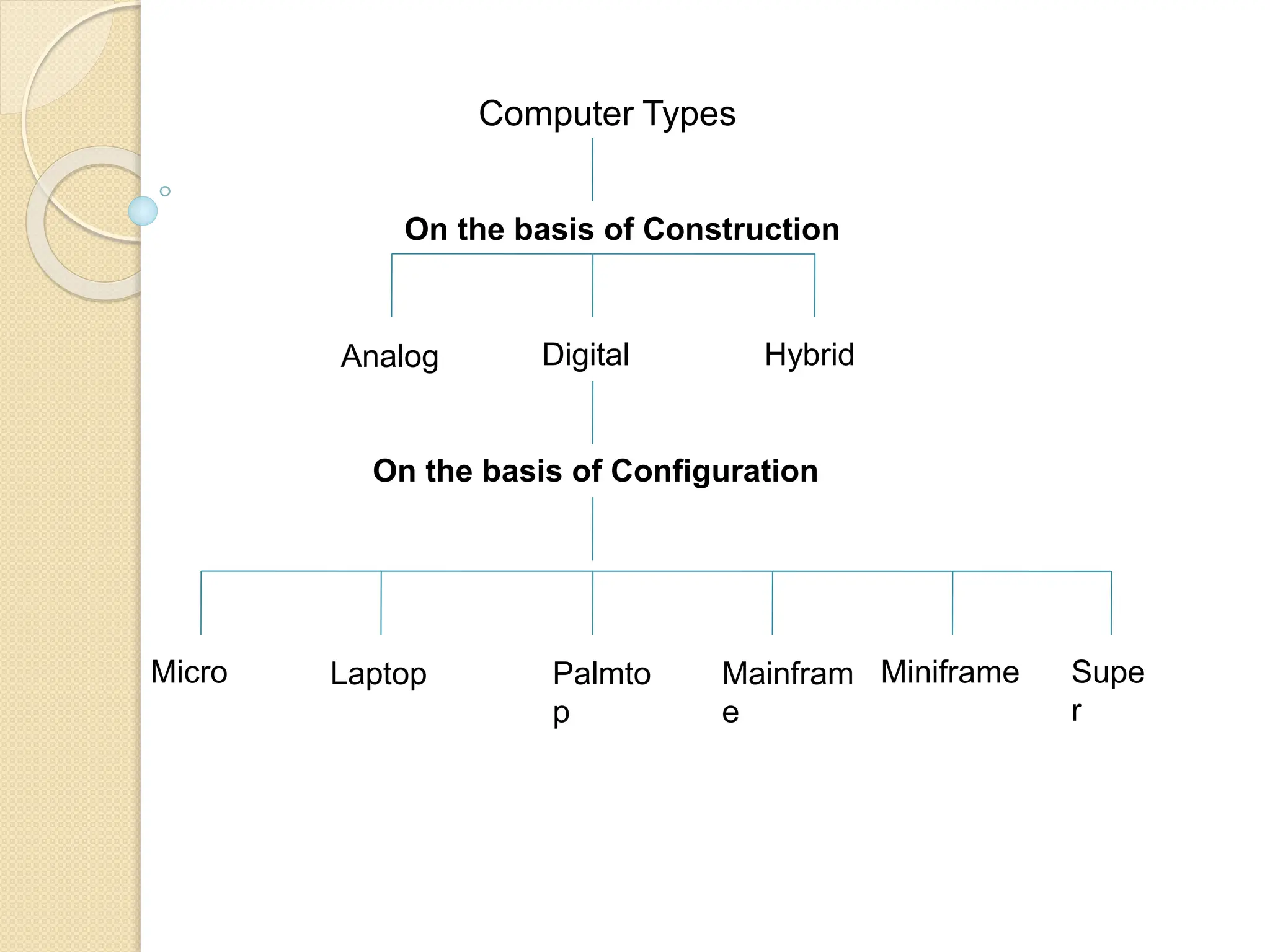
Computers can be classified into different types based on construction (analog, digital, hybrid) and configuration (micro, laptop, palmtop, mainframe, miniframe, supercomputer). Analog computers are designed for specific tasks using continuous measurements, while digital computers perform routine tasks and are more versatile. Hybrid computers combine features of both, with examples including laptops and supercomputers which are used in varied applications from personal use to complex scientific calculations.