A password or secret key may be used to encrypt data, making it difficult for anybody except the person who knows the password or key to access it. The two types are ciphertext (encrypted data) and plaintext (unencrypted information).
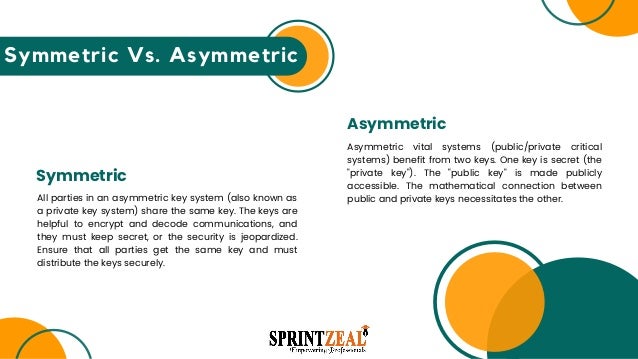
Many enterprises currently use a widespread and effective data security technology, encryption. Public-key and symmetrical asymmetric encryption are the two most used encryption methods for encrypting data. Know about the best coding language to learn.
Check Out The Full Blog Given In The Url Below
https://www.sprintzeal.com/blog/data-encryption