The document discusses multi-source replication in MariaDB, highlighting its features, benefits, and practical implementation details. Presenter Wagner Bianchi, an expert in database operations, outlines how multiple master connections can be managed and utilized for centralized data, backup, and multi-location database instances. It also covers common configurations and troubleshooting steps for effectively using multi-source replication with GTIDs and other features.







![Multi-Source Replication
• Below files will be created after adding sources to the multi-source slave:
• An entry on multi-master-info-file is created with the chosen names;
• A master-into-file-connection_name.info is created as the regular master.info;
• A set of relay logs files following the pattern relay-log-connection_name.xxxxxx;
• A relay-log-index-connection_name.info with the names of the active relay logs;
• A relay-log-info-file-connection_name.info containing current master position;
9
[root@box03 mysql]# ls -lh | egrep "us_east|us_west"
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 306 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_east.000001
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 619 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_east.000002
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 66 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_east.index
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 306 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_west.000001
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 619 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_west.000002
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 66 Apr 3 16:07 box03-relay-bin-us_west.index
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 155 Apr 3 16:07 master-us_east.info
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 155 Apr 3 16:07 master-us_west.info
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 61 Apr 3 16:07 relay-log-us_east.info
-rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 60 Apr 3 16:07 relay-log-us_west.info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-9-320.jpg)
![Implementing Multi-Source Replication
• The known commands are now support the connection’s names as below:
• CHANGE MASTER 'connection_name' TO…
• FLUSH RELAY LOGS ['connection_name']
• MASTER_POS_WAIT(....,['connection_name'])
• RESET SLAVE ['connection_name'] [ALL]
• SHOW RELAYLOG ['connection_name'] EVENTS
• SHOW SLAVE ['connection_name'] STATUS
• SHOW ALL SLAVES STATUS
• START SLAVE ['connection_name'...]]
• START ALL SLAVES ...
• STOP SLAVE ['connection_name'] ...
• STOP ALL SLAVES …
• Commands that omit the connection_name part deals with the default slave which is ''
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-10-320.jpg)




![Multi-Source Replication and GTIDs
• Basic configuration file for Multi-Source Replica instance (/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf):
[mariadb]
server_id=300
report_host=multisource_slave
log_bin=mariadb-bin
log_bin_index=mariadb-bin.index
log_slave_updates=true
gtid_domain_id=300
slave_parallel_threads=4
slave_domain_parallel_threads=2
[mariadb 10.1]
US_WEST.slave_parallel_mode=optimistic
US_EAST.slave_parallel_mode=optimistic
The implication of using multi-threaded is
that sql_slave_skip_counter cannot be used
to fix replication errors in case it’s OK to use
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-16-320.jpg)

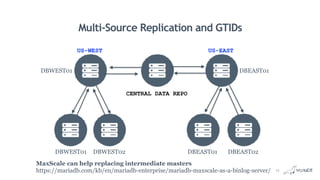
![Multi-Source Replication
Multi-Source Replica
US_WEST US_EAST
18
box03 [(none)]> start all slaves;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.01 sec)
box03 [(none)]> show warnings;
+-------+------+-------------------------+
| Level | Code | Message |
+-------+------+-------------------------+
| Note | 1937 | SLAVE 'US_WEST' started |
| Note | 1937 | SLAVE 'US_EAST' started |
+-------+------+-------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
box03 [(none)]> pager grep "Connection_name:"
PAGER set to 'grep "Connection_name:"'
box03 [(none)]> show all slaves statusG
Connection_name: US_EAST
Connection_name: US_WEST
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-18-320.jpg)
![Multi-Source Replication Implementation
• Let’s setup the source or connection name for US_WEST:
#: CREATING THE REPLICATION USER
box01 [(none)]> CREATE USER rpl@'192.168.0.13' IDENTIFIED BY 'xyz007';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
box01 [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO rpl@'192.168.0.13';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#: SETTING UP THE CONNECTION NAME
box03 [(none)]> CHANGE MASTER 'US_WEST' TO
-> MASTER_HOST=‘192.168.0.11’,
-> MASTER_USER='rpl',
-> MASTER_PASSWORD='xyz007',
-> MASTER_USE_GTID=SLAVE_POS;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-19-320.jpg)
![Multi-Source Replication Implementation
• Let’s setup the source or connection name for US_EAST:
#: CREATING THE REPLICATION USER
box02 [(none)]> SET SQL_LOG_BIN=0; CREATE USER rpl@'192.168.0.13' IDENTIFIED BY 'xyz007';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
box02 [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO rpl@'192.168.0.13'; SET SQL_LOG_BIN=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#: SETTING UP THE CONNECTION NAME
box03 [(none)]> CHANGE MASTER 'US_EAST' TO
-> MASTER_HOST='192.168.0.12',
-> MASTER_USER='rpl',
-> MASTER_PASSWORD='xyz007',
-> MASTER_USE_GTID=SLAVE_POS;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
20
Here, I used the switch SQL_LOG_BIN as 0
to avoid breaking replication when starting up
the threads for the connection name US_EAST.
One can reset master if possible on both sides in
order to clean up binary logs before start slave all](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-20-320.jpg)

![Multi-Source Replication Common Break/Fix
• When you have a bunch of connection names, you have the following to fix errors:
• single_threaded, use per connection name sql_slave_skip_counter!
box03 [(none)]> show all slaves statusG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Connection_name: US_EAST
Slave_SQL_State:
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: 192.168.0.12
Master_User: rpl
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000003
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 480
Relay_Log_File: box03-relay-bin-us_east.000002
Relay_Log_Pos: 619
Relay_Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000003
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: No
Last_Errno: 1062
Last_Error: Error 'Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: ''. Query:
'insert into test.t1 set i=1''insert into test.t1 set i=1'
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-22-320.jpg)
![Multi-Source Replication Common Break/Fix
• Using sql_slave_skip_counter for single_threaded and getting the replication resumed:
box03 [(none)]> set default_master_connection=US_EAST;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
box03 [(none)]> stop slave; set global sql_slave_skip_counter=1; start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-23-320.jpg)
![Multi-Source Replication Common Break/Fix
• When you have a bunch of connection names, you have the following to fix errors:
• sql_slave_skip_counter: when using parallel replication and GTID with
multiple replication domains, @@sql_slave_skip_counter can not be used. Instead,
setting @@gtid_slave_pos explicitly can be used to skip to after a given GTID
position.
box03 [test]> show all slaves statusG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Connection_name: US_EAST
Slave_SQL_State:
Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event
Master_Host: 192.168.0.12
Master_User: rpl
Master_Port: 3306
Connect_Retry: 60
Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000001
Read_Master_Log_Pos: 899
Relay_Log_File: box03-relay-bin-us_east.000001
Relay_Log_Pos: 4
Relay_Master_Log_File: mariadb-bin.000001
Slave_IO_Running: Yes
Slave_SQL_Running: No
Last_Errno: 1062
Last_Error: Error 'Duplicate entry '1' for key 'PRIMARY'' on query. Default database: ''. Query:
'insert into test.t1 set i=1'
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-24-320.jpg)
![Multi-Source Replication Common Break/Fix
• Using the right variable gtid_slave_pos, we need to do the below:
#: current gtid_slave_pos
box03 [test]> select @@global.gtid_slave_posG
*************************** 1. row ***************************
@@global.gtid_slave_pos: 100-100-2,200-200-3
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#: we need to increment one transaction for US_EAST which is gtid_domain_id 200
box03 [test]> stop all slaves;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 2 warnings (0.01 sec)
box03 [test]> stop slave; set global gtid_slave_pos='100-100-2,200-200-4'; start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
box03 [test]> start all slaves;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-25-320.jpg)
![Removing Multi-Source Connection Names
• To remove the connection names created:
#: deletes the master.info and relay-log.info files, all the relay log files, and starts a new relay log file
#: stop all slaves before, connection names will continue appearing out of show all slaves status
box03 [(none)]> reset slave 'US_WEST';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
box03 [(none)]> reset slave 'US_EAST';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#: checking how it is right now
box03 [(none)]> show all slaves statusG
Connection_name: US_EAST
Slave_IO_Running: No
Slave_SQL_Running: No
Connection_name: US_WEST
Slave_IO_Running: No
Slave_SQL_Running: No
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-26-320.jpg)
![Removing Multi-Source Connection Names
• To remove the connection names created:
#: permanent remove a connection names
#: ALL also resets the PORT, HOST, USER and PASSWORD parameters for the slave
box03 [(none)]> reset slave 'US_EAST' all;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
box03 [(none)]> reset slave 'US_WEST' all;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#: checking how it is right now
box03 [(none)]> show all slaves statusG
Empty set (0.00 sec)
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-mariadbprovidesthesolutiontoeasemulti-sourcereplication-170504182529/85/Webinar-MariaDB-Provides-the-Solution-to-Ease-Multi-Source-Replication-27-320.jpg)


