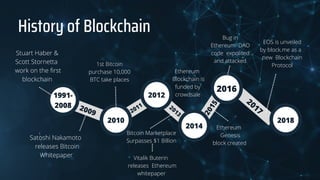
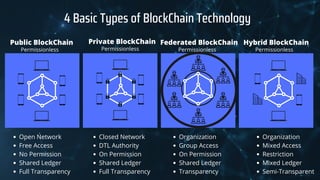
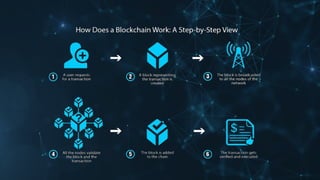
Blockchain technology allows transactions to be grouped into blocks and recorded in a ledger. Each block is cryptographically linked, making the record permanent and unalterable. This permits untrusting parties to co-create a shared record without relying on a central authority. Blockchains use cryptographic keys, peer-to-peer networks, and a shared ledger to securely transmit unique instances of value in a transparent manner that can be accessed by various servers. There are four basic types of blockchain: private, public, federated, and hybrid. Blockchain provides advantages like improved accuracy, reduced costs, decentralization, transparency, and security of transactions. However, it also faces challenges like needing high-performance and not replacing certain solutions like databases