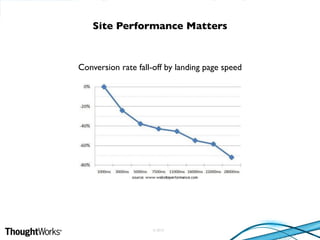
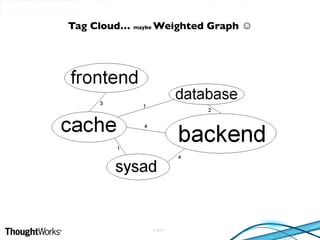
This document provides various suggestions for improving website performance beyond using YSlow. It discusses topics like acceptable page load times, frontend and backend optimizations, caching strategies, utilizing a content delivery network, and database optimizations. Specific recommendations include asynchronously loading JavaScript, separating static and dynamic content, avoiding third-party scripts that slow loading, and choosing an optimal data center location.