of behavior are learned. It mentions mirror neurons, which fire both when an action is performed and observed, allowing habits and behaviors to be reinforced. Discrimination occurs through domestication, genetic inheritance, and mental negligence. By containing "poisonous" cancer cells with healthy cells, the spread of cancer could potentially be stopped.